Ingénierie des réservoirs
Saturation (reservoir)
Saturation : Un Paramètre Clé dans l'Analyse des Réservoirs de Pétrole et de Gaz
Dans le monde de l'exploration et de la production pétrolières et gazières, la compréhension de la composition d'un réservoir est cruciale. La saturation joue un rôle vital dans cette compréhension, fournissant des informations sur les fluides présents dans la roche du réservoir.
Définition :
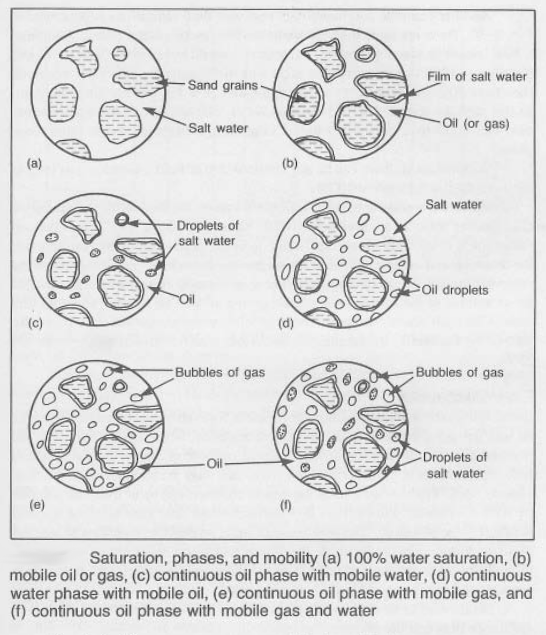
La saturation, dans le contexte des réservoirs de pétrole et de gaz, fait référence à la fraction de la porosité effective remplie par un fluide spécifique. Elle est exprimée en pourcentage. La porosité effective représente les espaces poreux dans la roche qui sont interconnectés et peuvent être remplis de fluides.
Types de saturation :
- Saturation en eau (Sw) : Le pourcentage de l'espace poreux occupé par l'eau.
- Saturation en huile (So) : Le pourcentage de l'espace poreux occupé par l'huile.
- Saturation en gaz (Sg) : Le pourcentage de l'espace poreux occupé par le gaz.
Importance de la saturation :
Les valeurs de saturation sont essentielles pour de nombreuses raisons :
- Caractérisation du réservoir : Connaître la saturation des différents fluides permet aux géologues et aux ingénieurs de déterminer le type et le volume d'hydrocarbures présents dans le réservoir.
- Potentiel de production : Une saturation élevée en huile ou en gaz indique un plus grand potentiel de récupération d'hydrocarbures.
- Écoulement des fluides : La saturation influence considérablement l'écoulement des fluides à travers le réservoir, affectant les débits de production.
- Gestion du réservoir : Comprendre la saturation aide à optimiser les stratégies de production, y compris les techniques d'injection d'eau et de gaz.
Techniques de mesure :
La saturation est généralement déterminée par diverses techniques :
- Analyse des carottes : L'analyse d'échantillons de roche en laboratoire fournit des mesures directes de la saturation des fluides.
- Logs de puits : Les logs enregistrés pendant le forage fournissent des mesures indirectes de la saturation basées sur des propriétés telles que la résistivité et la densité.
- Données sismiques : L'analyse sismique avancée peut estimer la saturation dans certains cas.
Implications de la saturation :
- Faible saturation : Une faible saturation en huile ou en gaz indique un réservoir potentiellement moins productif.
- Haute saturation : Une saturation élevée peut indiquer un réservoir riche, mais elle peut également entraîner des difficultés dans l'écoulement des fluides.
- Changements de saturation : Au fil du temps, la saturation peut changer en raison du mouvement des fluides et des activités de production, influençant les performances du réservoir.
En conclusion :
La saturation est un paramètre fondamental dans l'analyse des réservoirs de pétrole et de gaz. En comprenant la saturation des différents fluides, les professionnels peuvent évaluer efficacement le potentiel du réservoir, optimiser la production et gérer les performances du réservoir tout au long de sa durée de vie. Une détermination et une interprétation précises de la saturation sont cruciales pour une exploration et un développement d'hydrocarbures efficaces et rentables.
Test Your Knowledge
Saturation Quiz
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What is the definition of saturation in the context of oil and gas reservoirs?
a) The total volume of pore space in a reservoir rock. b) The percentage of the pore space occupied by a specific fluid. c) The amount of hydrocarbons present in a reservoir. d) The pressure exerted by the fluids within the reservoir.
Answer
b) The percentage of the pore space occupied by a specific fluid.
2. Which of the following is NOT a type of saturation commonly used in reservoir analysis?
a) Water Saturation (Sw) b) Oil Saturation (So) c) Gas Saturation (Sg) d) Clay Saturation (Sc)
Answer
d) Clay Saturation (Sc)
3. Why is saturation important in reservoir characterization?
a) It helps determine the size of the reservoir. b) It indicates the type and volume of hydrocarbons present. c) It helps predict the lifespan of the reservoir. d) It determines the cost of extracting hydrocarbons.
Answer
b) It indicates the type and volume of hydrocarbons present.
4. Which of the following techniques is used to determine saturation directly from rock samples?
a) Well Logs b) Seismic Data c) Core Analysis d) Production Data
Answer
c) Core Analysis
5. What is the implication of a high oil saturation in a reservoir?
a) It indicates a potentially unproductive reservoir. b) It suggests a higher chance of successful hydrocarbon recovery. c) It means the reservoir is likely to be depleted quickly. d) It suggests the reservoir is filled with water.
Answer
b) It suggests a higher chance of successful hydrocarbon recovery.
Saturation Exercise
Scenario: A geologist is analyzing a core sample from a newly discovered reservoir. The core analysis shows the following:
- Porosity: 20%
- Water Saturation (Sw): 30%
- Gas Saturation (Sg): 10%
Task: Calculate the Oil Saturation (So) for this reservoir.
Exercice Correction
The total saturation should always add up to 100%. Therefore:
So = 100% - Sw - Sg
So = 100% - 30% - 10%
So = 60%
Books
- Petroleum Reservoir Engineering by Dake, L.P. (This book provides a comprehensive overview of reservoir engineering principles, including saturation concepts.)
- Reservoir Engineering Handbook by Craft, B.C., Hawkins, M.F., Terry, R.E., and Stone, H.L. (This handbook offers detailed explanations and practical applications of saturation calculations and their impact on reservoir behavior.)
- Applied Petroleum Reservoir Engineering by Amyx, J.W., Bass, D.M., and Whiting, R.L. (This textbook covers various aspects of reservoir engineering, including saturation analysis and its role in production optimization.)
Articles
- "Saturation: A Key Parameter in Reservoir Characterization" by K. Azom (This article provides an overview of saturation concepts and its importance in reservoir evaluation.)
- "Estimating Reservoir Saturation from Seismic Data" by S. Chopra and G. Chilingarian (This article discusses techniques for estimating saturation from seismic data, highlighting its implications for reservoir development.)
- "Fluid Saturation and Its Effect on Reservoir Performance" by J.P. Brill and J.F. Roberts (This article explores the relationship between saturation and reservoir performance, emphasizing its impact on fluid flow and production rates.)
Online Resources
- Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE): The SPE website offers a vast collection of technical papers and resources on reservoir engineering, including saturation analysis and its applications.
- Schlumberger: Schlumberger provides online resources on reservoir characterization, including information on saturation determination using well logs and other techniques.
- Halliburton: Halliburton offers online resources and technical articles on reservoir engineering, covering topics like saturation, fluid flow, and reservoir performance.
- Oil & Gas Journal: This online resource provides news and technical articles related to the oil and gas industry, including discussions on saturation and its significance in reservoir development.
Search Tips
- Use specific keywords like "reservoir saturation," "water saturation," "oil saturation," "gas saturation," "saturation calculation," "saturation measurement," and "saturation interpretation."
- Combine keywords with terms related to your specific interest, such as "reservoir characterization," "production optimization," "reservoir performance," "well logs," "seismic data," and "core analysis."
- Use advanced search operators like "site:" to target specific websites like SPE, Schlumberger, or Halliburton for relevant information.
- Include the term "PDF" in your search query to find downloadable technical papers and articles on saturation.
- Utilize quotation marks (" ") to search for exact phrases, ensuring greater accuracy in your search results.
Techniques
Saturation (Reservoir): A Comprehensive Guide
Here's a breakdown of the topic of reservoir saturation, divided into chapters as requested. Note that some overlap between chapters is inevitable due to the interconnected nature of the subject.
Chapter 1: Techniques for Saturation Determination
The accurate determination of fluid saturations (water, oil, gas) within a reservoir is crucial for effective reservoir management. Several techniques are employed, each with its strengths and limitations:
- Core Analysis: This is the most direct method. Core samples are extracted from the wellbore and analyzed in a laboratory setting. Techniques include:
- Porosity determination: Measuring the pore space volume within the rock sample.
- Saturation measurement: Determining the volume of each fluid phase (water, oil, gas) within the pore space using techniques like Dean-Stark distillation, centrifuge methods, or nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR).
- Capillary pressure measurements: Determining the relationship between capillary pressure and saturation, which is crucial for understanding fluid distribution within the reservoir. This helps predict fluid movement and recovery efficiency.
- Well Logging: While indirect, well logs are a cost-effective and widely used method to estimate saturation across a well's entire length. Key log types and their applications:
- Resistivity logs: Measure the electrical resistance of the formation, which is inversely related to water saturation. High resistivity suggests lower water saturation (higher hydrocarbon saturation).
- Neutron logs: Measure the hydrogen index of the formation, which is related to the pore fluid content. This helps distinguish between water and hydrocarbons.
- Density logs: Measure the bulk density of the formation, which can be used to calculate porosity and, in conjunction with other logs, estimate saturation.
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) logging: Provides information about pore size distribution and fluid mobility, which helps in characterizing the reservoir and determining saturation.
- Seismic Data: Advanced seismic techniques, such as amplitude variation with offset (AVO) analysis and 4D seismic, can provide indirect estimates of saturation by detecting subtle changes in seismic wave reflections related to fluid properties. These methods are less precise than core analysis or well logging but offer a larger-scale view of the reservoir.
Chapter 2: Saturation Models
Various models are used to interpret the data obtained from saturation determination techniques and predict saturation profiles within the reservoir. These models consider the complex interplay between rock properties, fluid properties, and pressure conditions. Key models include:
- Archie's Equation: A classic empirical equation that relates formation resistivity to water saturation, porosity, and water resistivity. It is widely used but has limitations, particularly in complex reservoirs.
- Waxman-Smits Equation: An extension of Archie's equation that accounts for the effect of clay minerals on the formation resistivity. This is more accurate for shaly formations.
- Capillary Pressure Curves: These curves describe the relationship between capillary pressure and saturation. They are essential for understanding fluid distribution and relative permeability, which affects fluid flow during production. Different models exist to predict these curves, depending on the reservoir characteristics.
- Simulation Models: Numerical reservoir simulation models use complex algorithms to simulate fluid flow, pressure changes, and saturation distribution within the reservoir. These models integrate data from various sources, including core analysis, well logs, and seismic data, to provide a comprehensive understanding of reservoir behavior.
Chapter 3: Software for Saturation Analysis
Numerous software packages are available for saturation analysis, ranging from simple spreadsheet programs to sophisticated reservoir simulation suites. The choice of software depends on the complexity of the reservoir and the type of analysis required. Examples include:
- Petrel (Schlumberger): A comprehensive reservoir simulation and characterization platform offering advanced tools for saturation analysis.
- Eclipse (Schlumberger): A powerful reservoir simulator widely used for predicting reservoir performance under different operating conditions.
- CMG (Computer Modelling Group): Another leading reservoir simulation software suite.
- Interactive Petrophysics Software: Various specialized software packages focus specifically on petrophysical interpretation, including well log analysis and saturation estimation.
- MATLAB/Python: Programming environments often used for developing custom saturation estimation algorithms and processing large datasets.
Chapter 4: Best Practices in Saturation Analysis
Accurate and reliable saturation determination requires careful planning and execution. Best practices include:
- Careful Core Selection and Handling: Representativeness of core samples is crucial for reliable core analysis. Proper handling minimizes alteration of fluid saturation.
- Quality Control of Well Logs: Thorough quality control of well log data is essential to minimize errors and ensure accurate saturation estimates.
- Integration of Data: Combining data from multiple sources (core analysis, well logs, seismic) improves the accuracy and reliability of saturation estimates.
- Calibration and Validation: Models used for saturation estimation should be calibrated against laboratory measurements and field data.
- Uncertainty Analysis: Accounting for uncertainty in input parameters and model assumptions is crucial for reliable reservoir management decisions.
Chapter 5: Case Studies of Saturation Analysis
Real-world examples demonstrate the application of saturation analysis techniques and the impact on reservoir management decisions. Case studies should include:
- Case Study 1: A heterogeneous carbonate reservoir: Illustrating the challenges and solutions in saturation determination for complex rock formations. Emphasis on the application of advanced logging techniques and simulation models.
- Case Study 2: An offshore oil field: Highlighting the importance of seismic data integration for large-scale saturation mapping. The impact on field development planning will be discussed.
- Case Study 3: An enhanced oil recovery (EOR) project: Demonstrating how saturation monitoring during EOR operations (e.g., waterflooding) can optimize production strategies and maximize hydrocarbon recovery.
These case studies would detail the techniques used, the results obtained, and the implications for reservoir management. They would emphasize the importance of integrating various data sources and using appropriate models for accurate saturation determination.
- Critical Saturation Saturation Critique : Un Fact…
- Developed Reserves (reservoir) Réserves développées : La sou…
- DP (reservoir) DP (Réservoir) : Une Clé pour…
- Fluid Saturation Comprendre la saturation des …
- F (reservoir) Comprendre le F (Réservoir) :…
- Gas Saturation Comprendre la Saturation en G…
- HCPV (reservoir) HCPV : Le Coeur de la Caracté…
- Irreducible Water Saturation L'eau immobile : Comprendre l…
- Isosaturation Comprendre l'Isosaturation : …
- MBE (reservoir) Dévoiler les Secrets du Réser…
- Oil Saturation (reservoir) Comprendre la saturation pétr…
- Pr (reservoir) Le rôle crucial de la Pressio…
- Saturation Exponent Comprendre l'Exposant de Satu…
- Saturation Pressure Pression de saturation : le p…
- Spill Point (reservoir) Le Point de Débordement : Où …
- Demande de justification des dépenses Naviguer dans la de… Planification et ordonnancement du projet
- Coût budgété du travail planifié Comprendre le Coût … Estimation et contrôle des coûts
- Les limites de batterie Comprendre les limi… Termes techniques généraux
- Outil DV Outil DV : Un éléme… Forage et complétion de puits
- SOMMAIRE TOC : Comprendre le… Termes techniques généraux
Comments