Forage et complétion de puits
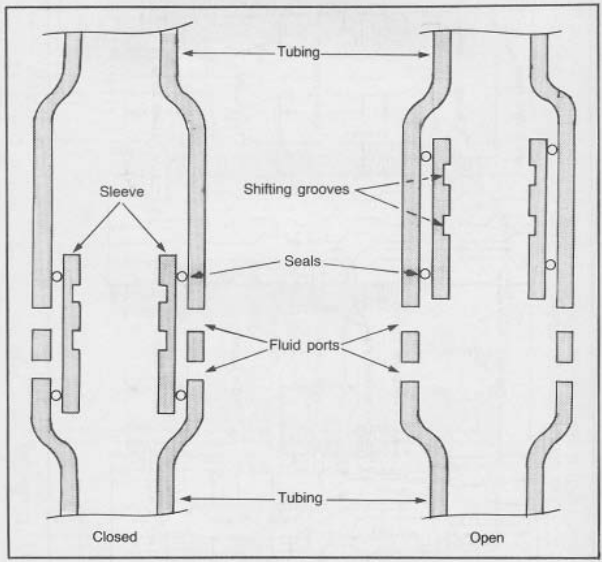
Sliding Sleeve
Manches Coulissantes : Combler le Gap dans la Production Pétrolière et Gazière
Dans le monde complexe de la production pétrolière et gazière, chaque composant joue un rôle crucial. Les équipements en fond de puits, souvent exploités sous d'immenses pressions et dans des conditions difficiles, ne font pas exception. Parmi ces outils essentiels, le **Manche Coulissant** se distingue comme un dispositif polyvalent et adaptable qui permet un écoulement contrôlé des fluides, optimisant la production et facilitant diverses interventions sur les puits.
**Qu'est-ce qu'un Manche Coulissant ?**
Un Manche Coulissant est un équipement spécialisé en fond de puits installé dans la colonne de tubing d'un puits. Il agit essentiellement comme une **vanne** qui permet un écoulement contrôlé de l'annulus (l'espace entre le revêtement du puits et le tubing) vers le tubing lui-même. Ce flux peut être dirigé vers la surface pour la production ou utilisé à d'autres fins comme l'injection de produits chimiques ou de fluides.
**Fonctionnalités et Caractéristiques Clés :**
- **Polyvalence :** Les manches coulissants peuvent être utilisés pour une variété d'applications, notamment :
- **Optimisation de la production :** Diriger la production à partir de différentes zones du puits.
- **Isolement de l'eau :** Isoler les zones aquifères pour améliorer la production de pétrole.
- **Gaz lift :** Injecter du gaz dans l'annulus pour améliorer la production de pétrole.
- **Stimulation des puits :** Injecter des produits chimiques ou des fluides pour améliorer les performances du puits.
- **Écoulement Contrôlé :** La capacité du manche à être ouvert et fermé permet un contrôle précis du flux de fluide.
- **Fonctionnement par Câble :** Les manches coulissants sont généralement ouverts et fermés à l'aide de la technologie de câblage, ce qui permet une manipulation à distance, même à des profondeurs importantes. Cela élimine la nécessité d'interventions coûteuses et perturbatrices.
**Fonctionnement :**
Un Manche Coulissant se compose d'un corps cylindrique avec un manche interne qui peut se déplacer vers le haut et vers le bas. Ce mouvement est contrôlé par un mécanisme actionné par câblage. Lorsque le manche est en position ouverte, il permet au fluide de passer de l'annulus vers le tubing. Lorsqu'il est fermé, le flux est restreint ou complètement arrêté.
**Avantages de l'utilisation de Manches Coulissants :**
- **Production Améliorée :** Les manches coulissants permettent une production efficace à partir de plusieurs zones et aident à isoler l'eau ou le gaz, améliorant le taux de récupération global du pétrole.
- **Réduction des Coûts :** Ils permettent des interventions efficaces et éliminent le besoin d'interventions coûteuses, permettant de gagner du temps et de l'argent.
- **Flexibilité :** Ils offrent une solution polyvalente pour différentes conditions de puits et défis de production.
**Conclusion :**
Les Manches Coulissants sont un outil précieux dans l'industrie pétrolière et gazière, offrant une flexibilité et un contrôle cruciaux sur le flux de fluide dans les opérations en fond de puits. Leur polyvalence, leur capacité d'opération à distance et leur rentabilité les rendent essentiels pour optimiser les performances des puits et obtenir une production efficace. Alors que l'industrie continue d'explorer de nouvelles technologies et techniques de production, les manches coulissants resteront sans aucun doute un élément crucial dans la quête d'une extraction pétrolière et gazière durable et efficace.
Test Your Knowledge
Quiz: Sliding Sleeves in Oil & Gas Production
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What is the primary function of a Sliding Sleeve in a well?
a) To prevent the flow of fluids from the annulus into the tubing.
Answer
Incorrect. The Sliding Sleeve allows for controlled flow.
b) To regulate the pressure within the wellbore.
Answer
Incorrect. While it can affect pressure, its primary function is controlling fluid flow.
c) To control the flow of fluids from the annulus into the tubing.
Answer
Correct. Sliding Sleeves act as valves, regulating fluid flow.
d) To seal off the wellbore completely.
Answer
Incorrect. This is not the primary function of a Sliding Sleeve.
2. How are Sliding Sleeves typically operated?
a) By a mechanical system attached to the surface.
Answer
Incorrect. They are typically operated remotely.
b) By hydraulic pressure from the surface.
Answer
Incorrect. While hydraulics can be used in some cases, wireline is more common.
c) By wireline technology.
Answer
Correct. Wireline allows for remote operation at depth.
d) By manual operation from the surface.
Answer
Incorrect. Manual operation at depth is not feasible.
3. Which of the following is NOT a potential application of Sliding Sleeves?
a) Isolating water-bearing zones.
Answer
Incorrect. This is a common application of Sliding Sleeves.
b) Injecting chemicals for well stimulation.
Answer
Incorrect. This is a valid application of Sliding Sleeves.
c) Replacing damaged tubing sections.
Answer
Correct. Sliding Sleeves are not used for tubing replacement.
d) Directing production from different zones.
Answer
Incorrect. This is a key function of Sliding Sleeves.
4. What is a major advantage of using Sliding Sleeves compared to traditional workovers?
a) Increased well production.
Answer
Incorrect. While Sliding Sleeves can enhance production, this is not the primary advantage compared to workovers.
b) Reduced downtime and costs.
Answer
Correct. Remote operation with wireline reduces downtime and costs compared to workovers.
c) Increased well lifespan.
Answer
Incorrect. While they can contribute to well longevity, this is not the main advantage over workovers.
d) Improved well safety.
Answer
Incorrect. While they can improve safety in some scenarios, this is not the primary advantage over workovers.
5. What is the key component of a Sliding Sleeve that allows for controlled fluid flow?
a) The cylindrical body.
Answer
Incorrect. The body provides structure but doesn't directly control flow.
b) The internal sleeve.
Answer
Correct. The movement of the internal sleeve regulates flow.
c) The wireline mechanism.
Answer
Incorrect. The wireline operates the sleeve, but the sleeve itself controls flow.
d) The annulus.
Answer
Incorrect. The annulus is the space between the tubing and casing.
Exercise: Designing a Well Intervention Strategy
Scenario: An oil well has been producing water alongside oil, reducing production efficiency. You are tasked with designing an intervention strategy using Sliding Sleeves to address the issue.
Task:
- Identify the problem: What is the specific issue impacting the well's performance?
- Propose a solution: How can a Sliding Sleeve be used to address the water production issue?
- Explain the implementation: Briefly describe the steps involved in using a Sliding Sleeve to solve this problem.
Exercise Correction
**1. Problem Identification:** The well is producing water alongside oil, leading to decreased oil production efficiency and potentially affecting the quality of the produced oil. **2. Proposed Solution:** Utilize a Sliding Sleeve to isolate the water-bearing zone from the oil-producing zone. This can be achieved by installing the Sliding Sleeve at a depth above the water zone, effectively blocking the flow of water into the production tubing. **3. Implementation:** a. **Installation:** The Sliding Sleeve is installed in the tubing string at the desired depth. b. **Wireline Operation:** The sleeve is initially open to allow normal production. c. **Isolation:** Once the well is stabilized, the wireline tool is used to close the Sliding Sleeve, effectively isolating the water zone. d. **Monitoring:** After isolation, production is monitored to assess the effectiveness of the intervention.
Books
- Oil Well Drilling and Production by John M. Campbell (This book covers a wide range of topics related to oil and gas production, including well completion and downhole equipment like sliding sleeves.)
- Petroleum Engineering: Drilling and Well Completions by William C. Lyons (This textbook provides detailed information on drilling and well completion techniques, including the use of sliding sleeves.)
- Production Operations in Petroleum Engineering by Larry W. Lake (This book focuses on the operational aspects of oil and gas production, including the application of downhole tools like sliding sleeves.)
Articles
- "Sliding Sleeve Applications and Technology" by Schlumberger (This article provides a comprehensive overview of different sliding sleeve types and their applications in various well conditions.)
- "Sliding Sleeve Technology: An Essential Tool for Well Intervention" by Baker Hughes (This article highlights the benefits of sliding sleeves and their role in well intervention and production optimization.)
- "Advances in Downhole Tools: The Role of Sliding Sleeves in Enhanced Oil Recovery" by SPE (This technical paper discusses the use of sliding sleeves in enhanced oil recovery techniques and their potential to improve production efficiency.)
Online Resources
- Schlumberger - Sliding Sleeves: https://www.slb.com/services/production/well-completion-and-intervention/sliding-sleeves (This website provides detailed information about Schlumberger's range of sliding sleeve products and their applications.)
- Baker Hughes - Sliding Sleeves: https://www.bakerhughes.com/en/products-services/production-and-reservoir-technologies/well-construction/completion-equipment/sliding-sleeves (This website provides information about Baker Hughes's sliding sleeve technology and their capabilities.)
- SPE - Sliding Sleeves: https://www.onepetro.org/search/?q=sliding%20sleeve (This website offers access to a wide range of technical papers and articles related to sliding sleeves and their applications.)
Search Tips
- Use specific keywords like "sliding sleeve" combined with "oil and gas," "production," "well completion," and "downhole equipment."
- Include the names of major oilfield service companies like Schlumberger, Baker Hughes, Halliburton, and Weatherford in your searches to find their product offerings and technical information.
- Utilize advanced search operators like "+" for required words and "-" for excluded words to refine your search results.
- Use quotation marks around specific phrases to find exact matches.
Techniques
Sliding Sleeves: A Comprehensive Overview
This document expands on the provided text to offer a more in-depth look at sliding sleeves, broken down into distinct chapters.
Chapter 1: Techniques
The successful deployment and operation of sliding sleeves rely on several key techniques:
1.1. Installation: Sliding sleeves are typically installed during the completion phase of a well. This involves carefully lowering the sleeve into the wellbore, positioning it at the desired depth, and securing it within the tubing string. Precise positioning is crucial to ensure proper isolation of the targeted zones. Specialized tools and techniques are employed to guarantee a secure and leak-free installation. Factors like wellbore trajectory and environmental conditions (temperature, pressure) significantly influence the installation process.
1.2. Actuation: Sliding sleeves are actuated remotely using wireline technology. This involves sending a wireline tool down the wellbore to engage with the sleeve's actuation mechanism. The tool then either opens or closes the sleeve, allowing for precise control of fluid flow. Different actuation mechanisms exist, each with its own advantages and limitations. These mechanisms must be robust enough to withstand the harsh downhole environment. Understanding the specific actuation mechanism is critical for proper operation and troubleshooting.
1.3. Testing and Verification: After installation and actuation, thorough testing is essential to verify the integrity and functionality of the sliding sleeve. This often involves pressure testing to ensure there are no leaks and functional testing to confirm that the sleeve can be reliably opened and closed. Accurate pressure readings are crucial during these tests to ensure the sleeve is functioning as intended and to avoid any damage to the well.
1.4. Retrieval (if necessary): While designed for long-term deployment, situations might arise where sleeve retrieval is necessary. This is a complex procedure requiring specialized tools and expertise, as it involves safely removing the sleeve from the wellbore without damaging surrounding equipment or the well itself. This process can significantly impact production timelines.
Chapter 2: Models
Sliding sleeves are available in a variety of designs and configurations, each suited to specific well conditions and operational requirements. Key model variations include:
2.1. Single Sleeves: These are the simplest type, allowing for the isolation of a single zone.
2.2. Multiple Sleeves: These allow for the isolation and independent control of multiple zones within a single well. The number of sleeves and their arrangement are customizable to meet specific needs. This configuration allows for advanced production optimization strategies.
2.3. Packer-type Sleeves: These sleeves incorporate a packer element to provide enhanced zonal isolation and prevent fluid bypass. The packer element provides a superior seal compared to other sleeve designs.
2.4. Retrievable vs. Permanent Sleeves: Retrievable sleeves can be removed from the wellbore if needed, offering flexibility. Permanent sleeves, as the name suggests, remain in place for the lifetime of the well. The choice between these types depends on the anticipated well life and the possibility of future interventions.
2.5. Material Considerations: The materials used in the construction of sliding sleeves are crucial for ensuring their longevity and reliability under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions. Careful selection of materials is essential to prevent corrosion and other forms of degradation.
Chapter 3: Software
Software plays a crucial role in the design, simulation, and operation of sliding sleeves. Key software applications include:
3.1. Well Completion Design Software: This type of software assists engineers in designing optimal completion strategies that incorporate sliding sleeves, considering wellbore geometry, reservoir characteristics, and production goals.
3.2. Simulation Software: Reservoir simulation software can model the behavior of a well with sliding sleeves, allowing engineers to predict production performance and optimize well management strategies.
3.3. Wireline Control Software: This software manages the remote actuation of sliding sleeves via wireline technology, providing real-time control and monitoring of sleeve operation. It includes safety mechanisms to prevent accidental activation or damage.
3.4. Data Acquisition and Analysis Software: Software is used to collect and analyze data from pressure sensors and other monitoring devices installed near the sliding sleeve, ensuring its proper functioning and providing insight into well performance.
Chapter 4: Best Practices
Implementing best practices is essential for maximizing the effectiveness and lifespan of sliding sleeves. These include:
4.1. Proper Design and Selection: Careful consideration of well conditions, production goals, and future intervention plans is crucial for selecting the appropriate sliding sleeve model.
4.2. Rigorous Quality Control: Thorough inspection and testing of all components before installation are necessary to ensure the reliability and integrity of the system.
4.3. Skilled Personnel: The installation, actuation, and maintenance of sliding sleeves require specialized expertise and training.
4.4. Comprehensive Documentation: Maintaining detailed records of all operations related to the sliding sleeve, including installation procedures, actuation logs, and maintenance records, is essential for effective troubleshooting and long-term management.
4.5. Preventative Maintenance: Regular inspection and scheduled maintenance help to identify potential issues before they become major problems, extending the life of the system and minimizing downtime.
Chapter 5: Case Studies
This section would contain specific examples of how sliding sleeves have been successfully used in real-world oil and gas operations. These case studies would highlight the benefits and challenges of using sliding sleeves in different well scenarios. Examples could include:
- Case Study 1: Improved oil production in a mature field by isolating water-bearing zones using multiple sliding sleeves.
- Case Study 2: Successful gas lift application to enhance oil recovery in a low-permeability reservoir using a packer-type sleeve.
- Case Study 3: Cost savings achieved through reduced workovers by using retrievable sleeves for targeted well interventions.
Each case study would detail the specific challenges, the solutions implemented using sliding sleeve technology, and the positive outcomes achieved. This would provide valuable practical insights into the applications and effectiveness of sliding sleeves.
- Shifting A Sleeve Déplacement d'un Manchon : Un…
- sleeve Manchons : Les héros méconnus…
- Sliding ROP ROP glissant : un indicateur …
- Sliding Time Temps de glissement : Un fact…
- Demande de justification des dépenses Naviguer dans la de… Planification et ordonnancement du projet
- Coût budgété du travail planifié Comprendre le Coût … Estimation et contrôle des coûts
- Les limites de batterie Comprendre les limi… Termes techniques généraux
- Outil DV Outil DV : Un éléme… Forage et complétion de puits
- SOMMAIRE TOC : Comprendre le… Termes techniques généraux
Comments