Wastewater Treatment
activated sludge process
Cleaning Up Our Act: The Activated Sludge Process and Wastewater Treatment
Our modern lives generate a vast amount of wastewater, posing a significant threat to the environment if not properly treated. Fortunately, the activated sludge process, a biological wastewater treatment method, plays a crucial role in safeguarding our water resources.
The Essence of Activated Sludge:
The activated sludge process harnesses the power of microorganisms to break down organic matter in wastewater. It involves a carefully orchestrated dance between wastewater and a specially cultivated "activated sludge." This sludge consists of a dense concentration of microorganisms, primarily bacteria, that thrive on consuming organic pollutants.
A Step-by-Step Look:
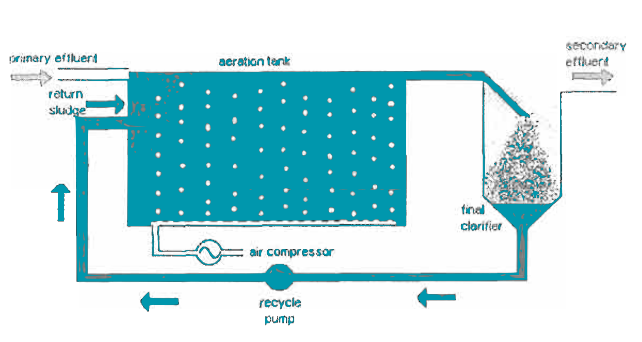
- Wastewater Arrival: Wastewater enters the treatment plant and undergoes initial pre-treatment, removing large debris and grit.
- Mixing with Activated Sludge: The pre-treated wastewater is then introduced to a well-aerated tank, where it is mixed with activated sludge.
- Aerobic Feast: Oxygen is continuously supplied to the mixture, creating an aerobic environment. This oxygen is essential for the bacteria in the sludge, allowing them to efficiently break down organic matter like fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.
- Sludge Settlement: The mixture flows to a sedimentation tank, where the heavier sludge settles to the bottom.
- Sludge Recycling: A portion of the settled sludge is returned to the aeration tank, replenishing the microbial population and ensuring ongoing decomposition.
- Treated Water Discharge: The clarified water, now significantly cleaner, is discharged to a receiving body of water or undergoes further treatment.
- Sludge Disposal: The remaining sludge undergoes further treatment, such as digestion or dewatering, before being disposed of or reused.
Benefits of Activated Sludge:
- High Efficiency: Activated sludge processes are incredibly efficient at removing organic matter, suspended solids, and nutrients from wastewater.
- Versatile: The process can be adapted to treat a wide range of wastewater types, including municipal, industrial, and agricultural waste.
- Stable and Reliable: The microbial communities in activated sludge are relatively stable, ensuring consistent treatment performance.
- Nutrient Removal: Modified activated sludge processes can effectively remove nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, which are major contributors to water pollution.
Challenges and Future Directions:
While highly effective, the activated sludge process faces challenges. Maintaining optimal conditions for microbial activity, managing sludge disposal, and adapting to increasingly complex wastewater streams are key areas for ongoing research and development.
Conclusion:
The activated sludge process is a cornerstone of modern wastewater treatment. By harnessing the power of nature, this technology ensures cleaner water for our communities, protects our environment, and contributes to a more sustainable future. As we face growing challenges in managing wastewater, continuous innovation and optimization of this process will be essential for ensuring healthy water resources for generations to come.
Test Your Knowledge
Quiz: Activated Sludge Process
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What is the primary purpose of the activated sludge process?
a) To remove large debris and grit from wastewater. b) To chemically break down organic matter in wastewater. c) To use microorganisms to consume organic matter in wastewater. d) To filter out suspended solids from wastewater.
Answer
c) To use microorganisms to consume organic matter in wastewater.
2. What is the key component of the activated sludge process?
a) Chlorine b) Activated carbon c) Activated sludge d) UV light
Answer
c) Activated sludge
3. Why is oxygen essential in the activated sludge process?
a) To kill harmful bacteria in the wastewater. b) To facilitate the growth of algae that consume organic matter. c) To provide an environment for the bacteria in the sludge to break down organic matter. d) To prevent the formation of harmful gases during wastewater treatment.
Answer
c) To provide an environment for the bacteria in the sludge to break down organic matter.
4. Which of the following is NOT a benefit of the activated sludge process?
a) High efficiency in removing organic matter b) Versatility in treating different wastewater types c) Elimination of all harmful bacteria in the wastewater d) Stable and reliable treatment performance
Answer
c) Elimination of all harmful bacteria in the wastewater
5. What is a major challenge facing the activated sludge process?
a) The lack of effective sludge disposal methods b) The high cost of maintaining optimal treatment conditions c) The inability to treat wastewater containing heavy metals d) The limited effectiveness in removing nutrients from wastewater
Answer
a) The lack of effective sludge disposal methods
Exercise: Activated Sludge Process Design
Scenario: A small town is designing a new wastewater treatment plant using the activated sludge process. They need to determine the volume of the aeration tank required.
Information:
- The town produces 10,000 m³ of wastewater per day.
- The desired detention time in the aeration tank is 6 hours.
- The sludge age (the average time bacteria spend in the system) is 10 days.
Task: Calculate the required volume of the aeration tank.
Exercice Correction
Here's how to calculate the aeration tank volume:
1. **Convert detention time to days:** 6 hours / 24 hours/day = 0.25 days
2. **Calculate the flow rate per day:** 10,000 m³/day
3. **Calculate the required aeration tank volume:** (Flow rate * Detention time) = 10,000 m³/day * 0.25 days = **2500 m³**
Therefore, the required volume of the aeration tank is 2500 m³. However, this calculation does not account for the sludge age, which impacts the amount of sludge in the tank. A more detailed design would factor in the sludge age and the specific characteristics of the wastewater being treated.
Books
- Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Reuse by Metcalf & Eddy (Comprehensive resource on wastewater treatment including activated sludge)
- Biological Wastewater Treatment: Principles, Modelling and Design by Grady, Daigger, & Lim (Focuses on biological treatment processes like activated sludge)
- Activated Sludge Technology by R.M. Gerardi (Detailed guide to activated sludge operation and design)
Articles
- "Activated Sludge Process: A Review" by A.K. Chakraborty & P.K. Ghosh (Journal of Environmental Engineering and Landscape Management)
- "Advances in Activated Sludge Process for Wastewater Treatment: A Review" by M.A. Khan et al. (Journal of Environmental Management)
- "Activated Sludge: Past, Present and Future" by D.A. Jenkins (Water Science and Technology)
Online Resources
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): https://www.epa.gov/ (Provides information on wastewater treatment technologies, including activated sludge)
- Water Environment Federation (WEF): https://www.wef.org/ (A professional organization offering resources and research related to wastewater treatment)
- International Water Association (IWA): https://www.iwa-network.org/ (Global organization for water professionals, including resources on activated sludge)
Search Tips
- Use specific keywords: "activated sludge process," "wastewater treatment," "biological treatment," "activated sludge design," "activated sludge operation"
- Combine with other terms: "activated sludge + nutrient removal," "activated sludge + energy efficiency," "activated sludge + industrial wastewater"
- Add location: "activated sludge process + [your city/country]" to find local information
- Use advanced search operators:
- " " (quotation marks) to search for exact phrases, e.g., "activated sludge process"
- site: to limit search to specific websites, e.g., "site:epa.gov activated sludge"
- filetype: to search for specific file types, e.g., "filetype:pdf activated sludge"
Techniques
Chapter 1: Techniques in Activated Sludge Process
The activated sludge process relies on a variety of techniques to optimize the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms. These techniques are employed to control the environment and enhance the effectiveness of the process.
1.1 Aeration:
Aeration is the most crucial technique in the activated sludge process. It involves injecting air into the aeration tank to ensure a sufficient supply of dissolved oxygen for the aerobic bacteria to thrive. Various methods are used for aeration, including:
- Surface aeration: This involves using mechanical aerators that create surface agitation and introduce air.
- Diffused aeration: In this method, fine air bubbles are dispersed into the tank using diffusers.
- Fine bubble aeration: Similar to diffused aeration, but utilizes even smaller bubbles for greater oxygen transfer efficiency.
1.2 Mixing and Mixing Techniques:
Adequate mixing is essential for the proper distribution of oxygen, nutrients, and wastewater within the aeration tank. Effective mixing promotes contact between bacteria and organic matter, ensuring efficient decomposition. Mixing techniques include:
- Mechanical mixing: This utilizes impellers or propellers to create agitation and circulate the tank contents.
- Hydraulic mixing: This uses the flow of wastewater itself to promote mixing.
1.3 Sludge Age Control:
Sludge age is a critical factor in the activated sludge process. It refers to the average time the sludge remains in the system. Proper sludge age control is essential to maintain a healthy balance of microbial activity and prevent the build-up of excess sludge. Techniques for sludge age control include:
- Waste sludge removal: This involves removing a portion of the settled sludge from the system, thereby reducing sludge age.
- Return activated sludge (RAS): A portion of the settled sludge is recycled back to the aeration tank to replenish the microbial population and maintain optimal sludge age.
1.4 Nutrient Removal Techniques:
Advanced activated sludge processes often employ techniques to remove nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus. These include:
- Nitrification-denitrification: This process involves two steps:
- Nitrification: Conversion of ammonia (NH3) to nitrate (NO3-) by aerobic bacteria.
- Denitrification: Conversion of nitrate to nitrogen gas (N2) by anaerobic bacteria.
- Phosphorous removal: This involves using chemical precipitation or biological phosphorus removal techniques.
1.5 Monitoring and Control:
Regular monitoring and control of various parameters are essential to ensure the optimal performance of the activated sludge process. These parameters include:
- Dissolved oxygen levels: This ensures adequate oxygen for microbial activity.
- pH: This affects microbial growth and the effectiveness of the process.
- Sludge volume and concentration: This helps monitor the efficiency and stability of the process.
- Nutrient levels: This tracks the effectiveness of nutrient removal techniques.
Chapter 2: Models in Activated Sludge Process
Mathematical models play a crucial role in understanding and predicting the behavior of the activated sludge process. These models provide a framework for analyzing process performance, optimizing operating parameters, and designing new treatment plants.
2.1 Types of Models:
Several types of models are employed in the activated sludge process:
- Empirical models: These models are based on empirical observations and correlations. They provide a simplified representation of the process but may not be accurate in all situations.
- Mechanistic models: These models are based on a detailed understanding of the underlying biochemical and physical processes. They are more complex but offer greater accuracy and insight into the process dynamics.
- Hybrid models: These models combine aspects of empirical and mechanistic models to achieve a balance between simplicity and accuracy.
2.2 Key Modeling Parameters:
Activated sludge models typically incorporate various parameters, including:
- Microbial growth rate: This represents the rate at which bacteria multiply under specific conditions.
- Substrate uptake rate: This represents the rate at which bacteria consume organic matter.
- Oxygen uptake rate: This represents the rate at which bacteria consume oxygen.
- Nutrient removal rate: This represents the rate at which bacteria remove nitrogen and phosphorus.
- Sludge settling velocity: This represents the rate at which sludge settles in the sedimentation tank.
2.3 Applications of Modeling:
Activated sludge models find widespread applications in:
- Process design: Models help engineers optimize the design of new treatment plants by predicting performance and identifying potential bottlenecks.
- Process control: Models can be integrated into real-time control systems to adjust operational parameters and optimize process performance.
- Troubleshooting: Models assist in identifying and diagnosing problems in existing treatment plants by simulating various scenarios.
- Research and development: Models are essential tools for investigating new technologies and improving the efficiency of the activated sludge process.
2.4 Limitations of Models:
Despite their value, activated sludge models have limitations:
- Simplification: Models often make simplifying assumptions, which can affect accuracy.
- Data requirements: Accurate model predictions require extensive data, which may not always be available.
- Uncertainty: The complex nature of the activated sludge process introduces uncertainties in model predictions.
Chapter 3: Software for Activated Sludge Process
Various software tools are available to assist engineers and researchers in analyzing, designing, and managing activated sludge processes. These software programs incorporate advanced models, simulation capabilities, and data analysis tools to enhance understanding and optimize performance.
3.1 Types of Software:
- Process Simulation Software: This type of software allows users to simulate the operation of activated sludge plants, including the aeration, sedimentation, and sludge handling processes. Examples include:
- BioWin: A comprehensive software package for simulating wastewater treatment processes, including activated sludge.
- GPS-X: Another powerful software package for simulating and optimizing wastewater treatment processes.
- Data Acquisition and Control Software: These software programs collect real-time data from sensors in the plant and provide tools for monitoring and controlling the process. Examples include:
- SCADA systems: Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition systems are widely used for collecting and managing data in wastewater treatment plants.
- PLC systems: Programmable Logic Controllers provide automated control of various aspects of the activated sludge process.
- Modeling and Analysis Software: This type of software allows users to develop and analyze mathematical models of the activated sludge process. Examples include:
- MATLAB: A versatile software package for mathematical modeling and analysis, widely used in the field of wastewater engineering.
- Python: A popular programming language with various libraries for scientific computing and modeling.
3.2 Key Features of Software:
Common features of software used in activated sludge processes include:
- Graphical user interface (GUI): This provides an intuitive and user-friendly interface for interacting with the software.
- Modeling capabilities: This allows users to develop and analyze mathematical models of the process.
- Simulation capabilities: This enables users to simulate various scenarios and predict process performance.
- Data analysis tools: This provides tools for analyzing collected data and identifying trends and patterns.
- Report generation: This allows users to generate reports summarizing simulation results, data analysis, and process performance.
3.3 Benefits of Using Software:
Using software for activated sludge processes offers numerous benefits:
- Improved understanding: Software tools provide a visual and quantitative understanding of the process dynamics.
- Optimized design: Software allows engineers to optimize the design of treatment plants, leading to improved performance and reduced costs.
- Enhanced control: Real-time monitoring and control software help operators maintain optimal process conditions and prevent problems.
- Reduced downtime: Software aids in troubleshooting and identifying potential problems before they become major issues, minimizing downtime.
- Increased efficiency: Software can help optimize the use of resources, reducing energy consumption and minimizing sludge production.
Chapter 4: Best Practices in Activated Sludge Process
Following best practices is essential for the successful and efficient operation of the activated sludge process. These practices encompass a range of aspects, from design considerations to operational procedures, aimed at maximizing treatment performance, minimizing environmental impact, and ensuring long-term sustainability.
4.1 Design Considerations:
- Adequate sizing: The aeration tank, sedimentation tank, and other components must be appropriately sized to handle the expected wastewater flow and organic load.
- Efficient aeration: The aeration system should be designed to provide sufficient dissolved oxygen without excessive energy consumption.
- Proper mixing: The mixing system should ensure adequate distribution of oxygen, nutrients, and wastewater throughout the aeration tank.
- Effective sludge settling: The sedimentation tank should be designed to efficiently separate sludge from treated water.
- Nutrient removal considerations: If nutrient removal is required, the process design should incorporate appropriate techniques.
4.2 Operational Procedures:
- Monitoring and control: Regular monitoring of key parameters, such as dissolved oxygen, pH, and sludge volume, is crucial for maintaining optimal process conditions.
- Sludge age control: Proper waste sludge removal and return activated sludge (RAS) rates are essential for maintaining a healthy microbial population and preventing sludge build-up.
- Nutrient removal control: If nutrient removal is implemented, appropriate control measures should be in place to ensure efficient removal of nitrogen and phosphorus.
- Preventative maintenance: Regular maintenance of equipment, such as aeration systems and pumps, helps ensure reliable operation and minimize downtime.
- Operator training: Operators should be adequately trained in the operation and maintenance of the activated sludge process.
4.3 Sustainability Considerations:
- Energy efficiency: Optimization of aeration systems and other energy-intensive components can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Sludge management: Minimizing sludge production and maximizing sludge reuse or disposal options help minimize environmental impact.
- Nutrient recovery: Technologies for recovering nutrients from wastewater can contribute to circular economy principles.
- Process optimization: Continuous process optimization efforts can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact.
4.4 Emerging Technologies:
- Membrane bioreactors (MBRs): MBRs combine activated sludge with membrane filtration, providing higher treatment efficiency and reduced sludge production.
- Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs): AOPs can be integrated with activated sludge to enhance the removal of recalcitrant pollutants.
- Microalgae-based treatment: Integrating microalgae cultivation into activated sludge processes can improve nutrient removal and generate biofuel.
Chapter 5: Case Studies of Activated Sludge Process
Real-world case studies provide valuable insights into the practical applications and challenges of the activated sludge process. These studies showcase the diverse applications, innovations, and successes achieved through this technology.
5.1 Case Study 1: Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant
- Location: [City, Country]
- Challenge: The treatment plant faced challenges in meeting effluent standards for nutrient removal.
- Solution: Implementing advanced activated sludge processes, including nitrification-denitrification and phosphorus removal, enabled the plant to meet regulatory requirements.
- Results: The plant achieved significant reductions in nitrogen and phosphorus levels in the effluent, demonstrating the effectiveness of the process in addressing nutrient pollution.
5.2 Case Study 2: Industrial Wastewater Treatment
- Industry: [Industry sector]
- Challenge: The industry generated wastewater with high organic loads and toxic pollutants.
- Solution: A combination of activated sludge and advanced oxidation processes was employed to treat the wastewater.
- Results: The process effectively removed organic matter and toxic compounds, enabling safe discharge of the treated wastewater.
5.3 Case Study 3: Decentralized Wastewater Treatment
- Location: [Rural community]
- Challenge: The community lacked access to centralized wastewater treatment facilities.
- Solution: A small-scale activated sludge system was implemented to treat wastewater locally.
- Results: The system provided a sustainable solution for wastewater management, improving sanitation and protecting local water resources.
5.4 Lessons Learned:
Case studies highlight several key lessons learned:
- Process optimization: Effective process optimization is crucial for achieving desired treatment goals and maximizing efficiency.
- Flexibility: The activated sludge process is flexible and adaptable to various wastewater characteristics and treatment requirements.
- Innovation: Continuous research and development are essential for advancing activated sludge technology and addressing emerging challenges.
- Collaboration: Effective collaboration between engineers, operators, and researchers is critical for successful implementation and optimization of the activated sludge process.
5.5 Future Directions:
- Integration with other technologies: Combining activated sludge with other advanced treatment technologies, such as membrane bioreactors and AOPs, can further improve treatment efficiency and expand its applications.
- Sustainability focus: Emphasis on energy efficiency, sludge management, and nutrient recovery will enhance the environmental sustainability of the activated sludge process.
- Digitalization and automation: Utilizing digital technologies, such as sensors, data analytics, and artificial intelligence, can optimize process control and enhance operational efficiency.
By examining real-world applications and lessons learned, we can continue to refine and advance the activated sludge process, ensuring its role as a cornerstone of wastewater treatment for sustainable water management in the future.
- Activated Activated: Unlocking Nature's…
- activated biofilter Activated Biofilters: A Power…
- activated sludge Activated Sludge: A Microbial…
- attached growth process Attached Growth Processes: A …
- batch process Batch Processes in Environmen…
- biological process Harnessing Nature's Power: Bi…
- biosorption process Biosorption: A Natural Soluti…
- Block & Hong process The Block & Hong Process: A K…
- bulking sludge Bulking Sludge: A Filamentous…
- Carver-Greenfield process The Carver-Greenfield Process…
- contact process The Contact Process: A Versat…
- contact stabilization process Contact Stabilization: A Fast…
- Davis Process Davis Process: A Legacy of Wa…
- Densludge Densludge: A Key Component of…
- dewatered sludge Dewatered Sludge: A Solid Sol…
- activated alumina Activated Alumina: A Workhors…
- activated carbon (AC) Activated Carbon: A Powerful …
- advanced oxidation process (AOP) Advanced Oxidation Processes:…
- alum sludge Alum Sludge: A Byproduct of W…
- chemical sludge Chemical Sludge: A Persistent…
- meq/L Understanding Milli… Water Quality Monitoring
- theoretical oxygen demand (ThOD) Theoretical Oxygen … Wastewater Treatment
- calcium carbonate equivalent Calcium Carbonate E… Water Quality Monitoring
- volatile suspended solids (VSS) Understanding Volat… Wastewater Treatment
- MAF MAF: A Giant in the… Sustainable Water Management
Comments