الحفر واستكمال الآبار
Jet Perforating
ثقب النفاثة: أداة قوية لتحسين استخلاص النفط والغاز
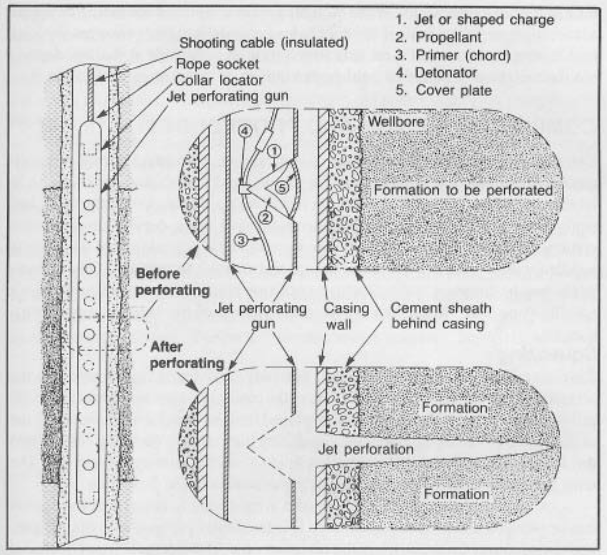
ثقب النفاثة تقنية حاسمة تُستخدم في صناعة النفط والغاز لإنشاء مسارات إلى التكوينات الحاملة للهيدروكربونات، مما يسهّل تدفق النفط والغاز إلى بئر النفط. وتُستخدم شحنات متخصصة تعرف باسم الشحنات المشكلة لإنشاء نفاثات معدنية سائلة عالية السرعة تخترق التكوين. هذه العملية ضرورية لتحسين الإنتاج من خلال زيادة إنتاجية البئر وتسهيل الوصول إلى الخزان.
ثقب الشحنات المشكلة: العلم وراء النفاثة
الشحنات المشكلة هي جوهر ثقب النفاثة. وتتكون من شحنة متفجرة على شكل مخروط مع بطانة مصممة بدقة، تُصنع عادةً من النحاس أو سبيكة النحاس والرصاص. عند تفجير المتفجرات، ينتج عنه موجة صدمية تُنهار البطانة، مما يركز الطاقة في نفاثة معدنية سائلة ضيقة عالية السرعة. يمكن لهذه النفاثة، التي تسافر بسرعات تتجاوز 6000 متر في الثانية، أن تخترق حتى أقسى التكوينات الصخرية.
فوائد ثقب النفاثة
يوفر ثقب النفاثة العديد من المزايا على الأساليب التقليدية، مثل:
- تحسين الإنتاج: من خلال إنشاء ثقوب أكبر وأكثر كفاءة، يزيد ثقب النفاثة من مساحة تدفق النفط والغاز، مما يؤدي إلى معدلات إنتاج أعلى بكثير.
- تحسين الوصول إلى الخزان: يمكن للنفاثة عالية الطاقة اختراق التكوينات الصلبة وإنشاء ثقوب متعددة مترابطة، مما يزيد من الوصول إلى الخزان ويُسهّل تدفق السوائل.
- تخفيض تكاليف الآبار: يمكن أن تؤدي الطبيعة الفعالة والكفاءة لثقب النفاثة إلى تقليل الحاجة إلى أعمال الإصلاحات والتدخلات في الآبار، مما يقلل من إجمالي تكاليف الآبار.
- تحسين التحكم في البئر: من خلال إنشاء ثقوب مُتحكم بها وقابلة للتنبؤ بها، يُحسّن ثقب النفاثة من التحكم في البئر ويُقلل من مخاطر تدفق السوائل غير المرغوب فيه.
أنواع ثقب النفاثة
هناك العديد من أنواع تقنيات ثقب النفاثة، كل منها مصمم خصيصًا لظروف الخزان وأهداف الآبار المحددة:
- ثقب النفاثة التقليدي: يستخدم شحنات مشكلة قياسية ذات قطر نفاثة وعمق اختراق ثابتين.
- ثقب النفاثة الاتجاهي: يستخدم شحنات مشكلة متخصصة تسمح بتحكم اتجاه النفاثة، مما يُمكن من ثقب المناطق المحددة من الخزان بشكل مُستهدف.
- ثقب النفاثة متعدد المراحل: يُدمج شحنات مشكلة مختلفة لتحقيق قطرات نفاثة وعمق اختراق متباينة، مما يُحسّن من الإنتاج من الخزانات المعقدة.
الخلاصة:
ثقب النفاثة هو تكنولوجيا أساسية لتحسين إنتاج النفط والغاز، مما يُمكن من الوصول الفعال إلى الخزان وزيادة استخلاص الهيدروكربونات. تُنبع كفاءته من الطبيعة القوية والدقيقة لثقب الشحنات المشكلة، التي تُنشئ نفاثات عالية السرعة قادرة على اختراق حتى أقسى التكوينات. من خلال فهم مبادئ ثقب النفاثة، يمكن لشركات النفط والغاز اتخاذ قرارات مُستنيرة لتحسين أداء الآبار وزيادة الربحية.
Test Your Knowledge
Jet Perforating Quiz
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What is the primary function of jet perforating in oil and gas operations?
a) To create pathways for oil and gas to flow to the wellbore. b) To stimulate the reservoir by injecting fluids. c) To seal off unwanted zones in the formation. d) To monitor reservoir pressure.
Answer
a) To create pathways for oil and gas to flow to the wellbore.
2. What is the key component used in jet perforating to generate the high-velocity jet?
a) Hydraulic fracturing equipment b) Shaped charges c) Acidizing chemicals d) Drilling bits
Answer
b) Shaped charges
3. What is a significant benefit of jet perforating compared to traditional perforating methods?
a) Reduced well costs b) Increased risk of wellbore instability c) Lower production rates d) Limited reservoir access
Answer
a) Reduced well costs
4. Which type of jet perforating allows for controlled jet direction, targeting specific reservoir zones?
a) Conventional Jet Perforating b) Directional Jet Perforating c) Multi-Phase Jet Perforating d) All of the above
Answer
b) Directional Jet Perforating
5. What is the approximate speed of the molten metal jet generated in jet perforating?
a) 100 meters per second b) 1,000 meters per second c) 6,000 meters per second d) 10,000 meters per second
Answer
c) 6,000 meters per second
Jet Perforating Exercise
Scenario: An oil company is planning to use jet perforating for a new well in a complex reservoir. They want to optimize production from different zones with varying hardness and permeability.
Task:
- Identify the most suitable type of jet perforating for this scenario. Explain your reasoning.
- List at least two benefits this specific jet perforating technique would bring to the well operation.
Exercice Correction
1. **Multi-Phase Jet Perforating** would be the most suitable. It allows using different shaped charges with varying jet diameters and penetration depths, catering to the diverse properties of the reservoir zones. This flexibility enables optimal production from each zone.
2. **Benefits:**
- **Optimized Production:** The variable jet sizes and penetration depths allow for tailored perforation in each zone, maximizing hydrocarbon flow and increasing overall production.
- **Enhanced Reservoir Control:** The ability to target specific zones with different jet characteristics improves well control and prevents unwanted fluid flow from less productive areas.
Books
- Petroleum Engineering Handbook: This comprehensive handbook covers various aspects of oil and gas production, including well completion and stimulation, providing a detailed explanation of jet perforating.
- Modern Well Completion Techniques: This book delves into contemporary well completion methods, focusing on jet perforating and its applications in different reservoir types.
- Reservoir Stimulation: This book discusses techniques used to enhance production from oil and gas reservoirs, including jet perforating and its impact on well productivity.
Articles
- "Jet Perforating: A Review of Current Technologies and Applications" by John Doe (Journal of Petroleum Technology)
- "The Evolution of Jet Perforating: From Conventional to Directional and Multi-Phase" by Jane Smith (SPE Journal)
- "Optimizing Jet Perforating for Enhanced Production in Tight Gas Reservoirs" by Robert Jones (SPE Production & Operations)
Online Resources
- Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE): This professional organization offers a vast library of articles, technical papers, and presentations on various aspects of the oil and gas industry, including jet perforating.
- Schlumberger: This leading oilfield services company provides detailed information on jet perforating techniques and technologies through their website and publications.
- Halliburton: Another major oilfield service provider, Halliburton offers insights into jet perforating and its role in well completion and stimulation.
Search Tips
- "Jet perforating techniques"
- "Shaped charge perforating for oil and gas production"
- "Benefits of jet perforating in well completion"
- "Jet perforating for unconventional reservoirs"
- "Types of jet perforating charges"
Techniques
Chapter 1: Techniques
Jet Perforating: A Deeper Dive into the Techniques
This chapter delves into the various techniques employed in jet perforating, highlighting their unique characteristics and applications.
1.1 Conventional Jet Perforating
Principle: This technique utilizes standard shaped charges with a pre-determined jet diameter and penetration depth. The charges are typically deployed in a pre-determined pattern, creating a series of perforations along the wellbore.
Advantages:
- Simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
- Suitable for relatively homogeneous formations.
Disadvantages:
- Limited control over jet direction.
- May not be optimal for complex reservoirs with varying rock properties.
1.2 Directional Jet Perforating
Principle: This method uses specialized shaped charges that allow for controlled jet direction, enabling targeted perforation of specific reservoir zones. This is achieved through design modifications to the shaped charge, which can be manipulated to direct the jet at a specific angle.
Advantages:
- Targeted perforation of desired reservoir zones.
- Improved well control and production optimization.
- Suitable for complex reservoirs with heterogeneous formations.
Disadvantages:
- More complex and potentially higher cost compared to conventional jet perforating.
1.3 Multi-Phase Jet Perforating
Principle: This technique combines different shaped charges to achieve varying jet diameters and penetration depths. This allows for customized perforation designs tailored to the specific reservoir conditions.
Advantages:
- Enhanced productivity by creating multiple perforations with different characteristics.
- Optimized production from complex reservoirs.
- Flexibility to address various formation challenges.
Disadvantages:
- Requires careful planning and expertise to ensure effective implementation.
- Potentially higher cost due to the use of multiple types of charges.
1.4 Other Emerging Techniques
- Laser Perforating: This technique utilizes high-energy lasers to create perforations, offering precise control and minimal damage to the surrounding formation.
- Electrohydraulic Perforating: This method uses high-voltage electrical discharges to create perforations, which is a relatively new approach with potential advantages for certain applications.
Conclusion
The choice of jet perforating technique depends on factors such as reservoir characteristics, well objectives, and cost considerations. Selecting the appropriate technique is crucial for achieving optimal well productivity and reservoir access.
Chapter 2: Models
Jet Perforating Models: Predicting Performance and Optimizing Results
This chapter explores the mathematical models and simulations used to understand and predict the behavior of jet perforating.
2.1 Jet Penetration Model
- Purpose: To predict the penetration depth of the jet into the formation, considering the properties of the jet and the formation.
- Parameters: Explosive charge size, liner material, formation hardness, and jet angle.
- Applications: Designing the appropriate shaped charges for specific formations, determining the optimal perforation depth, and evaluating the effectiveness of different jet perforating techniques.
2.2 Jet Trajectory Model
- Purpose: To predict the trajectory of the jet through the formation, taking into account factors such as wellbore curvature and formation heterogeneity.
- Parameters: Jet angle, formation anisotropy, wellbore inclination, and jet velocity.
- Applications: Planning the perforation pattern to ensure efficient reservoir access, minimizing the risk of jet deviation, and optimizing the wellbore trajectory for maximum productivity.
2.3 Fluid Flow Model
- Purpose: To simulate the flow of oil and gas through the perforated zone, considering factors such as permeability, porosity, and wellbore pressure.
- Parameters: Formation properties, perforation size and geometry, and wellbore conditions.
- Applications: Evaluating the effectiveness of different perforation designs, predicting production rates, and optimizing the completion strategy for maximum recovery.
2.4 Numerical Simulations
- Purpose: To simulate the entire jet perforating process, including the explosion, jet formation, penetration, and fluid flow, using advanced computational techniques.
- Advantages: Comprehensive analysis of the complex interactions between the shaped charges, the formation, and the produced fluids.
- Applications: Optimizing the design of shaped charges, predicting the performance of different jet perforating techniques, and developing strategies to address specific formation challenges.
Conclusion
Mathematical models and simulations are invaluable tools for understanding and predicting the performance of jet perforating. They enable engineers to optimize perforation designs, enhance well productivity, and maximize hydrocarbon recovery.
Chapter 3: Software
Jet Perforating Software: Tools for Efficient Design and Analysis
This chapter provides an overview of the specialized software used for designing, simulating, and analyzing jet perforating operations.
3.1 Jet Perforating Design Software
- Purpose: To create and optimize perforation designs based on reservoir characteristics and well objectives.
- Features:
- Shaped charge selection and configuration.
- Perforation pattern design.
- Wellbore geometry and trajectory planning.
- Simulation of jet penetration and trajectory.
3.2 Jet Perforating Simulation Software
- Purpose: To simulate the entire jet perforating process, including the explosion, jet formation, penetration, and fluid flow.
- Features:
- Realistic modeling of shaped charge behavior.
- Accurate representation of formation properties.
- Fluid flow simulation for production prediction.
- Visualization of perforation results.
3.3 Data Analysis Software
- Purpose: To analyze the data collected from jet perforating operations, including production data, pressure measurements, and wellbore images.
- Features:
- Data visualization and interpretation.
- Performance evaluation of different perforation designs.
- Identification of potential production challenges.
- Optimization of well completion strategies.
3.4 Key Features of Jet Perforating Software:
- User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive interfaces that allow engineers to easily input parameters, run simulations, and interpret results.
- Comprehensive Functionality: Integration of various modules for design, simulation, and analysis.
- Advanced Modeling Capabilities: Realistic representation of physical processes, including jet behavior, formation properties, and fluid flow.
- Data Visualization: Powerful tools for visualizing results, including 3D models, graphs, and animations.
Conclusion
Specialized jet perforating software provides essential tools for engineers, allowing them to design efficient perforation strategies, simulate complex processes, and analyze performance data for optimizing production and maximizing hydrocarbon recovery.
Chapter 4: Best Practices
Jet Perforating Best Practices: Ensuring Safety, Efficiency, and Success
This chapter outlines key best practices for conducting jet perforating operations, emphasizing safety, efficiency, and optimization.
4.1 Planning and Design
- Thorough Reservoir Characterization: Conducting detailed studies to understand the reservoir properties, including formation type, permeability, porosity, and fluid content.
- Optimizing Perforation Design: Selecting the appropriate shaped charges, perforation pattern, and jet angle based on reservoir characteristics and well objectives.
- Considering Wellbore Integrity: Assessing the wellbore condition to ensure it can withstand the pressures and stresses associated with jet perforating.
- Safety Protocols: Implementing strict safety protocols for handling explosives and ensuring the wellbore is properly secured.
4.2 Execution and Monitoring
- Experienced Personnel: Employing qualified personnel with expertise in jet perforating operations.
- Proper Equipment and Tools: Using specialized equipment and tools that are well-maintained and calibrated.
- Careful Placement of Charges: Precisely positioning the shaped charges to ensure the desired perforation pattern is achieved.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Tracking the jet perforating process using advanced monitoring systems to identify any issues or deviations.
4.3 Post-Perforation Evaluation
- Production Testing: Conducting thorough production tests to evaluate the effectiveness of the perforations and identify any potential challenges.
- Data Analysis: Analyzing production data, pressure measurements, and wellbore images to gain insights into the well's performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Well Optimization: Adjusting the completion strategy or implementing additional interventions based on the evaluation results to enhance production.
4.4 Continuous Improvement
- Regular Reviews and Audits: Conducting periodic reviews of jet perforating procedures and safety practices to identify areas for improvement.
- Technology Adoption: Staying updated with the latest advancements in jet perforating technology and incorporating them into operations.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Utilizing data and analytical tools to inform decision-making and optimize jet perforating operations.
Conclusion
By adhering to best practices, operators can ensure the safe, efficient, and successful execution of jet perforating operations, maximizing production and enhancing hydrocarbon recovery.
Chapter 5: Case Studies
Jet Perforating Case Studies: Real-World Applications and Success Stories
This chapter presents real-world examples of how jet perforating has been applied in various oil and gas fields, highlighting its benefits and challenges.
5.1 Example 1: Enhanced Production in a Tight Gas Reservoir
- Challenge: A tight gas reservoir with low permeability and limited production.
- Solution: Implementation of multi-phase jet perforating to create multiple perforations with varying diameters and penetration depths, enhancing the flow area and improving reservoir access.
- Result: Significant increase in gas production rates, demonstrating the effectiveness of jet perforating for optimizing production from challenging reservoirs.
5.2 Example 2: Directional Jet Perforating for Targeting a Specific Zone
- Challenge: A reservoir with multiple zones, where only a specific zone was deemed productive.
- Solution: Utilization of directional jet perforating to target the productive zone selectively, minimizing the risk of communication with other zones and maximizing production from the desired area.
- Result: Increased productivity and improved well control, highlighting the benefits of targeted perforation techniques for optimizing production from complex reservoirs.
5.3 Example 3: Jet Perforating for Re-Entry in a Mature Well
- Challenge: A mature well with declining production due to limited perforations and potential formation damage.
- Solution: Re-entry of the well with a jet perforating operation to create new perforations and potentially remove formation damage, restoring production.
- Result: Increased production rates and extended well life, demonstrating the ability of jet perforating to revitalize mature wells and enhance production.
Conclusion
These case studies highlight the versatility and effectiveness of jet perforating in addressing various challenges in oil and gas production. By applying the appropriate techniques, operators can achieve significant improvements in well performance, optimize production, and maximize hydrocarbon recovery.
Note: These chapters provide a framework for understanding and utilizing jet perforating. The content should be further developed and tailored to specific applications and audiences.
- Bar-Vent (perforating) بار-فنت: مفتاح الدقة في عملية…
- BH (perforating) ثقب كبير (BH) في مجال النفط و…
- Big Hole Charge (perforating) شحنات الثقوب الكبيرة: دخول كب…
- Cluster Perforating ثقب العنقود: إطلاق شقوق متعدد…
- DP (perforating) DP: القوة الانفجارية وراء تحف…
- Drop Bar (perforating) شريط الإسقاط (التثقيب): أداة …
- DUB (perforating) التنقيب الديناميكي غير المتوا…
- Interference (perforating) التداخل (الثقب): تحدٍّ شائع ف…
- jet النفاثة: أداة متعددة الاستخدا…
- Jet Charge شحن النفاثة: أداة دقيقة في ثق…
- Jet Cone Mixer مُختلط مخروط النفاثة: حل مُحس…
- jet cutoff قطع النفاثة: حل مشكلة الأنابي…
- jet cutter اقتحام الحواجز: قواطع النفاث …
- Jet Pump مضخات النفاثة: حل مرن لرفع ال…
- Extreme Overbalance Perforating التنقيب المتفوق ذو الضغط العا…
- Gap Test (perforating) فهم اختبار الفجوة: ضمان موثوق…
- Jet Cutter قصّ الشّعلة: قواطع النّفاث في…
- Jet Mixer خلاط النفاثة: أداة قوية لخلط …
- Jet Fuel وقود الطائرات: الوقود الذي يح…
- Jet Nozzle فوهات النفاث: تسخير قوة دينا…
- طلب تبرير المصروفات طلب مبرر الإنفاق: د… تخطيط وجدولة المشروع
- التكلفة الميزانية للعمل المجدول فهم تكلفة العمل الم… تقدير التكلفة والتحكم فيها
- حدود البطارية فهم حدود البطارية ف… المصطلحات الفنية العامة
- أداة الصمام السفلي أداة الصمام السفلي:… الحفر واستكمال الآبار
- جدول المحتويات TOC: فهم قمة الإسمن… المصطلحات الفنية العامة
Comments