Ingénierie des réservoirs
Reserves
Comprendre les réserves de pétrole et de gaz : un guide pour quantifier l'or noir
Dans le monde du pétrole et du gaz, les **réserves** sont un terme crucial qui quantifie la quantité d'hydrocarbures enfermés sous la surface de la Terre. Ces réserves ne sont pas seulement des gisements potentiels ; elles représentent une quantité **mesurable et récupérable** de pétrole et de gaz naturel, prête à être extraite et mise sur le marché.
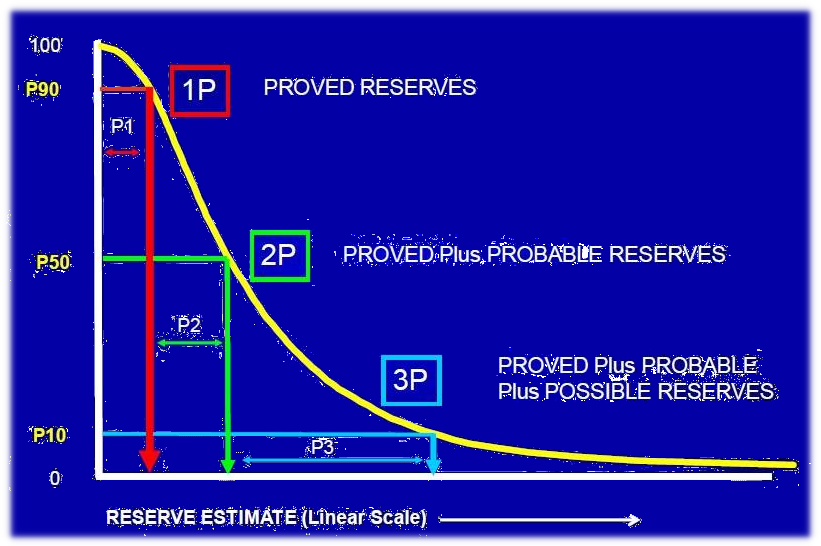
Comprendre les réserves est essentiel à la fois pour les entreprises pétrolières et gazières et pour les investisseurs. Cela permet aux entreprises de prendre des décisions éclairées concernant les plans de forage et de production, tandis que les investisseurs peuvent évaluer la rentabilité potentielle et la valeur future d'une entreprise en fonction de ses réserves prouvées.
Voici une ventilation des différents types de réserves dans le secteur pétrolier et gazier :
**1. Réserves prouvées :** Cette catégorie représente la quantité **la plus certaine** et **récupérable** d'hydrocarbures. Ces réserves sont étayées par des **données de production réelles**, des tests de puits et des techniques d'extraction éprouvées. Les réserves prouvées sont classées comme **1P** (prouvé) et sont considérées comme l'estimation la plus fiable pour les investisseurs.
**2. Réserves probables :** Ces réserves sont estimées sur la base de **données géologiques et d'ingénierie**, mais présentent un **niveau d'incertitude plus élevé** que les réserves prouvées. Elles sont classées comme **2P** (probable) et incluent généralement des ressources qui n'ont pas encore été entièrement explorées ou qui nécessitent des avancées technologiques supplémentaires pour leur extraction.
**3. Réserves possibles :** Cette catégorie englobe les **gisements d'hydrocarbures potentiels** qui sont moins certains que les réserves probables. Elles sont classées comme **3P** (possible) et reposent fortement sur des interprétations géologiques et des estimations spéculatives.
**Calcul des réserves :**
Le calcul des réserves implique un processus complexe qui prend en compte de multiples facteurs, notamment :
- **Données géologiques :** Cela comprend des informations sur la taille et la forme du réservoir, le type de roche et la présence d'hydrocarbures.
- **Données d'ingénierie :** Cela comprend des données de tests de puits, l'historique de production et des estimations du taux de récupération.
- **Facteurs économiques :** Des facteurs tels que les prix du pétrole et du gaz, les coûts de production et les contraintes réglementaires sont pris en compte pour déterminer la viabilité économique de l'extraction des réserves.
**Importance des réserves :**
Les réserves sont cruciales pour plusieurs raisons :
- **Évaluation des ressources :** Elles fournissent une estimation fiable de la quantité de pétrole et de gaz disponible pour la production.
- **Décisions d'investissement :** Les entreprises et les investisseurs utilisent les réserves pour évaluer la rentabilité potentielle et la valeur future d'un projet.
- **Planification de la production :** Les réserves sont essentielles pour développer des calendriers de production et allouer des ressources.
- **Évaluation du marché :** La taille et la qualité des réserves ont un impact direct sur la valeur marchande et le cours de l'action d'une entreprise.
**Comprendre les nuances des réserves de pétrole et de gaz** est essentiel pour une prise de décision éclairée dans l'industrie énergétique. En évaluant et en quantifiant avec précision ces ressources, les entreprises et les investisseurs peuvent naviguer dans la complexité du marché de l'énergie et faire des choix stratégiques pour un avenir durable.
Test Your Knowledge
Quiz: Understanding Oil & Gas Reserves
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. Which type of reserve represents the most certain and recoverable amount of hydrocarbons?
a) Probable Reserves
Answer
Incorrect
b) Possible Reserves
Answer
Incorrect
c) Proven Reserves
Answer
Correct
d) None of the above
Answer
Incorrect
2. What does "1P" refer to in the context of oil and gas reserves?
a) Possible Reserves
Answer
Incorrect
b) Probable Reserves
Answer
Incorrect
c) Proven Reserves
Answer
Correct
d) Potential Reserves
Answer
Incorrect
3. Which of the following factors is NOT considered when calculating oil and gas reserves?
a) Geological Data
Answer
Incorrect
b) Engineering Data
Answer
Incorrect
c) Economic Factors
Answer
Incorrect
d) Weather Patterns
Answer
Correct
4. What is the primary importance of oil and gas reserves for investors?
a) Understanding the environmental impact of extraction
Answer
Incorrect
b) Assessing the potential profitability and future value of a project
Answer
Correct
c) Determining the cost of production
Answer
Incorrect
d) Evaluating the impact of government regulations
Answer
Incorrect
5. Which of the following is NOT a reason why understanding oil and gas reserves is crucial?
a) Resource assessment
Answer
Incorrect
b) Investment decisions
Answer
Incorrect
c) Production planning
Answer
Incorrect
d) Determining the price of gasoline
Answer
Correct
Exercise: Estimating Reserves
Scenario: A company has discovered a new oil field with a potential reservoir size of 100 million barrels. They have completed initial exploration and testing, confirming the presence of oil and obtaining data on its quality. Based on this information, they have estimated the following:
- Proven Reserves: 20 million barrels
- Probable Reserves: 30 million barrels
Task:
- Calculate the Possible Reserves for this field, assuming the total potential reserves remain at 100 million barrels.
- Explain how the company could increase its Proven Reserves.
Solution:
Exercice Correction
Possible Reserves: Total potential reserves - Proven reserves - Probable reserves = Possible reserves 100 million barrels - 20 million barrels - 30 million barrels = 50 million barrels
Increasing Proven Reserves: The company can increase its Proven Reserves by:
- Conducting further exploration and drilling: This will provide more data and confirmation of the actual recoverable amount.
- Developing and implementing improved extraction technologies: This can increase the efficiency and recovery rate of the existing reservoir.
- Acquiring additional data and analysis: Continuously evaluating geological and engineering data will help refine estimates and increase confidence in the proven reserves.
Books
- Petroleum Geology by William D. Nesse: Provides a comprehensive overview of petroleum geology, including chapters on reservoir characterization and reserves estimation.
- Petroleum Engineering: Drilling and Well Completion by John A. Lee: Focuses on the engineering aspects of oil and gas production, covering well design, drilling, and production methods relevant to reserve estimation.
- The World Oil and Gas Review by The Energy Institute: Offers a global perspective on the oil and gas industry, including analysis of reserve trends, production, and market dynamics.
- Economics of Petroleum Exploration and Production by Harold L. Stout: Explores the economic aspects of oil and gas exploration and production, including reserve valuation and project profitability.
Articles
- "Reserves: A Guide for Investors" by the Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE): This article provides a clear explanation of different reserve categories and their significance for investors.
- "Understanding Oil and Gas Reserves" by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA): A comprehensive guide to oil and gas reserves, including definitions, classification, and estimation methods.
- "The Importance of Reserves in the Oil and Gas Industry" by Oil & Gas Journal: Explores the critical role of reserves in decision-making for oil and gas companies.
- "Reserves Estimation and Reporting: A Review of Best Practices" by the American Association of Petroleum Geologists (AAPG): This article reviews current practices and standards for reserve estimation and reporting.
Online Resources
- Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE): https://www.spe.org/ Offers a wealth of information on petroleum engineering, including resources on reserves estimation and reporting.
- U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA): https://www.eia.gov/ Provides comprehensive data and analysis on energy resources, including oil and gas reserves.
- American Association of Petroleum Geologists (AAPG): https://www.aapg.org/ Offers publications, conferences, and resources for professionals in petroleum geology, including information on reserves.
- World Oil & Gas Review: https://www.worldoil.com/ A leading industry publication covering the latest news, trends, and analysis in the oil and gas industry.
Search Tips
- Use specific keywords: Include terms like "oil reserves", "gas reserves", "reserves estimation", "reserve reporting", "1P reserves", "2P reserves", "3P reserves".
- Combine keywords: Use combinations like "oil reserves calculation", "reserves and production", "reserves valuation".
- Search for specific organizations: Add terms like "EIA reserves data", "SPE reserves guidelines", "AAPG reserves standards".
- Use quotation marks: Surround phrases with quotation marks to find exact matches, such as "proven oil reserves".
- Narrow your search: Use filters like "time" and "language" to refine your results.
Techniques
Understanding Oil & Gas Reserves: A Guide to Quantifying the Black Gold
This guide expands on the initial text, breaking down the topic into chapters focusing on specific aspects of oil and gas reserve quantification.
Chapter 1: Techniques for Estimating Oil & Gas Reserves
Estimating oil and gas reserves is a complex process requiring a multidisciplinary approach. Several techniques are employed, often in combination, to arrive at a reliable estimate. These techniques can be broadly classified into:
Geological Techniques: These techniques focus on understanding the subsurface geology of the reservoir. They involve:
- Seismic Surveys: Using sound waves to image subsurface rock formations and identify potential hydrocarbon traps. Different seismic techniques (e.g., 2D, 3D, 4D) provide varying levels of detail.
- Well Logging: Measuring various physical properties of the rock formations penetrated by a wellbore (e.g., porosity, permeability, resistivity) to characterize reservoir quality.
- Core Analysis: Analyzing physical samples of rock (cores) from the reservoir to determine porosity, permeability, fluid saturation, and other key parameters.
- Geological Modeling: Creating 3D models of the reservoir based on geological and geophysical data to visualize the distribution of hydrocarbons.
Engineering Techniques: These techniques focus on the engineering aspects of hydrocarbon extraction. They include:
- Well Testing: Conducting tests on producing wells to measure reservoir pressure, flow rates, and other parameters to estimate reservoir properties and productivity.
- Production History Analysis: Analyzing historical production data to understand reservoir performance and predict future production.
- Reservoir Simulation: Using computer models to simulate the behavior of the reservoir under different production scenarios. This helps predict future production rates and ultimate recovery.
- Material Balance Calculations: Applying principles of fluid mechanics and thermodynamics to estimate the amount of hydrocarbons in place and the recovery factor.
Statistical Techniques: These techniques are used to quantify uncertainty and risk associated with reserve estimations:
- Monte Carlo Simulation: A probabilistic method used to incorporate uncertainty in input parameters and generate a range of possible reserve estimates.
- Bayesian Methods: Statistical methods that allow updating reserve estimates as new data become available.
The choice of techniques depends on the stage of exploration and development, the availability of data, and the level of uncertainty acceptable. A combination of techniques is usually employed to minimize uncertainty and increase confidence in the reserve estimate.
Chapter 2: Models Used in Oil & Gas Reserve Estimation
Various models are employed to represent the complexity of hydrocarbon reservoirs and estimate reserves. These models can be broadly categorized as:
Deterministic Models: These models rely on a single set of input parameters and provide a single estimate of reserves. While simpler, they don't account for uncertainty.
Probabilistic Models: These models incorporate uncertainty in input parameters using statistical techniques like Monte Carlo simulation. They provide a range of possible reserve estimates with associated probabilities, allowing for a more realistic assessment of risk.
Specific examples of models include:
Volumetric Models: Simple models used for early-stage reserve estimation, based on the geometry of the reservoir and the properties of the hydrocarbons. Suitable for relatively homogeneous reservoirs.
Material Balance Models: These models use principles of fluid mechanics to estimate reserves by tracking changes in reservoir pressure and fluid volumes over time. Useful for mature fields with extensive production history.
Reservoir Simulation Models: Complex numerical models that simulate fluid flow and pressure changes in the reservoir under different production scenarios. These models provide detailed predictions of reservoir performance and ultimate recovery. They are computationally intensive and require significant data input.
The choice of model depends on the available data, the complexity of the reservoir, and the desired level of accuracy.
Chapter 3: Software for Oil & Gas Reserve Estimation
Specialized software packages are used to perform the complex calculations and simulations involved in reserve estimation. These software packages often incorporate multiple modeling techniques and allow for integration of various data sources. Examples include:
Petrel (Schlumberger): A widely used integrated reservoir modeling and simulation platform.
Eclipse (Schlumberger): A powerful reservoir simulation software capable of handling complex reservoir models.
CMG (Computer Modelling Group): Another popular reservoir simulation software suite.
Roxar RMS (Emerson Automation Solutions): Offers a range of reservoir characterization and simulation tools.
These software packages are typically expensive and require specialized training to use effectively. They allow for automation of many tasks, reducing manual effort and improving accuracy. Furthermore, they provide visualization tools to help geoscientists and engineers better understand the reservoir and make informed decisions.
Chapter 4: Best Practices in Oil & Gas Reserve Estimation
To ensure reliable and transparent reserve estimation, several best practices should be followed:
Data Quality: Accurate and reliable data is crucial for accurate reserve estimation. Data should be thoroughly validated and checked for errors.
Transparency and Documentation: The entire process of reserve estimation, including data sources, methodologies, and assumptions, should be documented thoroughly and transparently.
Independent Verification: It's advisable to have an independent third party verify reserve estimates to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Use of Standard Guidelines: Adhering to industry standards and guidelines, such as those from the Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE) and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), is crucial to maintain consistency and credibility.
Regular Updates: Reserve estimates should be regularly updated as new data become available and uncertainties are reduced.
Uncertainty Assessment: A proper assessment of uncertainty should be performed and communicated clearly. This includes quantifying the range of possible reserve estimates and identifying the main sources of uncertainty.
Following these best practices helps ensure the reliability and credibility of reserve estimates, which are essential for investment decisions and regulatory compliance.
Chapter 5: Case Studies in Oil & Gas Reserve Estimation
Case studies showcasing successful (and unsuccessful) reserve estimations can provide valuable lessons. These studies should highlight:
The geological setting and reservoir characteristics: This provides context for understanding the challenges and opportunities in the estimation process.
The methodologies and techniques employed: Describing the approaches used allows for comparison and evaluation.
The results and uncertainties: Detailed results with a clear quantification of uncertainties help illustrate the complexities.
Lessons learned: Highlighting successes and failures allows for improvement in future estimations.
Examples could include case studies detailing the estimation of reserves in giant oil fields, unconventional reservoirs (e.g., shale gas), or fields with complex geological structures. Analyzing these cases provides practical insights into the challenges and rewards of accurate reserve estimation. Access to such case studies often requires subscriptions to industry databases or reports.
- Behind Pipe Reserves Réserves derrière le tubage :…
- Demonstrated Reserves Décrypter les réserves démont…
- Developed Reserves (reservoir) Réserves développées : La sou…
- Discovered (reserves) "Réserves Découvertes" dans l…
- Non-Producing Reserves Libérer le potentiel : Compre…
- PDNP (reserves) Réserves PDNP : Les géants si…
- PD (reserves) Comprendre les réserves PD (D…
- Possible Reserves (3P) Les 3P de l'ingénierie des ré…
- Probable Reserves Plonger dans le domaine des r…
- Probable Reserves (2P) Débloquer le Potentiel : Les …
- Proved Developed Reserves Libérer le potentiel : Les ré…
- Proved Reserves Comprendre les Réserves Prouv…
- Proved Undeveloped Reserves Réserves prouvées non dévelop…
- Proven Reserves (1P) Débloquer le réservoir : comp…
- PUD (reserves) PUD (Réserves) : Comprendre l…
- Contracted Reserves Réserves contractuelles : Un …
- Dry Gas (reserves) Gaz sec : La machine à gaz ma…
- Entitlement (reserves/production) Droits d'exploitation (Réserv…
- Managerial Reserves Réserves de gestion : le file…
- Possible Reserves Débloquer le potentiel : Comp…
- Demande de justification des dépenses Naviguer dans la de… Planification et ordonnancement du projet
- Coût budgété du travail planifié Comprendre le Coût … Estimation et contrôle des coûts
- Les limites de batterie Comprendre les limi… Termes techniques généraux
- Outil DV Outil DV : Un éléme… Forage et complétion de puits
- SOMMAIRE TOC : Comprendre le… Termes techniques généraux
Comments