Forage et complétion de puits
Rotary Drilling
Forage Rotatif : Le Cœur de l'Exploration Pétrolière et Gazière
Le forage rotatif est la méthode dominante utilisée dans l'industrie pétrolière et gazière pour accéder aux ressources souterraines. Il implique une plate-forme de forage qui fait tourner un train de tiges de forage, équipé d'un trépan spécialisé en bas, pour couper les formations rocheuses et créer un puits. Ce processus, une symphonie de mécanismes complexes et d'ingénierie sophistiquée, constitue la base de l'exploration et de la production pétrolières et gazières.
Les Composants Principaux :
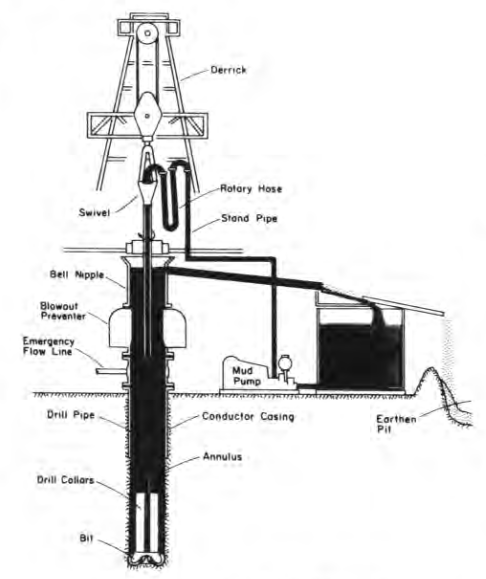
- Plate-forme de forage : Le centre névralgique des opérations, une plate-forme de forage abrite les machines et les équipements nécessaires au forage. Cela comprend :
- Derrick : Une structure imposante qui soutient le train de tiges de forage et les équipements de levage.
- Treuil : Une machinerie puissante qui soulève et abaisse le train de tiges de forage.
- Table tournante : Une plate-forme rotative qui transmet la puissance du treuil au train de tiges de forage.
- Pompes à boue : Des pompes haute pression qui font circuler le fluide de forage (boue) dans le train de tiges de forage et de retour à la surface.
- Train de tiges de forage : Une longue colonne creuse de tuyaux en acier reliés par des joints filetés, s'étendant de la table tournante jusqu'au trépan.
- Trépan : Un outil spécialisé situé en bas du train de tiges de forage, conçu pour couper les formations rocheuses. Les types de trépans comprennent les trépans à rouleaux coniques, les trépans diamantés et les trépans à compact de diamant polycristallin (PDC), chacun étant adapté à différents types de roches et conditions de forage.
- Fluide de forage (boue) : Un mélange d'eau, d'argile et d'autres additifs qui remplit plusieurs fonctions :
- Refroidissement et lubrification : Réduit la friction entre le trépan et les formations rocheuses.
- Évacuation des débris rocheux : Transporte les débris de forage à la surface.
- Soutien des parois du puits : Empêche les effondrements et maintient l'intégrité du puits.
- Contrôle de la pression de formation : Empêche les écoulements incontrôlés de fluides de la formation.
Le Processus de Forage :
- Installation de forage : La plate-forme est assemblée à l'emplacement choisi et le train de tiges de forage est abaissé dans le puits.
- Forage : La table tournante fait tourner le train de tiges de forage, ce qui fait que le trépan coupe les formations rocheuses. Le fluide de forage est circulé dans le train de tiges de forage et de retour à la surface, enlevant les débris de forage et en assurant le refroidissement et la lubrification.
- Tubage : Une fois une certaine profondeur atteinte, un tubage en acier est installé pour renforcer le puits et prévenir l'effondrement.
- Cimentage : L'espace entre le tubage et le puits est rempli de ciment pour sceller le puits et fournir une intégrité structurelle.
- Forage et complétion : Le processus de forage se poursuit jusqu'à ce que la formation cible soit atteinte. Le puits est ensuite complété par l'installation d'équipements de production, permettant l'extraction d'hydrocarbures.
Avantages du Forage Rotatif :
- Efficacité : Le forage rotatif est une méthode rapide et efficace, capable de forer des puits profonds rapidement.
- Polyvalence : Il peut être utilisé pour forer une grande variété de types de puits, y compris des puits de pétrole et de gaz, des puits d'eau et des puits géothermiques.
- Taux de production élevés : Le forage rotatif permet d'obtenir des taux de production élevés, maximisant la récupération des ressources.
Défis du Forage Rotatif :
- Impact environnemental : Les activités de forage peuvent avoir un impact sur l'environnement, y compris des déversements potentiels et la destruction de l'habitat.
- Coût : Le forage rotatif peut être coûteux, surtout pour les puits profonds et les formations géologiques difficiles.
- Sécurité : Les opérations de forage présentent des risques potentiels pour la sécurité des travailleurs.
Progrès du Forage Rotatif :
- Forage directionnel : Permet de forer des puits dans une direction horizontale ou déviée, permettant d'accéder aux ressources dans des formations difficiles.
- Forage intelligent : Utilise l'analyse de données et les technologies de capteurs pour optimiser les performances de forage et réduire les coûts.
- Forage automatisé : Les technologies d'automatisation sont de plus en plus utilisées pour rationaliser les opérations et améliorer la sécurité.
Le forage rotatif reste la méthode principale pour accéder aux ressources pétrolières et gazières. Alors que la technologie continue d'avancer, l'efficacité, la sécurité et les performances environnementales du forage rotatif s'améliorent constamment, assurant sa pertinence continue dans l'industrie énergétique pour les années à venir.
Test Your Knowledge
Rotary Drilling Quiz:
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What is the primary function of the drilling rig's drawworks?
a) Rotate the drill string. b) Circulate drilling fluid. c) Support the drill string and hoisting equipment. d) Raise and lower the drill string.
Answer
d) Raise and lower the drill string.
2. Which of the following is NOT a function of drilling fluid (mud)?
a) Cooling and lubricating the drill bit. b) Removing rock cuttings from the wellbore. c) Strengthening the drill string. d) Supporting borehole walls to prevent cave-ins.
Answer
c) Strengthening the drill string.
3. What type of drill bit is best suited for drilling through hard, abrasive rock formations?
a) Roller cone bit. b) Diamond bit. c) PDC bit. d) Both b) and c) are suitable.
Answer
d) Both b) and c) are suitable.
4. What is the main advantage of directional drilling?
a) Drilling deeper wells. b) Accessing resources in challenging formations. c) Reducing the environmental impact of drilling. d) Increasing the speed of drilling.
Answer
b) Accessing resources in challenging formations.
5. Which of the following is a major challenge associated with rotary drilling?
a) Low production rates. b) Inability to drill in different geological formations. c) Potential environmental impact. d) Limited applications in the energy industry.
Answer
c) Potential environmental impact.
Rotary Drilling Exercise:
Scenario: You are working as a drilling engineer on a new oil exploration project. Your team has encountered a particularly challenging rock formation that is slowing down the drilling process.
Task:
- Identify two potential issues that could be causing the drilling slowdown.
- Suggest two specific solutions for each issue that could improve drilling efficiency.
Example:
- Issue: The drill bit is not penetrating the rock formation effectively due to its dullness or improper type.
- Solution:
- Replace the drill bit with a more suitable type.
- Sharpen or re-condition the current drill bit.
Exercice Correction
Here are some possible issues and solutions:
Issue 1: The drill bit is not penetrating the rock formation effectively due to its dullness or improper type.
- Solution 1: Replace the drill bit with a more suitable type. For example, if the rock is particularly hard, a diamond or PDC bit may be more effective than a roller cone bit.
- Solution 2: Sharpen or re-condition the current drill bit. This can extend the life of the bit and improve its performance.
Issue 2: The drilling fluid is not effectively removing rock cuttings from the wellbore.
- Solution 1: Adjust the drilling fluid properties. This might involve changing the density, viscosity, or additives in the fluid.
- Solution 2: Increase the circulation rate of the drilling fluid. This will help to more quickly remove cuttings and prevent them from accumulating and hindering the drilling process.
Issue 3: The wellbore is unstable and prone to collapse.
- Solution 1: Increase the weight on the bit. This will help to stabilize the wellbore and prevent collapse.
- Solution 2: Install a casing string at the appropriate depth. Casing will reinforce the wellbore and prevent collapse.
Books
- Petroleum Engineering: Drilling and Well Completions by John A. Davies and Ronald A. Dake
- Drilling Engineering by John C. Reese and William R. Storm
- Fundamentals of Drilling Engineering by B.C. Craft and H.F. Holditch
- Drilling Engineering: Principles and Practices by Robert F. Schmidt
Articles
- "Rotary Drilling: A Review of Its History, Technology, and Future" by S.M. Gupta and M.S. Singh (Journal of Petroleum Technology)
- "Directional Drilling: A Technological Overview" by M.A. Shor (Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering)
- "Intelligent Drilling: A New Era in Oil and Gas Exploration and Production" by J.P. Loveless and D.W. Hale (SPE Journal)
- "Automated Drilling: The Next Frontier in Oil and Gas Operations" by R.J. Smith and A.B. Johnson (Journal of Energy Resources Technology)
Online Resources
- Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE): https://www.spe.org/
- American Petroleum Institute (API): https://www.api.org/
- International Association of Drilling Contractors (IADC): https://www.iadc.org/
- Schlumberger: https://www.slb.com/
- Halliburton: https://www.halliburton.com/
Search Tips
- "Rotary Drilling" + "History" - Explore the development and evolution of rotary drilling techniques.
- "Rotary Drilling" + "Types of Drill Bits" - Learn about different drill bit designs and their applications.
- "Rotary Drilling" + "Drilling Fluid" - Research the composition, functions, and importance of drilling mud.
- "Rotary Drilling" + "Directional Drilling" - Understand the principles and applications of drilling horizontally or deviated.
- "Rotary Drilling" + "Environmental Impact" - Examine the environmental challenges and mitigation strategies associated with drilling operations.
- "Rotary Drilling" + "Safety" - Investigate the safety protocols and procedures used in rotary drilling.
- "Rotary Drilling" + "Technology Trends" - Discover the latest innovations and advancements in rotary drilling technology.
Techniques
Rotary Drilling: A Comprehensive Overview
This document expands on the provided text, breaking down the subject of rotary drilling into separate chapters for clarity and depth.
Chapter 1: Techniques
The success of rotary drilling hinges on a variety of techniques employed throughout the drilling process. These techniques are constantly refined and improved upon to enhance efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
1.1 Drill Bit Selection and Application: The choice of drill bit (roller cone, diamond, PDC) is crucial and depends on the formation's hardness, abrasiveness, and geological composition. Techniques like bit optimization – selecting the right bit for specific rock types and optimizing drilling parameters – are essential for maximizing Rate of Penetration (ROP). Specialized bits, such as those designed for directional drilling or extended reach drilling (ERD), further enhance the technique's capabilities.
1.2 Mud Engineering and Management: The properties of the drilling mud (density, viscosity, pH) are carefully controlled to maintain wellbore stability, remove cuttings effectively, and control formation pressures. Techniques such as lost circulation control (managing fluid loss into porous formations) and shale inhibition (preventing shale swelling and instability) are critical for successful drilling operations. Advanced mud systems, incorporating specialized chemicals and polymers, are continuously developed to tackle increasingly challenging formations.
1.3 Directional and Horizontal Drilling: These advanced techniques allow wells to deviate from a vertical path, reaching reservoirs that would be inaccessible with vertical drilling. Measurements While Drilling (MWD) and Logging While Drilling (LWD) technologies are crucial for guiding the drill bit precisely to the target zone. Techniques such as steerable motors and bent subs are integral to controlling the wellbore trajectory.
1.4 Wellbore Stability Management: Maintaining the integrity of the wellbore throughout the drilling process is paramount. This involves careful monitoring of formation pressures, managing drilling fluid properties, and implementing casing and cementing programs. Techniques such as pre-emptive casing, stress-sensitive mud design, and advanced geomechanical modeling help mitigate wellbore instability issues.
1.5 Managed Pressure Drilling (MPD): MPD is a sophisticated technique that precisely controls the pressure at the bottom of the wellbore, minimizing the risk of kicks (uncontrolled influx of formation fluids) and improving wellbore stability. This technique is particularly useful in challenging wells with complex pressure regimes.
Chapter 2: Models
Understanding and predicting wellbore behavior is crucial for efficient and safe rotary drilling. This understanding relies heavily on the use of various models.
2.1 Geomechanical Models: These models use geological data to predict the stresses and strains within the formations, helping to assess wellbore stability risks and optimize drilling parameters. Factors considered include rock strength, pore pressure, and tectonic stress.
2.2 Hydraulic Models: These models predict the flow of drilling fluids in the wellbore and annulus, assisting in the design of efficient circulation systems and the prevention of pressure-related problems. They are used to optimize drilling fluid properties and design strategies for managing fluid losses.
2.3 Reservoir Simulation Models: These models predict the flow of hydrocarbons in the reservoir, aiding in the planning and optimization of well placement and completion designs. This information is vital for maximizing production efficiency.
2.4 Drilling Performance Models: These models predict drilling rates, torque, drag, and other drilling parameters based on various factors such as bit type, formation properties, and drilling fluid characteristics. They are used for optimizing drilling operations and predicting drilling costs.
Chapter 3: Software
Sophisticated software is essential for planning, executing, and monitoring rotary drilling operations.
3.1 Drilling Simulation Software: Software packages simulate the entire drilling process, allowing engineers to test different scenarios and optimize drilling parameters before actual drilling commences. This significantly reduces risks and improves operational efficiency.
3.2 Well Planning Software: This software is used to design the well trajectory, select appropriate drill bits and drilling parameters, and plan casing and cementing operations. It also integrates data from various sources, including seismic surveys and geological models.
3.3 Data Acquisition and Management Software: Software is used to acquire, process, and analyze data from various sensors and instruments during drilling operations. This data is essential for monitoring wellbore conditions, optimizing drilling parameters, and detecting potential problems.
3.4 Real-time Monitoring and Control Systems: These systems provide real-time feedback on drilling parameters, allowing for immediate adjustments to optimize drilling performance and prevent problems. They integrate data from multiple sources and use advanced algorithms to detect anomalies and provide alerts.
Chapter 4: Best Practices
Best practices are crucial for ensuring safe, efficient, and environmentally responsible rotary drilling operations.
4.1 Rig Site Selection and Preparation: Thorough site surveys are essential to identify potential hazards and optimize rig placement. Careful planning and preparation minimize environmental impact and ensure efficient operations.
4.2 Risk Management: Implementing a robust risk management system is paramount to identify and mitigate potential hazards throughout the drilling process. This includes detailed hazard analysis, emergency response planning, and regular safety training.
4.3 Environmental Protection: Adhering to environmental regulations and implementing best practices to minimize the environmental impact of drilling activities is crucial. This includes proper waste management, spill prevention, and habitat protection.
4.4 Well Control: Strict adherence to well control procedures is essential to prevent uncontrolled flows of formation fluids. Regular training and drills are necessary to ensure the competency of personnel in well control procedures.
4.5 Data Management and Analysis: Efficient data management and analysis are crucial for optimizing drilling performance and identifying areas for improvement. Collecting and analyzing data from various sources allows for informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
Chapter 5: Case Studies
Real-world examples demonstrate the application and outcomes of rotary drilling techniques, models, software, and best practices.
(Note: This section requires specific examples. The following are hypothetical examples to illustrate the structure.)
5.1 Case Study 1: Successful Application of MPD in a High-Pressure, High-Temperature (HPHT) Well: This case study would detail how managed pressure drilling techniques helped overcome challenges related to wellbore instability and uncontrolled formation fluid influx in a demanding environment.
5.2 Case Study 2: Optimization of Drilling Parameters Using Drilling Simulation Software: This case study would show how drilling simulation software was used to predict optimal drilling parameters, resulting in significant cost savings and improved drilling efficiency.
5.3 Case Study 3: Environmental Mitigation Strategies in a Sensitive Ecosystem: This case study would demonstrate how environmental protection measures were implemented to minimize the impact of rotary drilling operations on a fragile ecosystem.
5.4 Case Study 4: Accident Prevention Through Robust Risk Management: This case study would illustrate how a comprehensive risk management system prevented a potential drilling accident, highlighting the importance of proactive safety measures.
This expanded overview provides a more detailed and structured exploration of rotary drilling, encompassing its core techniques, supporting models, essential software, best practices, and illustrative case studies. Remember to replace the hypothetical case studies with real-world examples for a complete and impactful document.
- Ballooning (drilling) Le gonflement : un voleur sil…
- B c (drilling) Comprendre le B c (Forage) : …
- Below Rotary Time (drilling) Comprendre le Temps Hors Rota…
- Bit Weight (drilling) Le Poids sur Mèche : Le Moteu…
- Bit Whirl (drilling) Tourbillon de Mèche : Le Tueu…
- Brake (drilling) Freiner le train de forage : …
- Breakout (drilling) Éclatement : Élargissement du…
- BRT (drilling) BRT : Le héros méconnu sous l…
- BUR (drilling) BUR en forage : Comprendre le…
- C/K (drilling) C/K (Forage) : Comprendre le …
- Clean Circulation (drilling) Circulation Propre : Le Tueur…
- Coiled Tubing Drilling Forage avec tubing enroulé : …
- Company Man (drilling) L'homme de compagnie : un mai…
- Cycle Time (drilling) Temps de Cycle en Forage : Pl…
- daily drilling report L'épine dorsale des opération…
- Daily Drilling Report Garder le forage en marche : …
- DC (drilling) DC (Forets): L'épine dorsale …
- Deflection (drilling) Comprendre la Déflexion en Fo…
- directional drilling Naviguer la Terre : Plongez d…
- Directional Drilling Naviguer les profondeurs de l…
- Demande de justification des dépenses Naviguer dans la de… Planification et ordonnancement du projet
- Coût budgété du travail planifié Comprendre le Coût … Estimation et contrôle des coûts
- Les limites de batterie Comprendre les limi… Termes techniques généraux
- Outil DV Outil DV : Un éléme… Forage et complétion de puits
- SOMMAIRE TOC : Comprendre le… Termes techniques généraux
Comments