Ingénierie des réservoirs
Reserves, 2P
Dévoiler le mystère du pétrole et du gaz : Comprendre les réserves 2P
Dans le monde du pétrole et du gaz, comprendre les classifications des réserves est crucial pour les investisseurs, les entreprises et les gouvernements. L'un des termes les plus courants que vous rencontrerez est les **réserves 2P**, souvent désignées comme **réserves prouvées plus probables**. Cet article plonge dans la signification et l'importance des réserves 2P, vous aidant à naviguer dans les complexités des estimations du pétrole et du gaz.
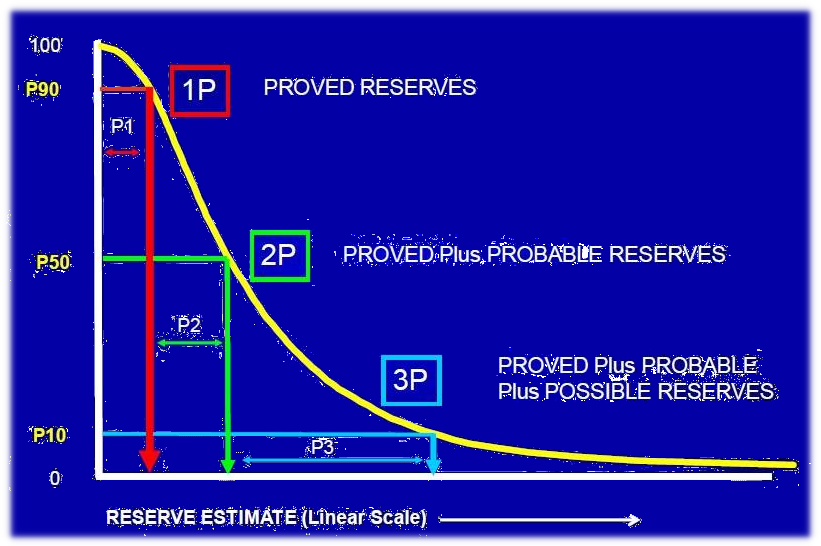
**Le spectre des réserves :**
Les réserves de pétrole et de gaz sont classées en fonction du niveau de certitude associé à leur récupération potentielle. Ce système de classification aide les parties prenantes à évaluer la fiabilité des volumes de ressources estimés.
- **Réserves prouvées (1P) :** Ce sont les réserves les plus certaines, avec un degré élevé de confiance quant à leur existence et à leur récupérabilité. Elles sont basées sur des tests de puits, des données géologiques et un historique de production établi.
- **Réserves probables (2P) :** Cette catégorie comprend les réserves qui sont considérées comme susceptibles d'être récupérées, mais avec un degré de certitude légèrement inférieur à celui des réserves prouvées. Ces estimations reposent sur des preuves géologiques similaires à celles des réserves prouvées, mais peuvent nécessiter des explorations ou des développements supplémentaires pour confirmer leur plein potentiel.
- **Réserves possibles (3P) :** Les réserves possibles représentent les ressources qui sont considérées comme potentiellement récupérables, mais avec une certitude nettement inférieure à celle des réserves prouvées ou probables. Leur récupération est conditionnelle à des conditions géologiques favorables et à des efforts d'exploration réussis.
**La puissance de 2P :**
Les réserves 2P combinent à la fois les réserves prouvées et probables, offrant une vision plus complète de la base de ressources potentielle d'une entreprise. C'est souvent ce que préfèrent les investisseurs et les analystes car cela prend en compte à la fois les ressources les plus certaines et les plus susceptibles d'être récupérées.
- **Confiance des investisseurs :** Les réserves 2P fournissent une estimation réaliste des ressources qu'une entreprise peut potentiellement extraire, renforçant la confiance des investisseurs. Cela leur permet d'évaluer le potentiel futur de l'entreprise et sa viabilité financière.
- **Planification stratégique :** Les réserves 2P sont essentielles pour les entreprises dans leurs décisions de planification stratégique et d'allocation des ressources. Elles peuvent guider les efforts d'exploration et de développement, en veillant à ce que les ressources soient dirigées vers les zones ayant le plus grand potentiel de récupération.
- **Réglementation gouvernementale :** Les réserves 2P sont souvent utilisées par les gouvernements pour fixer les redevances, les impôts et autres réglementations relatives à l'extraction du pétrole et du gaz.
**Considérations clés :**
- **Méthodes d'estimation des réserves :** Différentes entreprises emploient diverses méthodes pour estimer les réserves, ce qui peut entraîner des variations potentielles dans leurs chiffres 2P. Il est crucial d'analyser les méthodologies utilisées et de les comparer entre différentes entreprises.
- **Facteurs de risque :** Bien que les réserves 2P soient considérées comme plus fiables que les réserves possibles, elles ne sont pas garanties. Des facteurs externes, tels que les progrès technologiques, les fluctuations des prix du pétrole et les réglementations environnementales, peuvent avoir un impact significatif sur leur récupération réelle.
- **Évaluation continue :** Les estimations des réserves sont dynamiques et sujettes à changement en fonction des nouvelles découvertes géologiques, des progrès technologiques et des facteurs économiques. Les entreprises sont censées mettre à jour régulièrement leurs estimations des réserves pour refléter les dernières informations disponibles.
**Conclusion :**
Comprendre les réserves 2P est crucial pour tous ceux qui naviguent dans le secteur du pétrole et du gaz. Cela donne une image claire de la base de ressources potentielle d'une entreprise, aidant les investisseurs à prendre des décisions éclairées et les entreprises à élaborer des stratégies pour le développement futur. En tenant compte des nuances de la classification des réserves et en recherchant constamment des informations actualisées, vous pouvez naviguer en toute confiance dans les complexités du paysage pétrolier et gazier.
Test Your Knowledge
Quiz: Unveiling the Oil & Gas Mystery: Understanding 2P Reserves
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What does "2P" stand for in oil and gas reserves? a) Proven and Possible Reserves b) Probable and Possible Reserves c) Proved and Probable Reserves d) Potential and Probable Reserves
Answer
c) Proved and Probable Reserves
2. Which of the following is NOT a benefit of using 2P reserves for investors? a) Provides a realistic estimate of a company's potential resource base. b) Allows investors to assess a company's future potential and financial viability. c) Guarantees the actual recovery of the estimated resources. d) Helps investors make informed decisions.
Answer
c) Guarantees the actual recovery of the estimated resources.
3. Which category of reserves has the highest degree of certainty? a) Proved Reserves (1P) b) Probable Reserves (2P) c) Possible Reserves (3P) d) All categories have equal certainty.
Answer
a) Proved Reserves (1P)
4. What is a key consideration when analyzing 2P reserves? a) The company's marketing strategy. b) The company's financial history. c) The reserve estimation methods used. d) The company's social media presence.
Answer
c) The reserve estimation methods used.
5. Why are 2P reserves considered dynamic and subject to change? a) Fluctuating oil prices. b) Changes in government regulations. c) New geological discoveries and technological advancements. d) All of the above.
Answer
d) All of the above.
Exercise: Applying 2P Reserves
Scenario:
You are an investor considering investing in an oil and gas company. Two companies, Alpha Oil and Beta Gas, are presenting their reserve estimates:
- Alpha Oil: 1P Reserves: 100 million barrels, 2P Reserves: 150 million barrels
- Beta Gas: 1P Reserves: 80 million barrels, 2P Reserves: 120 million barrels
Task:
- Based on the provided information, which company appears to have a larger potential resource base?
- Explain your reasoning, considering the significance of 2P reserves.
Exercice Correction
1. Alpha Oil appears to have a larger potential resource base. 2. Although Beta Gas has a higher percentage increase from 1P to 2P reserves (50% compared to Alpha Oil's 50%), Alpha Oil has a larger overall 2P reserve estimate (150 million barrels vs. 120 million barrels). This indicates that Alpha Oil has a greater potential to recover more oil, making it a potentially more attractive investment.
Books
- Petroleum Resources Management System (PRMS): This book published by the Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE) outlines the comprehensive methodology for classifying and evaluating oil and gas reserves, including the 2P category. https://www.spe.org/en/bookstore/products/petroleum-resources-management-system-prms
- Oil and Gas Reserves: A Comprehensive Guide to Resource Evaluation and Management: This book by S. M. Ali provides a detailed explanation of different reserve classification systems, including 2P, and the factors that influence their estimation. https://www.amazon.com/Oil-Gas-Reserves-Comprehensive-Management/dp/1466594062
Articles
- "Understanding Oil and Gas Reserve Classifications: 1P, 2P, and 3P" by Investopedia: Provides a concise overview of the different reserve classifications, focusing on the significance of 2P reserves for investors. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/o/oil-and-gas-reserves.asp
- "What are 2P reserves?" by Energy Voice: Explains the concept of 2P reserves in a clear and accessible manner, highlighting their importance in assessing company performance and investment potential. https://www.energyvoice.com/oilandgas/162605/what-are-2p-reserves/
Online Resources
- Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE): SPE is a leading professional organization in the oil and gas industry. Their website offers a wealth of resources, including technical papers, webinars, and guidelines related to reserve estimation and classification. https://www.spe.org/
- World Petroleum Council: The World Petroleum Council is another important organization in the industry, providing information on global oil and gas trends, including reserve data and regulatory frameworks. https://www.worldpetroleum.org/
Search Tips
- Use specific keywords: Instead of just "2P reserves," try phrases like "2P reserves meaning," "2P reserves vs 1P," or "how to estimate 2P reserves."
- Include relevant industry terms: Combine "2P reserves" with terms like "oil & gas," "petroleum," or "exploration and production" to narrow down your search.
- Use advanced search operators: Utilize operators like quotation marks (" ") to find exact phrases, or a minus sign (-) to exclude irrelevant results.
Techniques
Chapter 1: Techniques for Estimating 2P Reserves
This chapter explores the various methods employed by oil and gas companies to estimate 2P reserves, highlighting their strengths and limitations.
1.1 Volumetric Methods
- Description: These methods rely on geological data, including reservoir size, porosity, and hydrocarbon saturation, to calculate the total volume of hydrocarbons in place. This volume is then adjusted based on recovery factors, which account for the percentage of oil and gas that can be extracted economically.
- Strengths: Simple and widely used, particularly in early exploration stages when limited production data is available.
- Limitations: Relies heavily on geological assumptions and can be inaccurate if the reservoir's characteristics are not well understood.
1.2 Analogue Methods
- Description: These methods use data from similar reservoirs with known production histories to estimate the potential of the target reservoir. This approach leverages past experience and geological correlations.
- Strengths: Useful when limited well data is available, particularly in early development phases.
- Limitations: Relies on the accuracy of the analogue reservoir data and the assumption that the target reservoir behaves similarly.
1.3 Production Decline Curve Analysis
- Description: This method uses past production data to project future production rates. It assumes that production will decline at a predictable rate, allowing for estimation of remaining recoverable reserves.
- Strengths: Based on real production data, offering a more accurate picture of potential reserves than volumetric or analogue methods.
- Limitations: Relies on the assumption that production will follow a predictable pattern, which may not always hold true.
1.4 Material Balance Methods
- Description: These methods analyze the production history and reservoir pressure data to estimate the remaining hydrocarbons. This approach considers the physical properties of the reservoir and the movement of fluids.
- Strengths: Provides a more sophisticated and accurate estimate of reserves by accounting for reservoir fluid dynamics.
- Limitations: Requires detailed data and can be complex to implement, often applied later in the development stage.
1.5 Reservoir Simulation
- Description: This advanced technique uses computer models to simulate the behavior of the reservoir over time. It integrates geological, engineering, and production data to create a detailed representation of the reservoir.
- Strengths: Provides the most comprehensive and accurate estimate of reserves, taking into account various factors impacting production.
- Limitations: Requires significant data collection and analysis, making it costly and time-consuming.
1.6 Choosing the Right Technique
The choice of estimation technique depends on the availability of data, the stage of development, and the specific characteristics of the reservoir. Combining different methods often provides a more robust and reliable estimate of 2P reserves.
Chapter 2: Models for 2P Reserves Estimation
This chapter explores the various models used by oil and gas companies to calculate 2P reserves.
2.1 Deterministic Models
- Description: These models use a single set of assumptions to estimate reserves, leading to a single point estimate.
- Strengths: Relatively simple and straightforward to implement, often used for initial estimates.
- Limitations: Do not account for uncertainties in the input data and may not reflect the true range of possible outcomes.
2.2 Probabilistic Models
- Description: These models incorporate uncertainties in the input data by using probability distributions for key parameters. They provide a range of possible reserve estimates, along with their likelihoods.
- Strengths: Provide a more comprehensive and realistic picture of the uncertainty surrounding reserve estimates.
- Limitations: More complex to implement and require significant data analysis.
2.3 Monte Carlo Simulation
- Description: A specific type of probabilistic model that uses random sampling to generate multiple possible outcomes for reserves. This method provides a distribution of possible values, allowing for the calculation of key statistics like mean, median, and percentiles.
- Strengths: Most commonly used for estimating reserves as it provides a robust and comprehensive assessment of uncertainty.
- Limitations: Requires significant computing power and expertise to implement effectively.
2.4 Choosing the Right Model
The choice of model depends on the level of uncertainty in the input data, the desired level of detail, and the company's resources and expertise. Simple deterministic models may suffice for initial estimates, while probabilistic models are preferred when greater accuracy and uncertainty assessment are needed.
Chapter 3: Software for 2P Reserves Estimation
This chapter provides an overview of the software tools available for estimating 2P reserves, highlighting their features and functionalities.
3.1 Petrel
- Description: A comprehensive software package for reservoir characterization and modeling, offering advanced features for 2P reserves estimation.
- Features: Volumetric and analogue methods, production decline curve analysis, reservoir simulation.
- Strengths: Industry-standard software with powerful capabilities for complex reservoir modeling.
- Limitations: Expensive and requires significant technical expertise to use effectively.
3.2 Eclipse
- Description: A powerful reservoir simulator for simulating the flow of oil and gas in complex reservoirs. It enables companies to optimize production and estimate reserves.
- Features: Reservoir simulation, history matching, production forecasting.
- Strengths: Highly accurate and reliable, used by many major oil and gas companies.
- Limitations: Complex and computationally demanding, requiring experienced engineers to operate.
3.3 EasyRes
- Description: A user-friendly software package specifically designed for reserve estimation. It offers various methods, including volumetric, analogue, and decline curve analysis.
- Features: Simple interface, easy to learn and use, suitable for small and medium-sized companies.
- Strengths: Cost-effective and accessible, providing a good starting point for reserve estimation.
- Limitations: Limited in its capabilities compared to advanced software packages.
3.4 Other Tools
Numerous other software tools are available for 2P reserves estimation, including:
- Geologic Modeling Software: For building geological models of reservoirs.
- Production Data Analysis Software: For analyzing production data and projecting future production.
- Statistical Software: For performing probabilistic analyses and Monte Carlo simulations.
Chapter 4: Best Practices for Estimating 2P Reserves
This chapter outlines best practices for estimating 2P reserves, ensuring accuracy, reliability, and transparency.
4.1 Data Quality and Integrity
- Focus on: Ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of all data used for reserve estimation.
- Actions: Conduct thorough data audits, validate sources, and implement quality control measures.
4.2 Methodology Selection and Application
- Focus on: Choosing appropriate estimation techniques and models based on the specific characteristics of the reservoir and the stage of development.
- Actions: Clearly document the methodology used, including any assumptions made.
4.3 Uncertainty Analysis
- Focus on: Quantifying the uncertainty associated with reserve estimates, taking into account variations in input data, geological assumptions, and future events.
- Actions: Perform probabilistic analyses, sensitivity analyses, and Monte Carlo simulations.
4.4 Independent Verification
- Focus on: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of reserve estimates by obtaining independent verification from qualified third parties.
- Actions: Engage independent reserve auditors, consultants, or experts to review and validate estimates.
4.5 Transparency and Disclosure
- Focus on: Communicating reserve estimates clearly and transparently to stakeholders, including investors, regulators, and the public.
- Actions: Prepare comprehensive reserve reports, disclose key assumptions and limitations, and adhere to industry standards for reporting.
4.6 Continuous Monitoring and Updating
- Focus on: Regularly monitoring and updating reserve estimates based on new data, technological advancements, and changes in market conditions.
- Actions: Conduct periodic reserve reviews, re-evaluate assumptions, and revise estimates as needed.
Chapter 5: Case Studies in 2P Reserves Estimation
This chapter presents case studies from the oil and gas industry, demonstrating the application of various techniques and models for estimating 2P reserves.
5.1 Case Study 1: Unconventional Shale Reservoir
- Objective: Estimate 2P reserves in a large shale gas play using probabilistic methods and Monte Carlo simulations.
- Methodology: A combination of volumetric and analogue methods, incorporating uncertainties in geological parameters, well performance, and gas prices.
- Outcome: A range of possible reserve estimates, providing a comprehensive assessment of the play's potential.
5.2 Case Study 2: Offshore Oil Field
- Objective: Estimate 2P reserves in a mature offshore oil field using production decline curve analysis and reservoir simulation.
- Methodology: Analyzing historical production data, calibrating reservoir models, and simulating future production under different scenarios.
- Outcome: A detailed estimate of remaining reserves, along with projections for future production.
5.3 Case Study 3: Tight Oil Play
- Objective: Estimate 2P reserves in a newly discovered tight oil play using deterministic methods and production forecasts.
- Methodology: Applying volumetric techniques, adjusting for recovery factors, and projecting production based on similar plays.
- Outcome: Initial estimates of reserves, providing a basis for further development planning.
5.4 Lessons Learned
Case studies illustrate the diversity of approaches to estimating 2P reserves, highlighting the importance of selecting appropriate techniques based on specific reservoir characteristics and data availability. They also emphasize the need for transparency, uncertainty analysis, and continuous monitoring in reserve estimation.
- Probable Reserves (2P) Débloquer le Potentiel : Les …
- Reserves, 1P Comprendre les Réserves : Déb…
- Reserves, 3P Réserves : Guide pour compren…
- Reserves, Behind Pipe Derrière le Tubage : Débloque…
- Reserves, Developed Comprendre les "Réserves Déve…
- Reserves, Entitlement Comprendre les réserves et le…
- Reserves, Extension Extension des réserves : élar…
- Reserves, Non Producing Comprendre les "Réserves non …
- Reserves, Possible Libérer le potentiel : Compre…
- Reserves, Probable Comprendre les réserves proba…
- Reserves, Producing Débloquer le Potentiel : Comp…
- Reserves, Proved Comprendre les Réserves Prouv…
- Reserves, Proved Developed Démythifier les réserves de p…
- Reserves, Unproved Débloquer le potentiel : Comp…
- Reserves, Recoverable Comprendre les réserves et le…
- Reserves, Undeveloped Potentiel inexploité : Compre…
- Demande de justification des dépenses Naviguer dans la de… Planification et ordonnancement du projet
- Coût budgété du travail planifié Comprendre le Coût … Estimation et contrôle des coûts
- Les limites de batterie Comprendre les limi… Termes techniques généraux
- Outil DV Outil DV : Un éléme… Forage et complétion de puits
- SOMMAIRE TOC : Comprendre le… Termes techniques généraux
Comments