Astronomie stellaire
Cynosura
L'étoile Polaire : Cynosure et Polaris
Dans la vaste tapisserie du ciel nocturne, certains corps célestes revêtent une importance particulière, servant de balises pour les navigateurs d'antan comme pour les astronomes modernes. L'un de ces repères célestes est Cynosure, un nom chargé d'histoire et de mythologie, souvent utilisé pour désigner l'étoile polaire – Polaris.
L'Origine Mythique de Cynosure :
Le terme "Cynosure" lui-même trouve ses origines dans la mythologie grecque. Il fait référence à un groupe de nymphes, les "Cynosurae", qui étaient les compagnes de la déesse Artémis, déesse de la chasse. Selon la légende, ces nymphes furent transformées en étoiles après avoir accidentellement tué un chien appartenant à Zeus.
Bien que la constellation associée à Cynosure fasse l'objet de discussions, il est généralement admis qu'elle représente la Petite Ourse, la Petite Casserole, qui contient Polaris.
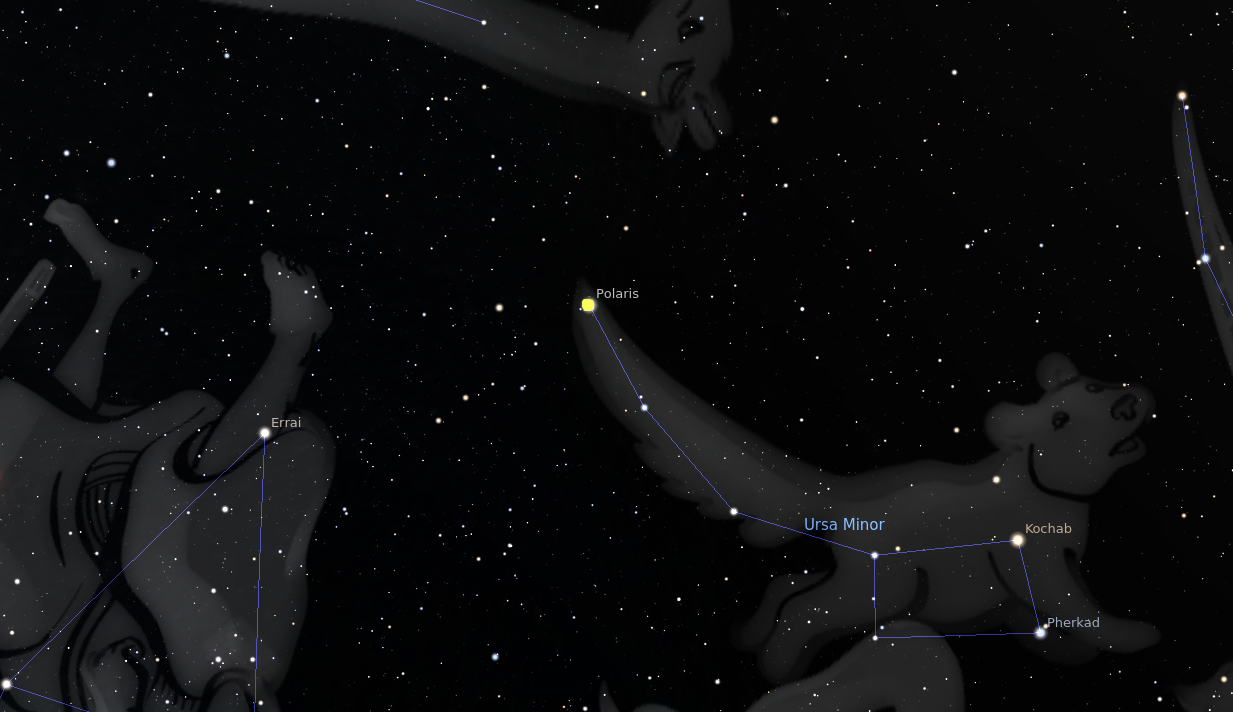
Polaris : L'Étoile Polaire :
Polaris, l'étoile du Nord, a été un outil essentiel pour la navigation depuis les temps anciens. Située près du pôle nord céleste, elle apparaît presque immobile dans le ciel nocturne tandis que les autres étoiles tournent autour d'elle. Cette propriété unique a fait de Polaris un point de référence précieux pour les marins et les voyageurs.
L'Importance de Cynosure :
Le nom "Cynosure" appliqué à Polaris reflète son importance en tant qu'étoile guide. Tout comme les nymphes du même nom guidaient les voyageurs sur terre, l'étoile du Nord a guidé les explorateurs à travers les océans et à travers le globe. Sa position immuable dans le ciel a fourni un point de référence fixe, permettant une navigation et une cartographie précises.
Applications Modernes :
Bien que la navigation moderne s'appuie fortement sur la technologie, le concept d'"étoile guide" reste pertinent. Polaris, et son association avec Cynosure, continuent de symboliser la recherche de direction et de but. Au-delà de son utilisation en navigation, l'étoile du Nord sert de rappel du pouvoir durable des corps célestes à guider et à inspirer l'humanité.
Conclusion :
Cynosure, un nom chargé de mythes et d'histoire, reflète le rôle puissant que Polaris a joué dans la guidée de l'humanité. Si sa signification littérale peut faire l'objet de débats, son association avec l'étoile du Nord symbolise un phare constant, nous rappelant le pouvoir durable des étoiles à nous guider et à nous inspirer à travers la vaste étendue du ciel nocturne.
Test Your Knowledge
Quiz: The Guiding Star
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What is the mythical origin of the term "Cynosura"? a) A group of nymphs transformed into stars after accidentally killing Zeus' hound. b) A constellation representing a mythical dog guarding the North Star. c) A celestial body that guided ancient Greek sailors. d) A star associated with the god of the sea, Poseidon.
Answer
a) A group of nymphs transformed into stars after accidentally killing Zeus' hound.
2. Which constellation is generally believed to be associated with Cynosura? a) Ursa Major (the Big Dipper) b) Orion c) Ursa Minor (the Little Dipper) d) Cassiopeia
Answer
c) Ursa Minor (the Little Dipper)
3. What is the most important characteristic of Polaris that makes it a valuable navigational tool? a) Its brightness b) Its proximity to the sun c) Its near-stationary position in the night sky d) Its constellation pattern
Answer
c) Its near-stationary position in the night sky
4. Why is Cynosura considered a "guiding star"? a) It marks the beginning of the celestial equator. b) It helps identify the location of the Milky Way galaxy. c) It serves as a reference point for navigation, similar to how the nymphs guided travelers. d) It is the brightest star in the night sky.
Answer
c) It serves as a reference point for navigation, similar to how the nymphs guided travelers.
5. What is the modern-day relevance of the concept of "guiding star"? a) It symbolizes the pursuit of direction and purpose. b) It indicates the precise location of other celestial bodies. c) It helps predict weather patterns. d) It serves as a source of inspiration for astronomers.
Answer
a) It symbolizes the pursuit of direction and purpose.
Exercise: Finding the North Star
Instructions:
- Go outside on a clear night.
- Locate the Big Dipper constellation (Ursa Major). It resembles a dipper with a handle.
- Imagine a line drawn through the two stars that form the "end" of the dipper's bowl.
- Follow that line upwards, about five times the distance between the two stars.
- The star you find at the end of this imaginary line is Polaris, the North Star.
Note: If you are in the Northern Hemisphere, Polaris will always be in the north.
Exercise Correction:
Exercice Correction
You should have successfully located Polaris, the North Star, using the Big Dipper as a guide. This method works because Polaris is very close to the celestial north pole. This means that as the Earth rotates, all other stars appear to rotate around Polaris, while it remains relatively stationary. Congratulations on finding your way with the stars!
Books
- "The Stargazer's Guide to the Night Sky" by Michael Covington: This book provides a comprehensive guide to the night sky and covers constellations, including Ursa Minor and Polaris.
- "The Mythology of the Night Sky" by E.C. Krupp: This book delves into the mythological stories surrounding constellations, including the Cynosurae.
- "The Oxford Companion to World Mythology" by Michael Mallory: This reference book explores the myths and legends from various cultures, including the Greek myth of the Cynosurae.
Articles
- "The North Star: A History of Polaris" by Bradley Schaefer: This article delves into the history of the North Star and its significance in navigation.
- "The Cynosurae and the Myth of the North Star" by David M. Evans: This article discusses the origins of the term "Cynosura" and its connection to Ursa Minor.
- "Polaris: The Guiding Star of the North" by Joe Rao: This article explores the properties of Polaris and its importance in navigation.
Online Resources
- The International Astronomical Union (IAU) website: This website provides information about the constellations, including Ursa Minor and Polaris.
- NASA's website: This website contains resources on astronomy and space exploration, including information about the North Star.
- The University of Texas McDonald Observatory website: This website offers a variety of resources for learning about astronomy, including information about the constellations.
Search Tips
- Use specific keywords: When searching for information on Cynosura, try searching for "Cynosura Polaris," "Cynosura myth," or "Cynosura navigation."
- Use quotation marks: Enclosing your keywords in quotation marks will ensure that Google searches for the exact phrase, increasing the accuracy of your search results.
- Use advanced search operators: Use operators like "+" to include specific keywords, "-" to exclude keywords, or "site:" to search within a specific website.
Techniques
The Guiding Star: Cynosura - A Deeper Dive
This expanded exploration of Cynosura and its association with Polaris delves into specific aspects, presented in separate chapters. Remember that "Cynosura" in this context refers primarily to its metaphorical use as a guiding principle, drawing parallels from Polaris's navigational role.
Chapter 1: Techniques for Identifying and Utilizing Cynosura (Polaris)
This chapter explores the practical methods used to locate and utilize Polaris for navigation and orientation.
1.1 Celestial Navigation: Detailed explanation of traditional celestial navigation techniques, emphasizing Polaris's role. This includes discussions of:
- Using a sextant: How to measure Polaris's altitude to determine latitude.
- Identifying surrounding constellations: Techniques for locating Polaris using nearby constellations like Ursa Major (the Big Dipper).
- Accounting for atmospheric refraction: Understanding and correcting for the bending of light as it passes through the atmosphere.
- Charting a course: Using Polaris's position to plot a course and track progress.
1.2 Modern Methods: While less reliant on Polaris, modern navigation still benefits from understanding fundamental principles.
- GPS and Polaris: How GPS systems can be cross-referenced with visual observation of Polaris for increased accuracy and redundancy.
- Smartphone apps: Review of smartphone apps that utilize augmented reality to aid in locating and identifying Polaris.
- Star charts and planispheres: Using these tools to find Polaris and understand its movement in the sky throughout the year.
Chapter 2: Models for Understanding Cynosura's Significance
This chapter looks at different frameworks for interpreting the symbolic meaning of Cynosura, going beyond its literal astronomical meaning.
2.1 Mythological Models: Analyzing the Greek myth of the Cynosurae nymphs and its connection to guidance and protection. Exploring interpretations of the myth's symbolic meaning.
2.2 Psychological Models: How the concept of a "guiding star" relates to psychological concepts of purpose, direction, and aspiration. Exploring the psychological impact of having a clear goal and pursuing it.
2.3 Societal Models: Examining how the concept of Cynosura has been used throughout history as a metaphor for leadership, inspiration, and societal progress.
Chapter 3: Software and Tools for Observing and Studying Cynosura (Polaris)
This chapter explores software and tools that aid in observing Polaris and understanding its celestial position.
3.1 Planetarium Software: Review of popular planetarium software (Stellarium, Celestia, etc.), highlighting their capabilities in simulating the night sky and locating Polaris. Instructions on utilizing these programs to track Polaris’ movement.
3.2 Astronomical Databases: Discussion of online databases providing precise positional data of Polaris and other celestial objects.
3.3 Navigation Apps: Analysis of smartphone and other device apps designed to aid in navigation, particularly those utilizing celestial data.
Chapter 4: Best Practices for Using Cynosura as a Guiding Principle
This chapter moves beyond the astronomical and explores the practical application of the "guiding star" metaphor.
4.1 Setting Clear Goals: Strategies for defining personal or professional goals, drawing parallels to the unwavering nature of Polaris.
4.2 Maintaining Focus and Persistence: Techniques for staying on track towards objectives, inspired by the steadfast presence of Polaris.
4.3 Adapting to Challenges: How to navigate obstacles and setbacks, similar to how navigators adjusted their courses based on weather and other variables.
4.4 Seeking Guidance and Support: The importance of mentorship and collaboration in achieving goals, reflecting the community aspect of navigation in the past.
Chapter 5: Case Studies: Cynosura in History and Modern Life
This chapter presents examples of how the concept of Cynosura has manifested throughout history and in contemporary society.
5.1 Historical Navigation: Case studies detailing how Polaris was used in historical navigation, highlighting specific voyages and explorations.
5.2 Modern Applications of Guiding Principles: Examples of individuals or organizations that have utilized the "guiding star" principle to achieve remarkable results in various fields, from science and business to the arts and social activism. These could include stories of inspirational figures who had a clear vision and pursued it relentlessly.
5.3 The Symbolic Power of Polaris: Discussions of its cultural significance across different civilizations, emphasizing how the North Star has served as a powerful symbol of hope, direction, and aspiration.
This expanded structure provides a more comprehensive and detailed look at Cynosura, considering its astronomical reality and its rich metaphorical meaning. Remember to replace the placeholder image with the actual image.
Comments