Forage et complétion de puits
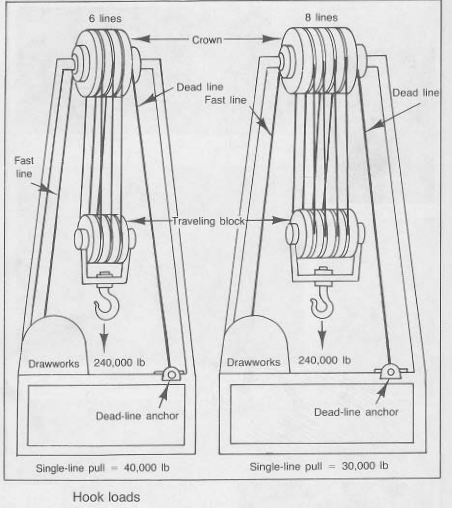
hook load
Comprendre la Charge au Crochet dans le Forage & la Complétion de Puits
Dans l'industrie pétrolière et gazière, le terme "charge au crochet" fait référence au poids total du train de forage et de ses composants associés qui sont suspendus au crochet du derrick de forage. Ce poids est un facteur crucial dans les opérations de forage, car il a un impact direct sur la stabilité du derrick, l'efficacité du forage et la sécurité du personnel.
Composants de la Charge au Crochet :
La charge au crochet est composée de plusieurs composants, notamment :
- Tube de forage : Le composant principal du train de forage, reliant l'équipement de surface au trépan au fond du puits.
- Collets de forage : Sections lourdes de tuyauterie placées au-dessus du trépan pour fournir un poids de forage.
- Ensemble de fond de trou (BHA) : Comprend divers outils et équipements placés au-dessus du trépan, tels que des stabilisateurs, des alésoirs et des moteurs à boue.
- Tube de forage à poids lourd (HWDP) : Utilisé pour augmenter le poids sur le trépan et améliorer l'efficacité du forage.
- Tubage : Tuyaux en acier utilisés pour revêtir le puits et fournir un support structurel.
- Tubage : Tuyaux de plus petit diamètre utilisés pour transporter les hydrocarbures produits du puits à la surface.
Facteurs affectant la Charge au Crochet :
Plusieurs facteurs influencent la charge au crochet pendant les opérations de forage :
- Profondeur du puits : Au fur et à mesure que le puits s'approfondit, la longueur du train de forage augmente, ce qui entraîne une charge au crochet plus élevée.
- Type de train de forage : Le poids du train de forage dépend de la taille et du matériau du tube de forage, des cols et des autres composants.
- Poids sur trépan (WOB) : La force appliquée au trépan, qui est contrôlée en ajustant la charge au crochet.
- Équipement supplémentaire : La présence de tubage, de tubage ou d'autres équipements suspendus au crochet ajoutera à la charge totale.
Importance de la Gestion de la Charge au Crochet :
La gestion de la charge au crochet est essentielle pour diverses raisons :
- Sécurité du derrick : Le dépassement de la capacité du crochet peut entraîner une défaillance structurelle du derrick, provoquant des accidents catastrophiques.
- Efficacité du forage : L'optimisation de la charge au crochet permet un forage efficace, assurant un poids approprié sur le trépan pour une pénétration efficace de la roche.
- Stabilité du puits : Le maintien d'une charge au crochet équilibrée permet d'éviter l'instabilité du puits et un effondrement potentiel.
- Contrôle des coûts : Une gestion attentive de la charge au crochet minimise le risque d'arrêts coûteux dus à des pannes d'équipement ou à des accidents.
Surveillance et contrôle :
La charge au crochet est surveillée en continu à l'aide de capteurs et affichée sur le tableau de bord du derrick de forage. Les opérateurs utilisent ces informations pour ajuster le poids sur le trépan et gérer efficacement la charge au crochet.
Conclusion :
La charge au crochet est un paramètre essentiel dans les opérations de forage et de complétion de puits, affectant directement la sécurité, l'efficacité et l'intégrité globale du puits. Comprendre les composants qui contribuent à la charge au crochet et la gérer efficacement est crucial pour des opérations de forage réussies. En surveillant et en contrôlant attentivement la charge au crochet, les opérateurs garantissent la sécurité du personnel, optimisent les performances de forage et minimisent le risque d'arrêts coûteux.
Test Your Knowledge
Quiz: Understanding Hook Load
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What does "hook load" refer to in the oil and gas industry? a) The weight of the drill bit. b) The total weight of the drill string and its components suspended from the hook. c) The pressure exerted on the drill bit. d) The amount of drilling fluid used.
Answer
b) The total weight of the drill string and its components suspended from the hook.
2. Which of the following is NOT a component of the hook load? a) Drill pipe b) Drill collars c) Mud pumps d) Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (HWDP)
Answer
c) Mud pumps
3. What factor does NOT influence the hook load? a) Depth of the well b) Type of drilling fluid c) Weight on Bit (WOB) d) Additional equipment
Answer
b) Type of drilling fluid
4. Why is managing hook load important for drilling efficiency? a) It helps to prevent the drill bit from wearing down too quickly. b) It allows for the use of heavier drilling fluids. c) It optimizes the weight on bit for effective rock penetration. d) It reduces the amount of time needed to drill a well.
Answer
c) It optimizes the weight on bit for effective rock penetration.
5. How is the hook load monitored? a) By observing the drilling fluid flow rate. b) Using sensors and displaying the data on the control panel. c) By measuring the pressure at the bottom of the well. d) Through visual inspection of the drill string.
Answer
b) Using sensors and displaying the data on the control panel.
Exercise: Calculating Hook Load
Instructions: Calculate the hook load for the following scenario:
- Depth of well: 10,000 ft
- Drill pipe weight: 18 lb/ft
- Drill collars weight: 50 lb/ft
- Number of drill collars: 10
- Bottom Hole Assembly (BHA) weight: 5,000 lb
- Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (HWDP) weight: 40 lb/ft
- Length of HWDP: 2,000 ft
Show your calculations and express the final answer in pounds.
Exercice Correction
**1. Calculate the weight of the drill pipe:** * 10,000 ft * 18 lb/ft = 180,000 lb **2. Calculate the weight of the drill collars:** * 10 collars * 50 lb/ft * 30 ft/collar = 15,000 lb **3. Calculate the weight of the Heavy Weight Drill Pipe (HWDP):** * 2,000 ft * 40 lb/ft = 80,000 lb **4. Add up all the weights to find the total hook load:** * 180,000 lb + 15,000 lb + 5,000 lb + 80,000 lb = 280,000 lb **Therefore, the total hook load is 280,000 pounds.**
Books
- "Drilling Engineering" by J.P. Brill and H.J.R. Weijers: A comprehensive text on drilling engineering, covering hook load and other related concepts.
- "Petroleum Engineering Handbook" by Tarek Ahmed: A widely-used reference for petroleum engineers, containing chapters on drilling and well completion, including sections on hook load.
- "Drilling Engineering: Principles and Practice" by William C. Lyons: Another comprehensive text on drilling engineering, with dedicated sections on hook load management.
Articles
- "Hook Load Management: A Critical Element for Drilling Safety and Efficiency" by SPE: This Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE) article provides a detailed overview of hook load management, its importance, and best practices.
- "Understanding and Managing Hook Load in Drilling Operations" by Rigzone: This article from Rigzone focuses on understanding hook load calculations, factors influencing it, and methods for monitoring and control.
- "Hook Load Considerations in Deepwater Drilling" by Offshore Technology: This article discusses specific challenges and considerations for hook load management in deepwater drilling operations.
Online Resources
- SPE Website: The SPE website offers numerous articles, technical papers, and presentations related to drilling and hook load management.
- Rigzone: Rigzone is a valuable online resource for the oil and gas industry, providing news, articles, and technical information, including articles on hook load.
- Offshore Technology: Offshore Technology provides comprehensive coverage of offshore oil and gas operations, including articles on hook load and other drilling-related topics.
Search Tips
- Use specific keywords: Include terms like "hook load," "drilling," "well completion," "weight on bit," "drilling rig," "safety," and "efficiency."
- Combine keywords with operators: Utilize operators like "AND" and "OR" to refine your search, e.g., "hook load AND drilling AND safety."
- Filter by source: Limit your search to reputable sources like SPE, Rigzone, Offshore Technology, or academic journals.
- Check advanced search options: Utilize Google's advanced search features to narrow down your search results by date, file type, and other criteria.
Techniques
Chapter 1: Techniques for Measuring and Managing Hook Load
This chapter delves into the practical methods used to measure and manage hook load during drilling operations.
1.1 Hook Load Measurement:
- Load Cells: These sensors are installed in the drilling rig's hoisting system, directly measuring the weight suspended from the hook.
- Torque and Tension Measurement: Advanced drilling rigs use torque and tension sensors to determine hook load indirectly, calculated from the torque applied to the drill string and the tension in the hoisting cable.
- Weight Indicator Display: Real-time hook load information is displayed on the rig's control panel, allowing operators to monitor the load continuously.
1.2 Hook Load Management Techniques:
- Weight on Bit (WOB) Control: The primary method for managing hook load involves adjusting the WOB, which directly affects the weight on the hook. This is achieved through the hoisting system and various control mechanisms.
- Drill String Optimization: Using the appropriate drill pipe, drill collars, and BHA configurations can help minimize the hook load while maintaining the desired WOB.
- Casing and Tubing Management: Careful planning and execution of casing and tubing runs are critical to avoid exceeding the hook load capacity.
- Drill String Make-Up and Break-Out: Managing the process of connecting and disconnecting drill pipe sections is essential to ensure that hook load remains within safe limits.
1.3 Importance of Accurate Hook Load Management:
- Preventing Rig Failure: Accurate hook load management is essential to avoid exceeding the rig's hoisting capacity, which could lead to catastrophic failure.
- Optimizing Drilling Efficiency: Proper hook load management ensures the optimal WOB, maximizing drilling efficiency and reducing drilling time.
- Wellbore Stability: Maintaining a balanced hook load helps prevent wellbore instability, borehole collapse, and other complications.
1.4 Challenges and Best Practices:
- Variations in Hook Load: Hook load is constantly changing due to various factors, requiring continuous monitoring and adjustments.
- Calibration and Maintenance: Load cells and other sensors must be regularly calibrated and maintained to ensure accurate hook load measurements.
- Operator Training: Operators require thorough training on hook load management techniques and the associated safety protocols.
Chapter 2: Models and Calculations for Hook Load Estimation
This chapter explores different models and calculations used to estimate hook load in drilling operations.
2.1 Hook Load Calculation Formula:
- Hook Load = Weight of Drill String + Weight of BHA + Weight of Casing/Tubing + Weight of Other Equipment
2.2 Factors Affecting Hook Load Calculation:
- Drill String Weight: The weight of the drill string depends on the length, pipe size, and material of the drill pipe, collars, and other components.
- BHA Weight: The BHA's weight depends on the tools and equipment included, such as stabilizers, reamers, and mud motors.
- Casing and Tubing Weight: The weight of casing and tubing varies based on the size, grade, and length of the pipes used.
- Additional Equipment: Any other equipment hanging from the hook, such as drilling mud pumps or other surface equipment, must be factored into the calculation.
2.3 Static vs. Dynamic Hook Load:
- Static Hook Load: Represents the weight of the suspended components when the drill string is stationary.
- Dynamic Hook Load: Represents the load experienced during drilling operations, considering forces from the drill string rotation, vibration, and other dynamic factors.
2.4 Software Programs for Hook Load Calculation:
- Drilling Engineering Software: Specialized software programs are used to calculate hook load based on various factors, such as wellbore geometry, drilling fluid properties, and drill string design.
- Spreadsheet Tools: Simpler calculations can be performed using spreadsheet programs, such as Microsoft Excel, with pre-defined formulas for hook load estimation.
2.5 Importance of Accurate Hook Load Estimation:
- Safe Operation: Accurate hook load estimation is crucial to ensure that the drilling rig's capacity is not exceeded, preventing equipment failure and accidents.
- Efficient Planning: Accurate calculations aid in planning drilling operations, optimizing the selection of drill string components, and minimizing the risk of delays.
- Cost Optimization: By accurately estimating hook load, operators can minimize the use of heavy equipment and unnecessary weight, resulting in cost savings.
Chapter 3: Software Tools and Technologies for Hook Load Management
This chapter focuses on the software tools and technologies used for hook load management and monitoring in the drilling industry.
3.1 Drilling Automation Systems:
- Real-time Hook Load Monitoring: Advanced drilling automation systems continuously monitor the hook load and provide operators with real-time information through dedicated displays.
- Automatic Load Control: These systems can automatically adjust the WOB and manage hook load based on pre-defined parameters, ensuring that the load remains within acceptable limits.
3.2 Data Acquisition and Logging:
- Hook Load Data Logging: Software tools capture and store hook load data, providing a historical record of the drilling operations.
- Data Analysis: The logged data can be analyzed to identify trends, predict future hook load behavior, and optimize drilling strategies.
3.3 Visualization and Reporting:
- Graphical Displays: Software tools provide graphical representations of hook load data, facilitating easy analysis and monitoring.
- Reports and Alerts: Automated reports and alerts can be generated to notify operators of potential issues related to hook load, enabling prompt action.
3.4 Benefits of Software-Based Hook Load Management:
- Improved Safety: Continuous monitoring and automated control reduce the risk of exceeding the rig's capacity, enhancing operational safety.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Real-time data and automated control optimize drilling performance and minimize downtime.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Comprehensive data analysis supports informed decision-making for improving drilling practices and operational optimization.
3.5 Future Trends in Hook Load Management Software:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms can analyze historical data and predict future hook load behavior, allowing for proactive adjustments and optimized drilling operations.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Advanced software systems enable remote monitoring and control of hook load, providing operators with greater flexibility and access to information.
Chapter 4: Best Practices for Hook Load Management
This chapter provides valuable insights and recommendations for implementing best practices for hook load management in drilling operations.
4.1 Planning and Preparation:
- Thorough Planning: Thorough pre-drilling planning is essential, including defining the expected hook load, evaluating rig capacity, and selecting appropriate drill string components.
- Risk Assessment: Conducting a comprehensive risk assessment helps identify potential hazards associated with hook load management and implement appropriate mitigation strategies.
4.2 Operational Procedures:
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Establish clear and concise SOPs for managing hook load throughout the drilling process.
- Operator Training: Provide operators with comprehensive training on hook load management techniques, safety protocols, and the use of monitoring software.
4.3 Monitoring and Control:
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement a system for continuous monitoring of hook load, utilizing load cells, sensors, and automated software tools.
- Load Control Procedures: Establish clear procedures for adjusting the WOB and managing hook load based on real-time data and pre-defined parameters.
4.4 Communication and Collaboration:
- Clear Communication: Ensure effective communication between operators, engineers, and other personnel involved in hook load management.
- Data Sharing: Share hook load data and analysis results with relevant stakeholders, facilitating informed decision-making and improved operational efficiency.
4.5 Maintenance and Calibration:
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain load cells, sensors, and other equipment involved in hook load monitoring to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Calibration: Calibrate load cells and sensors according to established protocols and manufacturer's recommendations.
4.6 Continuous Improvement:
- Data Analysis: Continuously analyze hook load data to identify areas for improvement, optimize drilling practices, and enhance operational efficiency.
- Industry Best Practices: Stay updated on industry best practices and advancements in hook load management techniques and technologies.
Chapter 5: Case Studies in Hook Load Management
This chapter presents real-world examples of how effective hook load management has contributed to successful drilling operations.
5.1 Case Study 1: Optimizing Hook Load for Increased Drilling Efficiency
- Scenario: A drilling company faced challenges with slow drilling rates due to inefficient hook load management.
- Solution: By implementing advanced hook load monitoring systems, the company optimized the WOB and minimized downtime.
- Results: The company achieved significant improvements in drilling efficiency, reducing drilling time and operational costs.
5.2 Case Study 2: Preventing Rig Failure Through Effective Hook Load Control:
- Scenario: A drilling rig experienced a near-miss incident due to excessive hook load, highlighting the need for improved load management.
- Solution: The company implemented a new hook load control system with automated alerts for potential overload situations.
- Results: The new system prevented future incidents and improved operational safety.
5.3 Case Study 3: Using Hook Load Data for Wellbore Stability Optimization:
- Scenario: A drilling project encountered wellbore instability issues, leading to downtime and increased costs.
- Solution: By analyzing hook load data and other relevant parameters, the drilling team identified the root cause of the instability and implemented corrective measures.
- Results: The project was successfully completed with improved wellbore stability and reduced overall costs.
Conclusion:
These case studies demonstrate the significant impact of effective hook load management on drilling operations, leading to improved safety, efficiency, and cost optimization. By adhering to best practices and utilizing advanced technologies, operators can achieve successful drilling outcomes while minimizing risks and maximizing operational efficiency.
- Axial Load Comprendre la Charge Axiale :…
- Critical Velocity (unloading) Vitesse Critique : La Force M…
- Bed Load Charge de fond : Le héros méc…
- Critical Buckling Load Charge de Fluage Critique : U…
- Lateral (load) Latéral (Charge) : Une Poussé…
- Overload Surcharge : Un Terme Critique…
- Overload Surcharge : un problème criti…
- Critical Flow Rate (liquids unloading) Débit Critique : Le Débit Min…
- drilling hook Le Crochet de Forage : Un Lie…
- Drilling Hook and Swivel Crochet et Pivot de Forage : …
- Fish Hook Le Crochet de Pêche : Un Vira…
- Hook Le Crochet : Un Composant Ess…
- Hook Le crochet : un élément cruci…
- Hook (drilling rig) Le crochet : Un élément vital…
- Hook Load Comprendre la Charge au C…
- Hook Wall Packer Les obturateurs à crochet : u…
- Load Fluid Fluide de charge : Le héros m…
- Hooke’s Law La loi de Hooke : un principe…
- Indicator (mechanical load) Maintenir le Contrôle : Indic…
- Load Cell Capteurs de charge : peser le…
- Demande de justification des dépenses Naviguer dans la de… Planification et ordonnancement du projet
- Coût budgété du travail planifié Comprendre le Coût … Estimation et contrôle des coûts
- Les limites de batterie Comprendre les limi… Termes techniques généraux
- Outil DV Outil DV : Un éléme… Forage et complétion de puits
- SOMMAIRE TOC : Comprendre le… Termes techniques généraux
prasad
on 18 octobre 2024 at 06:31Third question answer is not correct as the type of drilling fluid also influences the hook load as the weight of the drill string effected by the buoyancy force in the drilling fluid which depends on the density of drilling fluid.
Response :
You’re absolutely right! The type of drilling fluid does indeed influence the hook load due to the buoyancy effect. When the drill string is submerged in the drilling fluid, the buoyant force reduces the effective weight of the drill string, which directly affects the hook load. The magnitude of this buoyant force is dependent on the density of the drilling fluid—higher density fluids provide greater buoyancy, which reduces the hook load, while lower density fluids provide less buoyancy, resulting in a higher hook load.
So, when considering the hook load, the type and density of the drilling fluid are key factors that must be accounted for in addition to other operational parameters.