Project Planning & Scheduling
Project Life Cycle
Navigating the Project Life Cycle: From Concept to Closure
In the world of project management, the Project Life Cycle serves as a roadmap, guiding projects from inception to completion. It defines the sequential phases through which every project progresses, ensuring a structured and controlled approach. This framework is universally applicable, regardless of the project's scope, industry, or complexity.
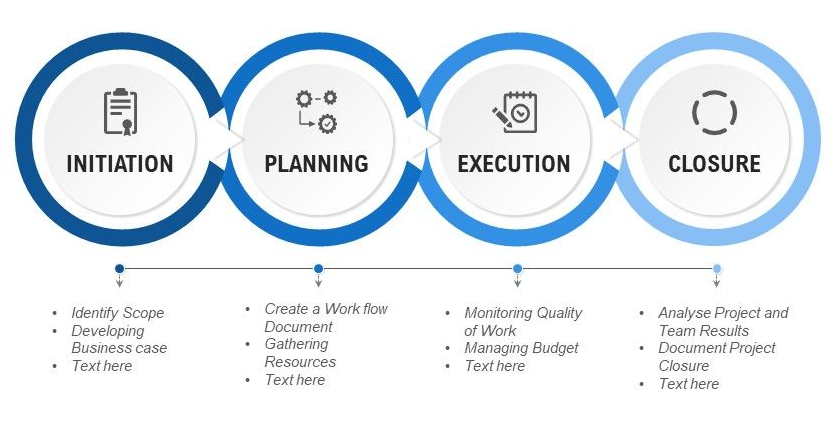
This article delves into the four core phases of the Project Life Cycle:
1. Concept (Initiation): This is the genesis of a project, where the initial idea takes shape. Here's what happens:
- Identifying the Need: A problem or opportunity arises, triggering the need for a project.
- Defining the Goal: The project's objectives are clearly articulated, outlining what success will look like.
- Preliminary Feasibility Study: This involves a high-level assessment to determine the project's viability, considering factors like cost, resources, and potential risks.
- Project Charter Creation: A formal document outlining the project's scope, objectives, deliverables, stakeholders, and initial budget is drafted.
2. Definition (Development): The project takes its form in this phase, where details are refined, and a concrete plan emerges:
- Project Planning: This involves breaking down the project into smaller, manageable tasks, defining dependencies, and setting deadlines.
- Resource Allocation: Identifying and securing the necessary resources - human, financial, and material - to execute the project.
- Risk Management Plan: Identifying and analyzing potential risks, developing mitigation strategies, and creating a contingency plan.
- Communication Plan: Establishing clear communication channels between stakeholders and defining how information will be shared throughout the project.
3. Execution (Implementation or Operation): This is the heart of the project, where the plan is put into action:
- Task Execution: Teams work diligently to complete assigned tasks, adhering to the project schedule and budget.
- Progress Monitoring: Regularly tracking the project's progress against the plan and making necessary adjustments.
- Quality Control: Ensuring that deliverables meet the defined standards and quality expectations.
- Communication & Collaboration: Maintaining effective communication between team members and stakeholders, resolving issues, and ensuring everyone is aligned.
4. Finishing (Termination or Close Out): This final phase marks the successful culmination of the project:
- Project Completion: Delivering all planned deliverables within the defined scope, budget, and timeline.
- Documentation & Closure: Finalizing project documentation, including lessons learned, and archiving all relevant information for future reference.
- Evaluation & Reporting: Assessing the project's performance against its goals, identifying successes and areas for improvement.
- Project Handoff: Transferring the project deliverables and knowledge to the appropriate parties for ongoing management or utilization.
Beyond the Core Phases: The four core phases can be further broken down into stages depending on the project's specific needs and context. For example, in software development, the execution phase might involve multiple stages like coding, testing, and deployment.
Benefits of Utilizing the Project Life Cycle:
- Structure and Control: Provides a clear framework for project management, leading to better organization and efficiency.
- Risk Mitigation: Early identification and management of potential risks help prevent costly delays and disruptions.
- Improved Communication: Fosters clear and consistent communication among stakeholders, minimizing misunderstandings and conflicts.
- Increased Accountability: Clearly defined roles and responsibilities ensure accountability throughout the project.
- Enhanced Success Rate: By following a structured approach, projects are more likely to achieve their goals within budget and timeline.
Understanding the Project Life Cycle is essential for any successful project manager. By effectively navigating these phases, organizations can ensure that their projects deliver tangible value and achieve their desired outcomes.
Test Your Knowledge
Quiz: Navigating the Project Life Cycle
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. Which phase of the Project Life Cycle involves identifying the need for a project and defining its objectives?
a) Execution b) Concept c) Definition d) Finishing
Answer
b) Concept
2. What is the primary focus of the Definition phase?
a) Completing tasks according to the project plan b) Identifying and mitigating potential risks c) Developing a detailed project plan and securing resources d) Evaluating project performance and delivering final deliverables
Answer
c) Developing a detailed project plan and securing resources
3. Which of the following activities is NOT typically part of the Execution phase?
a) Monitoring project progress b) Managing project risks c) Creating the project charter d) Ensuring quality control of deliverables
Answer
c) Creating the project charter
4. During the Finishing phase, what is the main goal?
a) Completing all project tasks and delivering final deliverables b) Identifying potential project risks c) Securing necessary resources for the project d) Creating a detailed project plan
Answer
a) Completing all project tasks and delivering final deliverables
5. What is a key benefit of using a structured Project Life Cycle approach?
a) Eliminating all project risks b) Ensuring that all projects are completed on time and within budget c) Providing a clear framework for project management and improving efficiency d) Reducing communication among stakeholders
Answer
c) Providing a clear framework for project management and improving efficiency
Exercise: Applying the Project Life Cycle
Scenario: You are a project manager tasked with organizing a company picnic for 100 employees.
Task: Using the four phases of the Project Life Cycle, outline a basic plan for organizing the company picnic.
Exercise Correction
Here is a sample solution outlining the plan for organizing the company picnic using the Project Life Cycle phases:
1. Concept (Initiation):
- Identify the Need: Company morale is low and team bonding is needed.
- Define the Goal: To organize a fun and enjoyable picnic for all 100 employees.
- Preliminary Feasibility Study: Assess budget, resources, and potential venue options.
- Project Charter Creation: Document the project scope, objectives, deliverables (e.g., food, entertainment, activities), stakeholders, and initial budget.
2. Definition (Development):
- Project Planning: Break down the project into tasks (e.g., venue selection, catering, activity planning, entertainment booking, communication, logistics).
- Resource Allocation: Identify required resources: budget, team members, volunteer help, equipment (e.g., tables, chairs, games), transportation, etc.
- Risk Management Plan: Identify potential risks (e.g., bad weather, low attendance, food allergies). Develop contingency plans.
- Communication Plan: Outline communication channels and methods to keep stakeholders informed (e.g., emails, company intranet, announcements).
3. Execution (Implementation or Operation):
- Task Execution: Teams work on assigned tasks (e.g., booking the venue, planning activities, organizing food).
- Progress Monitoring: Track progress against the timeline, budget, and goals. Adjust as needed.
- Quality Control: Ensure all aspects of the picnic meet the established standards (e.g., food safety, entertainment quality, activity suitability).
- Communication & Collaboration: Maintain communication between teams, resolve any issues, and ensure everyone is on track.
4. Finishing (Termination or Close Out):
- Project Completion: Deliver all planned deliverables (e.g., successfully held picnic with good attendance).
- Documentation & Closure: Create a post-event report documenting key learnings, attendee feedback, financial data, and photos. Archive all relevant information.
- Evaluation & Reporting: Analyze the success of the picnic against its goals, identify what worked well and areas for improvement.
- Project Handoff: If necessary, transition responsibilities to the appropriate party for future picnic planning.
Books
- A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) - This is the standard reference for project management practices, including a comprehensive section on the Project Life Cycle.
- Project Management: A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling by Harold Kerzner - A classic text covering various aspects of project management, with a dedicated chapter on the Project Life Cycle.
- Project Management for Dummies by Stanley E. Portny - A beginner-friendly guide to project management concepts, including the Project Life Cycle and its stages.
Articles
- The Project Life Cycle: A Definitive Guide - https://www.projectmanagement.com/blog/project-life-cycle/ - This article provides a detailed overview of the Project Life Cycle with examples and practical tips.
- Understanding the Project Life Cycle - https://www.mindtools.com/commsskills/project-life-cycle.htm - A clear and concise explanation of the Project Life Cycle and its phases.
- The Project Life Cycle: A Framework for Success - https://www.tutorialspoint.com/projectmanagement/projectmanagementprojectlife_cycle.htm - A comprehensive article exploring the Project Life Cycle, its phases, and benefits.
Online Resources
- Project Management Institute (PMI) - https://www.pmi.org/ - PMI is the leading professional organization for project managers, offering resources, certifications, and training on the Project Life Cycle.
- Project Management Institute (PMI) - Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) - https://www.pmi.org/learning/library/pmbok-guide-overview - The official website for the PMBOK Guide, providing access to the complete document and resources.
- Project Management Tools: Various project management software platforms like Asana, Trello, and Jira often include features and templates related to managing projects based on the Project Life Cycle.
Search Tips
- "Project Life Cycle" + "phases" - Find articles and resources detailing the different phases of the Project Life Cycle.
- "Project Life Cycle" + "examples" - Discover real-world examples of how the Project Life Cycle is applied in various industries.
- "Project Life Cycle" + "template" - Search for templates and tools to create your own Project Life Cycle plan.
- "Project Life Cycle" + "software development" - Explore how the Project Life Cycle is adapted for software development projects.
Techniques
Chapter 1: Techniques for Managing the Project Life Cycle
This chapter explores various techniques employed across the different phases of a project lifecycle to ensure efficient and effective project management. These techniques aim to optimize resource allocation, mitigate risks, and enhance communication and collaboration.
1. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): A hierarchical decomposition of the project into smaller, manageable tasks. This technique aids in planning, scheduling, and resource allocation. Each task is defined with clear deliverables and dependencies.
2. Gantt Charts: A visual representation of the project schedule, illustrating task dependencies, durations, and milestones. This technique facilitates monitoring progress, identifying potential delays, and managing resources effectively.
3. Critical Path Method (CPM): Identifies the longest sequence of tasks in a project, determining the minimum project duration. This technique highlights critical tasks that require close monitoring to avoid delays and ensures project completion within the defined timeframe.
4. Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT): Similar to CPM, but incorporates probabilistic estimations for task durations, accounting for uncertainty and risk. This technique provides a more realistic project timeline and helps in risk management.
5. Agile Methodologies: Iterative approaches that emphasize flexibility and adaptation. Techniques like Scrum and Kanban promote collaboration, continuous improvement, and quick feedback loops, ideal for projects with evolving requirements.
6. Risk Management Techniques: These include risk identification, analysis (qualitative and quantitative), response planning (avoidance, mitigation, transference, acceptance), and monitoring. Effective risk management is crucial throughout the project lifecycle.
7. Earned Value Management (EVM): A project performance measurement technique that integrates scope, schedule, and cost data to assess project progress and identify variances. This provides a comprehensive picture of project health and facilitates corrective actions.
Chapter 2: Models for the Project Life Cycle
Several models illustrate the Project Life Cycle, each with its own strengths and weaknesses depending on the project's nature and complexity.
1. Waterfall Model: A linear sequential approach where each phase must be completed before the next begins. This model is suitable for projects with well-defined requirements and minimal anticipated changes.
2. Iterative Model: An approach that involves repeating phases to refine the product incrementally. This is beneficial when dealing with uncertain requirements or complex projects.
3. Spiral Model: Combines iterative development with risk assessment. Each iteration involves planning, risk analysis, development, and evaluation. This model is effective for high-risk projects where early risk mitigation is crucial.
4. Agile Model (Scrum, Kanban): Iterative and incremental approaches that prioritize flexibility and collaboration. Scrum uses sprints, while Kanban uses a visual workflow system. These are suitable for projects with changing requirements and a need for rapid adaptation.
5. V-Model: An extension of the Waterfall model that emphasizes rigorous testing at each phase, ensuring quality throughout the project lifecycle. This is suitable for projects requiring high reliability and quality.
6. Prototype Model: Involves building a prototype to validate requirements and design before full-scale development. This minimizes the risk of building an unsuitable product.
Chapter 3: Software for Managing the Project Life Cycle
Various software tools support project management across all phases of the lifecycle. The choice of software depends on project size, complexity, and team preferences.
1. Project Management Software (PMS): Tools like Microsoft Project, Asana, Trello, Jira, and Monday.com offer features for task management, scheduling, resource allocation, risk management, communication, and reporting.
2. Collaboration Platforms: Tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Google Workspace facilitate communication and collaboration within project teams and with stakeholders.
3. Version Control Systems (VCS): Git, SVN, and Mercurial manage code changes in software development projects, ensuring collaboration and traceability.
4. Issue Tracking Systems: Tools like Jira and Bugzilla help manage defects and issues throughout the project lifecycle, ensuring timely resolution.
5. Reporting and Analytics Tools: Many PMS platforms offer built-in reporting capabilities, while others integrate with BI tools for comprehensive project performance analysis.
Chapter 4: Best Practices for the Project Life Cycle
Adopting best practices significantly enhances project success. These practices focus on proactive planning, effective communication, risk management, and continuous improvement.
1. Clear Project Definition: Start with a well-defined scope, objectives, and deliverables. This prevents scope creep and ensures everyone is on the same page.
2. Proactive Risk Management: Identify and assess potential risks early. Develop mitigation strategies and contingency plans to minimize their impact.
3. Effective Communication: Establish clear communication channels and protocols. Regular communication updates keep stakeholders informed.
4. Regular Monitoring and Control: Track project progress against the plan. Make necessary adjustments to keep the project on track.
5. Continuous Improvement: Learn from past experiences and incorporate lessons learned into future projects. Regular retrospectives identify areas for improvement.
6. Stakeholder Management: Actively involve stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle, managing their expectations and addressing concerns.
7. Documentation: Maintain thorough documentation of all project activities, decisions, and deliverables for future reference and audit trails.
Chapter 5: Case Studies of Project Life Cycles
This chapter presents real-world examples illustrating the successful (and unsuccessful) application of project life cycle management. Each case study highlights specific techniques, models, and challenges encountered.
(Note: Specific case studies would need to be added here. Examples could include the construction of a building, the development of a software application, the implementation of a new marketing campaign, etc. Each case study should detail the project phases, challenges encountered, solutions implemented, and outcomes.) For example:
Case Study 1: The Construction of a Skyscraper: This case study could illustrate the use of the Waterfall model, highlighting the importance of meticulous planning and risk management in a large-scale construction project.
Case Study 2: The Development of a Mobile App: This case study could showcase the use of an Agile methodology, emphasizing the iterative nature of software development and the importance of user feedback.
Case Study 3: The Implementation of a New Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) System: This case study could highlight the challenges of integrating different systems and the need for effective stakeholder management.
Each case study should analyze the success factors and lessons learned, providing valuable insights for future projects.
- ADM Project Understanding ADM Projects in…
- Approved Project Requirements Approved Project Requirements…
- Conceptual Project Planning Conceptual Project Planning: …
- Economic Life Economic Life: A Crucial Fact…
- Effectiveness, in project planning Effectiveness: A Crucial Elem…
- Area of Project Application Area of Project Application: …
- Control Cycle Mastering the Control Cycle: …
- Area of Project Management Application ("APMA") Understanding the Area of Pro…
- Direct Project Costs Direct Project Costs: The Bac…
- Bending Cycle (coiled tubing) The Bending Cycle: Understand…
- Corporate Business Life Cycle Navigating the Oil & Gas Corp…
- Cycle Time (drilling) Cycle Time in Drilling: A Dee…
- Closed Projects Closed Projects: The Silent T…
- Contractor Project Office Contractor Project Office: Th…
- Corporate Project Strategy Aligning Procurement with the…
- Cycle Gas Cycle Gas: The Fuel that Keep…
- Economic Life The Economic Life of an Oil &…
- Cycle Time Cycle Time: A Key Metric for …
- Cycle Time (plunger) Understanding Cycle Time (Plu…
- Education, in project management Drilling Down to Success: Pro…
- Application for Expenditure Justification Navigating the Appl… Project Planning & Scheduling
- Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled ("BCWS") Understanding Budge… Cost Estimation & Control
- Battery limit Understanding Batte… General Technical Terms
- Smoothing Smoothing the Way: … Data Management & Analytics
- DV Tool (cementing) DV Tool: A Crucial … Drilling & Well Completion
Comments