الحفر واستكمال الآبار
mud hopper
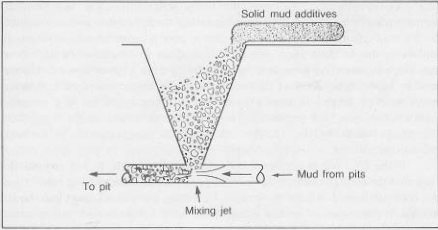
حوض الطين: عنصر أساسي في حفر الآبار وإكمالها
في عالم حفر الآبار وإكمالها، الكفاءة والدقة هما العاملان الأهم. كل قطعة من المعدات تلعب دورًا حيويًا في العملية المعقدة لاستخراج الموارد القيمة من باطن الأرض. من بين العديد من الأدوات المتخصصة، يبرز **حوض الطين** كعنصر أساسي في التعامل ونقل طين الحفر، وهو عنصر حاسم لاستقرار بئر الحفر وعمليات الحفر.
فهم حوض الطين: وصف تفصيلي
حوض الطين هو في الأساس حاوية كبيرة مفتوحة من الأعلى مصممة لحمل وإدارة طين الحفر، وهو السائل المتخصص المستخدم في حفر الآبار. إنه هيكل متين مصنوع عادة من الفولاذ، قادر على تحمل وزن وضغط الطين.
الميزات والمكونات الرئيسية:
- سعة كبيرة: يتم بناء أحواض الطين لتخزين كميات كبيرة من الطين، تتراوح من بضع مئات من البراميل إلى عدة آلاف من البراميل، اعتمادًا على حجم عملية الحفر.
- قمة مفتوحة: تسهل القمة المفتوحة تحميل وتفريغ الطين بسهولة باستخدام المضخات أو طرق النقل الأخرى.
- نظام التحريك: تُجهز العديد من أحواض الطين بنظام تحريك مدمج لمنع ترسيب الطين وضمان لزوجة ثابتة.
- مؤشرات مستوى الطين: هذه ضرورية لمراقبة مستوى الطين داخل الحوض ومنع الفيضان.
- ميزات السلامة: تم تصميم الأحواض بميزات أمان مثل سلالم الأمان، والدرابزينات، والمنصات للوصول إلى الهيكل والعمل عليه.
الوظيفة والأهمية في عمليات الحفر:
1. تخزين وتداول الطين: تعمل أحواض الطين كمركز مركزي لإدارة وتخزين طين الحفر. تسمح بتحميل وتفريغ فعال، مما يضمن إمدادًا ثابتًا من الطين إلى منصة الحفر.
2. معالجة الطين: توفر مساحة لمعالجة وتكييف الطين، لضمان تلبية متطلبات عملية الحفر المحددة. يشمل ذلك إضافة المواد الكيميائية أو ضبط الكثافة واللزوجة لتحسين الأداء.
3. نقل الطين بكفاءة: تسهل أحواض الطين نقل الطين بسلاسة من موقع إلى آخر، سواء من حفرة الطين إلى المنصة أو بين مراحل مختلفة من عملية الحفر.
4. إعادة تدوير الطين: تلعب أحواض الطين دورًا حاسمًا في إعادة تدوير طين الحفر، مما يقلل من النفايات ويقلل من التأثير البيئي.
5. إمداد احتياطي من الطين: في حالة حدوث أحداث غير متوقعة أو فشل في المعدات، يمكن لحوض الطين أن يعمل كمخزون احتياطي من الطين، مما يضمن تدفقًا مستمرًا لعملية الحفر.
الاستنتاج:
حوض الطين أداة لا غنى عنها في صناعة حفر الآبار وإكمالها. دورها في تخزين ومعالجة وتكييف طين الحفر ضروري للحفاظ على استقرار بئر الحفر، وتعظيم كفاءة الحفر، وضمان سلامة ونجاح العملية بأكملها. فهم دور وأهمية هذه المعدات ضروري لأي شخص يعمل في مجال استكشاف وإنتاج النفط والغاز.
Test Your Knowledge
Mud Hopper Quiz
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What is the primary function of a mud hopper?
a) To store and handle drilling mud b) To pump drilling mud down the wellbore c) To mix drilling mud with additives d) To filter drilling mud
Answer
a) To store and handle drilling mud
2. Which of the following is NOT a typical feature of a mud hopper?
a) Open top b) Agitation system c) Closed bottom d) Level indicators
Answer
c) Closed bottom
3. What is the main reason for agitating drilling mud in a mud hopper?
a) To increase the mud's viscosity b) To prevent the mud from settling c) To remove solids from the mud d) To add chemicals to the mud
Answer
b) To prevent the mud from settling
4. How does a mud hopper contribute to the efficiency of drilling operations?
a) By providing a backup supply of drilling mud b) By facilitating the transfer of mud between different locations c) By allowing for the recycling of drilling mud d) All of the above
Answer
d) All of the above
5. Why is it important to maintain a consistent supply of drilling mud during drilling operations?
a) To prevent the wellbore from collapsing b) To lubricate the drill bit c) To remove cuttings from the wellbore d) All of the above
Answer
d) All of the above
Mud Hopper Exercise
Scenario: You are working on a drilling rig and the mud hopper is currently empty. The mud pit has a large volume of mud that needs to be transferred to the hopper.
Task: Describe the steps involved in transferring mud from the mud pit to the mud hopper, ensuring a smooth and efficient process. Consider the safety measures that must be taken and the potential challenges that might arise.
Exercice Correction
Here's a possible solution to the exercise:
Steps for Transferring Mud:
- Safety First: Ensure all personnel involved are aware of safety procedures and are wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). Inspect the mud hopper and the mud pit for any potential hazards or leaks.
- Preparing the Mud Hopper: Open the hopper's top access hatch and ensure the agitation system is operational. Check the level indicators and ensure they are working correctly.
- Connecting the Mud Pump: Attach the mud pump to the mud pit and route the discharge hose to the mud hopper's inlet. The pump should have sufficient capacity to handle the mud flow rate.
- Starting the Mud Pump: Gradually start the mud pump, slowly increasing the flow rate to prevent sudden pressure surges. Monitor the mud level in the hopper using the level indicators.
- Monitoring and Adjustment: Continuously monitor the mud level in the hopper and the mud pit. Adjust the pump flow rate as needed to maintain a steady transfer rate, preventing overflow in the hopper.
- Cleaning and Inspection: Once the mud transfer is complete, stop the mud pump and disconnect the hose. Clean any spills or residue around the hopper and pit. Finally, inspect the equipment for any damage or wear and tear.
Potential Challenges:
- Clogging: The mud pump or the discharge hose may become clogged with solids in the mud.
- Mud Overflow: The mud level in the hopper may rise too quickly, potentially leading to overflow.
- Equipment Failure: The mud pump or other equipment may malfunction during the transfer process.
Safety Measures:
- Use proper PPE, including hard hats, safety glasses, gloves, and steel-toe boots.
- Follow all safety procedures outlined in the drilling operation's safety manual.
- Communicate clearly with other crew members during the transfer process.
- Be aware of the potential hazards associated with moving heavy equipment and working with mud.
Books
- Drilling Engineering: Principles and Practices by Robert F. Stewart and William L. McDonald. This comprehensive textbook covers all aspects of drilling, including mud handling and equipment like mud hoppers.
- Petroleum Engineering Handbook edited by Tarek Ahmed. This comprehensive handbook provides a detailed overview of various aspects of petroleum engineering, including drilling and well completion, which includes the use of mud hoppers.
- Drilling and Well Completion: A Practical Approach by Larry J. K. A thorough introduction to the principles and practice of drilling and well completion, including sections on mud handling and the role of mud hoppers.
Articles
- "Mud Handling Systems: A Review of Best Practices" by Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE). This technical paper provides an overview of mud handling systems, including the design and operation of mud hoppers.
- "The Importance of Mud Conditioning in Drilling Operations" by World Oil. This article discusses the role of mud conditioning in drilling, emphasizing the importance of equipment like mud hoppers.
- "Drilling Mud: A Vital Fluid in Oil and Gas Extraction" by Energy Voice. This article explores the critical role of drilling mud in various stages of drilling and highlights the use of mud hoppers for storage and management.
Online Resources
- Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE): SPE offers a vast library of technical papers, presentations, and publications covering various aspects of drilling and well completion, including mud handling and equipment.
- Oil & Gas IQ: This platform provides a comprehensive collection of articles, case studies, and industry news related to the oil and gas sector, including information on drilling equipment and mud hoppers.
- DrillingInfo: This website provides data and analysis related to the oil and gas industry, including information on drilling operations, mud handling, and equipment.
- Oilfield Glossary: This online glossary provides definitions of various terms used in the oil and gas industry, including mud hoppers and other equipment.
Search Tips
- Use specific keywords: Include terms like "mud hopper," "drilling," "well completion," "mud handling," "equipment," and "oil and gas" in your search queries.
- Refine your search: Use advanced search operators like "+" to include specific terms, "-" to exclude terms, and "" to search for exact phrases. For example, "mud hopper + drilling - oil & gas" or "mud hopper "design and operation"".
- Look for specific file types: Use the "filetype:" operator to find documents like PDFs, Word files, or presentations. For example, "mud hopper filetype:pdf".
- Explore different sources: Search for information on academic websites, industry journals, and professional organizations like SPE.
Techniques
Mud Hopper: A Deeper Dive
Here's a breakdown of the mud hopper topic into separate chapters, expanding on the provided text:
Chapter 1: Techniques for Mud Hopper Operation and Maintenance
This chapter will detail the practical aspects of using and maintaining a mud hopper.
1.1 Loading and Unloading Techniques: This section will cover various methods for loading and unloading mud, including pump types (positive displacement, centrifugal), hose management, and safety procedures during transfer operations. Specific details on preventing spills and maintaining consistent flow rates will be included. Diagrams illustrating optimal hose placement and pump configurations will enhance understanding.
1.2 Mud Agitation and Mixing Procedures: Different types of agitation systems (mechanical mixers, air injection) will be explained, along with best practices for achieving uniform mud consistency. The impact of mud properties (viscosity, density, solids content) on agitation requirements will be discussed. Troubleshooting common agitation problems will be addressed.
1.3 Level Monitoring and Control: Different level sensing technologies (float switches, ultrasonic sensors, radar level sensors) will be examined, comparing their advantages and disadvantages. Procedures for maintaining accurate level readings and preventing overflows will be detailed, along with the importance of regular calibration. Alarm systems and their integration with the overall mud management system will be covered.
1.4 Cleaning and Maintenance: Routine inspection procedures, including checking for leaks, corrosion, and structural damage, will be outlined. Methods for cleaning the hopper (high-pressure washing, chemical cleaning) and maintaining the agitation system will be described. A preventative maintenance schedule will be suggested, along with the importance of documenting maintenance activities.
1.5 Emergency Procedures: This section will cover actions to take in case of spills, leaks, or equipment malfunctions. Emergency shutdown procedures and containment strategies will be outlined, along with safety protocols for personnel.
Chapter 2: Models and Types of Mud Hoppers
This chapter will explore the diverse range of mud hopper designs.
2.1 Capacity and Size Variations: This section will categorize mud hoppers based on their capacity (e.g., small, medium, large), correlating capacity with typical applications (e.g., onshore drilling, offshore drilling, workover operations). The impact of hopper size on location constraints and logistical considerations will be discussed.
2.2 Material Construction and Durability: Different materials used in hopper construction (e.g., carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloys) will be evaluated based on their corrosion resistance, strength, and cost-effectiveness. The impact of environmental factors (e.g., temperature, salinity) on material selection will be considered.
2.3 Agitation System Designs: A comparison of different agitation system designs (e.g., mechanical impellers, jet mixers, air-powered agitators) will be provided, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses in terms of efficiency, energy consumption, and maintenance requirements.
2.4 Integrated Systems: This section will discuss mud hoppers integrated with other mud handling equipment, such as mud pumps, shale shakers, and degassers. The advantages and disadvantages of integrated systems will be analyzed.
2.5 Specialized Mud Hoppers: This section will address specialized designs for specific applications, such as those used in directional drilling, deepwater drilling, or unconventional resource extraction.
Chapter 3: Software and Technology for Mud Hopper Management
This chapter will cover the technological aspects of mud hopper operation.
3.1 Mud Management Software: This section will review different software packages used for monitoring mud properties, optimizing mud treatment, and managing mud inventory. The integration of these software packages with other drilling management systems will be discussed.
3.2 Data Acquisition and Monitoring Systems: The role of sensors and data loggers in providing real-time information on mud level, temperature, pressure, and other relevant parameters will be explained. Data visualization tools and reporting capabilities will be highlighted.
3.3 Predictive Maintenance Systems: The use of data analytics and machine learning techniques to predict potential equipment failures and optimize maintenance schedules will be explored.
3.4 Remote Monitoring and Control: This section will explore the use of remote monitoring and control systems to enhance safety, reduce downtime, and optimize operations from a distance.
3.5 Automation and Robotics: The potential of automation and robotics in optimizing mud hopper operations will be discussed, including automated loading and unloading systems.
Chapter 4: Best Practices for Mud Hopper Safety and Efficiency
This chapter emphasizes safety and efficient operation.
4.1 Safety Regulations and Compliance: This section will discuss relevant safety regulations and industry standards related to mud hopper operation and maintenance. Proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and emergency response procedures will be highlighted.
4.2 Preventing Spills and Leaks: Best practices for preventing spills and leaks during loading, unloading, and maintenance will be outlined, including regular inspections, proper hose handling, and emergency spill response plans.
4.3 Optimizing Mud Treatment and Recycling: Strategies for optimizing mud treatment to minimize waste and maximize recycling will be discussed, along with the environmental benefits of efficient mud management.
4.4 Efficient Mud Transfer Operations: Techniques for optimizing mud transfer operations to minimize downtime and improve efficiency will be outlined, including proper pump selection and hose management.
4.5 Personnel Training and Certification: The importance of properly trained personnel and appropriate certifications will be emphasized, along with the role of continuous training and improvement.
Chapter 5: Case Studies of Mud Hopper Applications
This chapter presents real-world examples.
This chapter will present several case studies illustrating the successful application of mud hoppers in various drilling scenarios. Each case study will include:
- Project Overview: Description of the drilling project, including location, type of well, and drilling challenges.
- Mud Hopper Selection and Specifications: Details on the type of mud hopper used, its capacity, and its key features.
- Operational Challenges and Solutions: Description of any operational challenges encountered and the solutions implemented using the mud hopper.
- Results and Outcomes: Discussion of the positive outcomes achieved using the mud hopper, including improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced safety.
- Lessons Learned: Key lessons learned from the project that can be applied to future drilling operations. This might include insights into optimized mud handling strategies or improved maintenance procedures.
Each chapter will include relevant diagrams, tables, and illustrations to enhance comprehension. The overall goal is to provide a comprehensive and practical guide to mud hopper technology and operation.
- bulk mud components in storage أساس سوائل الحفر: فهم مكونات …
- Bulk Mud Components in Storage مكونات الطين بالجملة في التخز…
- Condition the Mud تحضير الطين: خطوة حاسمة قبل ت…
- drilling mud بطل غير معروف في استخراج النف…
- Drilling Mud طين الحفر: البطل الخفي في است…
- Equivalent Mud Weight فهم وزن الطين المكافئ في عملي…
- gas-cut mud التهديد الرغوي: فهم طين القطع…
- hopper الحاويات: عنصر رئيسي في حفر ا…
- Invert Mud الطين المعكوس: غوص عميق في مس…
- Lift-Off Pressure (mud) فهم ضغط الانفصال في النفط وال…
- Low Solids Mud طين منخفض المواد الصلبة: حل س…
- mix mud مزيج الطين: البطل غير المعترف…
- mud الطين: البطل غير المعترف به ف…
- Mud الوحل: البطل الصامت في استكشا…
- Mud Acid حمض الطين: أداة قوية لتحفيز ا…
- Mud Anchor مرساة الطين: ضمان عمليات حفر …
- Mud Balance (fluid density) توازن الطين: أداة بسيطة لقياس…
- mud cake كعكة الطين: حاجز حيوي في حفر …
- Hopper القفزات: مايسترو المزج في عم…
- mud acid حمض الطين: أداة قوية ذات ملف …
- طلب تبرير المصروفات طلب مبرر الإنفاق: د… تخطيط وجدولة المشروع
- التكلفة الميزانية للعمل المجدول فهم تكلفة العمل الم… تقدير التكلفة والتحكم فيها
- حدود البطارية فهم حدود البطارية ف… المصطلحات الفنية العامة
- أداة الصمام السفلي أداة الصمام السفلي:… الحفر واستكمال الآبار
- جدول المحتويات TOC: فهم قمة الإسمن… المصطلحات الفنية العامة
Comments