Forage et complétion de puits
Casing Centralizer
Garder le cap : L'importance des centralisateurs de tubage dans le pétrole et le gaz
Dans l'industrie pétrolière et gazière, une construction de puits efficace et performante est primordiale. Un élément crucial de ce processus est de s'assurer que le tubage, qui borde le puits, reste centré sur toute sa longueur. C'est là que les centralisateurs de tubage entrent en jeu.
Que sont les centralisateurs de tubage ?
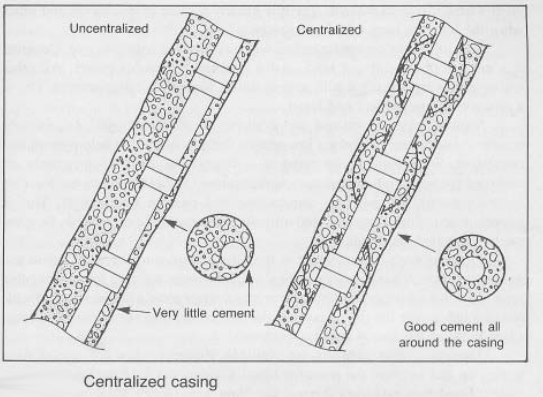
Les centralisateurs de tubage sont des dispositifs spécialisés conçus pour maintenir le tubage au centre du trou de forage pendant l'installation. Ils agissent comme des espaceurs, empêchant le tubage de toucher la paroi du trou de forage et créant un espace annulaire uniforme entre les deux. Cet espace est crucial pour des opérations de cimentation réussies, assurant une liaison adéquate et empêchant les fuites.
Pourquoi les centralisateurs sont importants ?
- Cimentation améliorée : Un tubage bien centré permet un écoulement uniforme de la boue de cimentation, ce qui se traduit par une liaison de ciment solide et complète. Cela empêche la migration de gaz et de fluides, minimisant les risques environnementaux et maximisant la production du puits.
- Réduction de la friction : Le centrage du tubage minimise la friction entre le tubage et la paroi du trou de forage, réduisant la force d'installation et les dommages potentiels à la colonne de tubage.
- Intégrité du puits améliorée : Le tubage centralisé garantit un joint solide et étanche, empêchant les fuites de fluides et maximisant la durée de vie opérationnelle du puits.
- Forage efficace : En minimisant la friction, les centralisateurs facilitent des opérations de forage plus fluides et plus rapides, ce qui conduit à une réduction des temps d'arrêt et à des économies de coûts.
Types de centralisateurs de tubage :
Il existe de nombreuses conceptions de centralisateurs, chacune étant adaptée à des conditions et des exigences spécifiques de puits. L'une des conceptions les plus utilisées est le **centralisateur à ressort en arc**.
Centralisateur à ressort en arc :
Ce type est constitué d'un arc à ressort qui appuie contre la paroi du trou de forage, maintenant le tubage au centre. La tension du ressort est réglable pour s'adapter aux différents diamètres de puits et tailles de tubage.
Caractéristiques clés des centralisateurs à ressort en arc :
- Tension de ressort réglable : Permet une personnalisation pour s'adapter aux différentes conditions de puits.
- Construction durable : Fabriqué à partir de matériaux de haute qualité pour résister aux conditions difficiles du trou de forage.
- Conception à faible friction : La surface lisse minimise la friction pendant l'installation.
- Application polyvalente : Adapté à diverses profondeurs de puits et tailles de tubage.
Conclusion :
Les centralisateurs de tubage sont des composants essentiels de la construction de puits de pétrole et de gaz, jouant un rôle vital pour obtenir des résultats optimaux en matière de cimentation et garantir l'intégrité du puits. Le centralisateur à ressort en arc, avec sa tension réglable et sa conception robuste, est un choix fiable pour maintenir un tubage centralisé et réaliser des opérations de puits efficaces et réussies.
Test Your Knowledge
Quiz: Casing Centralizers in Oil & Gas
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What is the primary function of casing centralizers?
a) To prevent the casing from collapsing under pressure.
Answer
Incorrect. Casing centralizers are not designed to prevent collapsing, but to maintain the casing's position.
b) To facilitate the flow of drilling mud.
Answer
Incorrect. Drilling mud flow is primarily influenced by the drill bit and mud circulation system.
c) To maintain the casing in the center of the borehole.
Answer
Correct. This is the primary function of casing centralizers.
d) To protect the casing from corrosion.
Answer
Incorrect. While corrosion protection is important, it's not the primary function of centralizers.
2. Which of the following is a direct benefit of using casing centralizers?
a) Increased drilling speed.
Answer
Correct. Reduced friction due to centralized casing leads to smoother and faster drilling.
b) Reduced well production.
Answer
Incorrect. Centralizers enhance well production by improving cementing and well integrity.
c) Increased risk of gas leaks.
Answer
Incorrect. Centralizers reduce the risk of leaks by ensuring a strong cement bond.
d) Increased wellbore diameter.
Answer
Incorrect. Centralizers don't affect the wellbore diameter; they maintain the casing's position within it.
3. What is the main advantage of a bow spring centralizer over other types?
a) It can be used in extremely high-pressure environments.
Answer
Incorrect. While bow spring centralizers are robust, their suitability for high-pressure environments depends on the specific design and material.
b) It is the most cost-effective option.
Answer
Incorrect. The cost-effectiveness depends on the specific well conditions and requirements.
c) It has adjustable spring tension.
Answer
Correct. Adjustable spring tension allows for customization to different well diameters and casing sizes.
d) It requires minimal maintenance.
Answer
Incorrect. All centralizers require some level of maintenance depending on their design and application.
4. Which of the following statements is TRUE about cementing in a well with centralized casing?
a) Cement slurry flow is inconsistent, resulting in a weak bond.
Answer
Incorrect. Centralized casing ensures a uniform cement slurry flow, leading to a strong bond.
b) The cement bond is stronger and more complete.
Answer
Correct. This is one of the primary benefits of using centralizers.
c) Cementing operations are more time-consuming.
Answer
Incorrect. Centralized casing often facilitates faster and more efficient cementing.
d) The risk of gas leaks is higher.
Answer
Incorrect. Centralizers reduce the risk of gas leaks by ensuring a strong cement bond.
5. Why is maintaining a uniform annular space between the casing and borehole wall important?
a) To prevent corrosion of the casing.
Answer
Incorrect. While corrosion is a concern, the annular space is primarily important for cementing.
b) To facilitate easier drilling operations.
Answer
Incorrect. While centralizers improve drilling efficiency, the annular space is crucial for cementing.
c) To allow for proper cementing operations and prevent leaks.
Answer
Correct. A uniform annular space ensures a strong and complete cement bond, preventing leaks.
d) To ensure the casing doesn't become stuck in the borehole.
Answer
Incorrect. While centralizers prevent the casing from sticking to the wall, the annular space is more important for cementing.
Exercise: Casing Centralizer Selection
Scenario:
You are tasked with selecting the appropriate casing centralizers for a new oil well. The well is expected to be 10,000 feet deep and will be drilled through various formations with varying hardness. The casing size is 9 5/8 inches.
Task:
- Identify three key factors you should consider when selecting centralizers for this well.
- Explain why each factor is crucial in this specific scenario.
- Suggest a type of centralizer that would be suitable based on your considerations.
Exercise Correction:
Exercise Correction
**1. Key Factors:**
- Well Depth: At 10,000 feet, the centralizers need to withstand high hydrostatic pressure and potential stress from the long casing string.
- Formation Hardness: Different formations will exert varying pressures on the casing. Centralizers need to provide enough support to prevent casing deformation.
- Casing Size: The centralizers need to fit the 9 5/8-inch casing and provide adequate spacing for a uniform cement sheath.
**2. Importance:**
- Well Depth: Centralizers designed for high-pressure environments are necessary to maintain the casing's position and prevent movement or deformation due to the weight of the casing and the pressure within the wellbore.
- Formation Hardness: Centralizers should be robust enough to withstand the forces exerted by varying formations. Softer formations may require less tension, while harder formations may require greater support.
- Casing Size: Centralizers must fit the casing size to ensure proper spacing and prevent the casing from contacting the borehole wall, which is essential for a successful cement bond.
**3. Suitable Centralizer:**
- Bow Spring Centralizers: These are a good choice due to their adjustable spring tension, allowing for customization based on the formation's hardness. Their durable construction makes them suitable for deep wells, and their design allows for a uniform annular space for proper cementing. However, it's crucial to select bow spring centralizers with a high load capacity and proper specifications for the casing size and expected pressures.
Books
- "Oil Well Drilling Engineering: A Practical Approach" by T.L. G. Dake: A comprehensive textbook covering various aspects of oil well drilling, including casing design and centralizers.
- "Well Completion Engineering" by John A. B. Willhite: Offers in-depth information on well completion processes, including casing centralizers and their role in cementing.
- "Petroleum Engineering Handbook" edited by William D. McCain Jr.: A multi-volume reference source with dedicated chapters on well construction and completion, including details on casing and centralizers.
Articles
- "Casing Centralizers - An Overview of Types, Applications, and Design Considerations" by SPE: This article from the Society of Petroleum Engineers provides a technical overview of different casing centralizer types, their applications, and design considerations.
- "The Importance of Casing Centralizers in Cementing Operations" by Schlumberger: A publication from Schlumberger, a leading oilfield services company, highlighting the significance of centralizers in achieving proper cement bonding and well integrity.
- "Optimizing Cementing Operations with Casing Centralizers" by Halliburton: Another industry leader, Halliburton, offers insights into selecting the right centralizers for optimal cementing performance.
Online Resources
- Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE): The SPE website offers a vast library of technical papers and presentations related to drilling and completion, including those discussing casing centralizers.
- *Schlumberger: * This website provides detailed information on their range of casing centralizers and their applications.
- Halliburton: Similar to Schlumberger, Halliburton's website offers technical resources on their products and services, including casing centralizers.
- Baker Hughes: Another major oilfield services provider with resources on casing centralizers and their applications.
Search Tips
- Use specific keywords: Instead of just "casing centralizers," be more precise. Try combinations like "casing centralizers types," "bow spring centralizers," "casing centralizer design," "casing centralizer selection," etc.
- Include industry terms: Use terms like "oil and gas," "well completion," "cementing," "drilling," etc., to narrow down your search results.
- Use quotation marks: When searching for specific phrases, enclose them in quotation marks to find exact matches. For example: "casing centralizer function."
- Combine keywords with operators: Use operators like "+" to include certain words and "-" to exclude others. For instance: "casing centralizers + bow spring - installation."
- Explore related terms: Once you find a relevant article or resource, look for links to other related content on the same website or in the search results.
Techniques
Keeping it Straight: The Importance of Casing Centralizers in Oil & Gas
(This section remains as the introduction and overview, providing context for the following chapters.)
Keeping it Straight: The Importance of Casing Centralizers in Oil & Gas
In the oil and gas industry, efficient and effective well construction is paramount. One crucial element in this process is ensuring the casing, which lines the wellbore, remains centered throughout its length. This is where casing centralizers come into play.
What are Casing Centralizers?
Casing centralizers are specialized devices designed to maintain the casing in the center of the borehole during installation. They act as spacers, preventing the casing from touching the borehole wall and creating a uniform annular space between the two. This space is crucial for successful cementing operations, ensuring proper bonding and preventing leaks.
Why Centralizers Matter?
- Improved Cementing: A well-centered casing allows for a uniform cement slurry flow, resulting in a strong and complete cement bond. This prevents gas and fluid migration, minimizing environmental risks and maximizing well production.
- Reduced Friction: Keeping the casing centered minimizes friction between the casing and the borehole wall, reducing installation force and potential damage to the casing string.
- Enhanced Well Integrity: Centralized casing ensures a strong and leak-proof seal, preventing fluid leaks and maximizing the well's operational lifespan.
- Efficient Drilling: By minimizing friction, centralizers facilitate smoother and faster drilling operations, leading to reduced downtime and cost savings.
This document will explore casing centralizers in detail, covering various aspects of their design, application, and importance in successful well completion.
Chapter 1: Techniques for Casing Centralizer Deployment
This chapter focuses on the practical aspects of using casing centralizers.
Placement Techniques:
- Even Spacing: The importance of evenly spacing centralizers along the casing string to ensure consistent centralization. Discussion of calculation methods and factors influencing spacing (e.g., wellbore geometry, casing size, expected doglegs).
- Strategic Placement in Challenging Wells: Techniques for placing centralizers in deviated wells, horizontal wells, and wells with significant doglegs. The role of specialized centralizers in these scenarios.
- Handling and Installation Procedures: Best practices for handling centralizers to prevent damage, proper installation methods, and avoiding common mistakes during deployment.
- Pre-Installation Inspection: Importance of inspecting centralizers before deployment to identify any defects or damage that could compromise their function.
- Post-Installation Verification: Methods for verifying the correct placement and functionality of the centralizers after installation (e.g., logging tools, downhole cameras).
Chapter 2: Models and Types of Casing Centralizers
This chapter delves into the various designs and functionalities of casing centralizers.
Types of Casing Centralizers:
- Bow Spring Centralizers: Detailed description of bow spring centralizers, including variations in design, materials, and applications. Discussion of advantages and limitations.
- Flexible Centralizers: Explanation of flexible centralizers and their suitability for deviated and horizontal wells. Comparison with bow spring centralizers.
- Hydraulic Centralizers: Description of hydraulic centralizers and their operation. Discussion of their advantages and limitations compared to other types.
- Other Specialized Centralizers: Overview of other specialized centralizers designed for specific well conditions, such as those with high temperatures or pressures.
- Material Selection and Considerations: Factors influencing the choice of materials for centralizers, including corrosion resistance, strength, and temperature tolerance.
Chapter 3: Software and Tools for Casing Centralizer Design and Placement
This chapter explores the technological tools used in centralizer planning.
Software Applications:
- Well Planning Software: How well planning software is used to model the wellbore trajectory and optimize centralizer placement. Examples of relevant software packages.
- Centralizer Design Software: Discussion of specialized software for designing and selecting appropriate centralizers based on well conditions and casing parameters.
- Simulation and Modeling: Use of simulation software to predict the behavior of centralizers during installation and cementing operations.
- Data Analysis and Reporting: How software aids in analyzing data from centralizer deployment and generating reports for well completion.
Chapter 4: Best Practices for Casing Centralizer Selection and Utilization
This chapter emphasizes optimal practices for successful application.
Best Practices:
- Centralizer Selection Criteria: Factors to consider when selecting appropriate centralizers, including wellbore geometry, casing size, depth, and anticipated conditions (temperature, pressure, etc.).
- Spacing Optimization: Methods and guidelines for optimal centralizer spacing to ensure effective centralization and consistent cementing.
- Quality Control and Assurance: Importance of quality control measures throughout the process, from centralizer manufacturing to installation and verification.
- Troubleshooting and Problem Solving: Common issues encountered with centralizers and strategies for troubleshooting and resolving problems.
- Regulatory Compliance: Overview of relevant regulations and standards related to casing centralizer usage and safety.
Chapter 5: Case Studies of Casing Centralizer Applications
This chapter illustrates real-world examples of centralizer effectiveness.
Case Studies:
- Case Study 1: A case study illustrating successful centralizer deployment in a challenging wellbore environment (e.g., highly deviated well, complex geology).
- Case Study 2: A case study demonstrating the impact of improper centralizer placement on cementing quality and well integrity.
- Case Study 3: A case study highlighting the cost savings and efficiency gains achieved through optimized centralizer placement and usage.
- Case Study 4: (And others as needed) Further case studies showcasing diverse applications and the benefits of proper centralizer implementation.
This structured approach provides a comprehensive guide to casing centralizers in the oil and gas industry. Remember to replace the placeholder text with specific details and examples. The image provided in your original text could be appropriately incorporated into one or more of these chapters depending on its content.
- Bottom Casing Packoff Comprendre le Joint de Fond d…
- Bow Spring Centralizer Centralisateurs à Ressort en …
- casing Le tubage : L'épine dorsale d…
- Casing L'épine dorsale de la pro…
- Casing-Annular Pressure Pression Annulaire du Tubage …
- casing centralizer Bien centré : Le rôle crucial…
- Casing Collar Log Journal des Colliers de Tubag…
- Casing Coupling Couplage de tubage : Le héros…
- casing coupling (collar) Accouplements de tubage : les…
- casing crew Les héros méconnus de la cons…
- Casing Crew Les héros méconnus du pétrole…
- casing cutter Coupe-tubage : Un outil cruci…
- Casing Cutter Coupe-gaines : L'outil de pré…
- Casing Grade Classe de tubage : L'épine do…
- casing gun Les canons de perforation : L…
- casing hanger Le Héros Insoupçonné de l'Ach…
- Casing Hanger Le héros méconnu de la produc…
- casinghead La Tête de Tubage : Un Compos…
- Casing Head Tête de tubage : Le lien cruc…
- Casing Cladding Revêtement de tubage : Colmat…
- Demande de justification des dépenses Naviguer dans la de… Planification et ordonnancement du projet
- Coût budgété du travail planifié Comprendre le Coût … Estimation et contrôle des coûts
- Les limites de batterie Comprendre les limi… Termes techniques généraux
- Outil DV Outil DV : Un éléme… Forage et complétion de puits
- SOMMAIRE TOC : Comprendre le… Termes techniques généraux
Comments