Reservoir Engineering
Oil Column
Understanding the Oil Column: A Key Concept in Oil & Gas Exploration
In the world of oil and gas exploration, the "oil column" represents a crucial concept that directly influences the viability of a potential reservoir. Simply put, the oil column refers to the vertical thickness of an oil accumulation above an oil/water contact (OWC). This means it's the height of the oil layer within a porous rock formation, starting from the top of the oil saturation and extending down to the point where oil transitions into water.
Why is the oil column significant?
- Reservoir potential: The height of the oil column is directly related to the amount of oil potentially recoverable from the reservoir. A larger oil column signifies a greater oil volume, making it more economically feasible to exploit.
- Pressure estimation: The oil column's height influences the pressure within the reservoir. This pressure plays a critical role in driving oil flow to production wells.
- Reservoir characterization: Analyzing the oil column helps geologists and engineers understand the reservoir's structure, connectivity, and overall potential. This information is vital for optimizing production strategies.
Factors influencing the oil column:
- Geological structure: The shape and size of the reservoir trap significantly influence the oil column's height.
- Porosity and permeability: The ability of the reservoir rock to hold and transmit fluids directly impacts the oil column's thickness.
- Fluid properties: The density and viscosity of the oil and water determine the OWC position, ultimately impacting the oil column.
How is the oil column determined?
- Seismic surveys: Seismic data can be used to identify the structural boundaries of the reservoir and approximate the oil column's height.
- Well logs: Logs from exploratory wells provide detailed information about the rock formations, fluid types, and the OWC, offering accurate measurements of the oil column.
- Reservoir modeling: Complex software simulations integrate various data sources to generate a comprehensive reservoir model, including a precise representation of the oil column.
Conclusion:
The oil column is a fundamental concept in oil and gas exploration. Understanding its significance and the factors influencing it is crucial for assessing the potential of a reservoir. By accurately determining the oil column's height, geologists and engineers can optimize production strategies and unlock the full potential of oil and gas reserves.
Test Your Knowledge
Quiz: Understanding the Oil Column
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What does the "oil column" refer to in oil and gas exploration?
a) The total volume of oil in a reservoir. b) The vertical thickness of oil above the oil/water contact (OWC). c) The horizontal distance between the oil reservoir and the production well. d) The pressure gradient within the oil reservoir.
Answer
The correct answer is **b) The vertical thickness of oil above the oil/water contact (OWC).**
2. Why is the height of the oil column significant?
a) It helps determine the type of drilling equipment needed. b) It indicates the age of the reservoir formation. c) It influences the amount of recoverable oil and the pressure within the reservoir. d) It defines the geographic location of the oil reservoir.
Answer
The correct answer is **c) It influences the amount of recoverable oil and the pressure within the reservoir.**
3. Which of the following factors DOES NOT directly influence the oil column's height?
a) The shape of the reservoir trap. b) The density of the surrounding rock. c) The porosity and permeability of the reservoir rock. d) The viscosity of the oil and water.
Answer
The correct answer is **b) The density of the surrounding rock.**
4. How is the oil column typically determined?
a) Using geological maps and satellite imagery. b) By analyzing the chemical composition of oil samples. c) Through seismic surveys, well logs, and reservoir modeling. d) By measuring the pressure fluctuations within the reservoir.
Answer
The correct answer is **c) Through seismic surveys, well logs, and reservoir modeling.**
5. A larger oil column generally indicates:
a) A higher risk of oil spills. b) A lower potential for oil recovery. c) A more challenging drilling operation. d) A greater amount of potentially recoverable oil.
Answer
The correct answer is **d) A greater amount of potentially recoverable oil.**
Exercise: Oil Column Estimation
Scenario: You are an oil and gas exploration geologist studying a potential reservoir. You have gathered the following data:
- Seismic survey: Indicates a reservoir trap with a vertical thickness of 100 meters.
- Well log: Shows the oil/water contact (OWC) at a depth of 2,500 meters.
- Reservoir modeling: Predicts oil saturation extends from the OWC to a depth of 2,400 meters.
Task: Calculate the estimated height of the oil column in this potential reservoir.
Exercise Correction
The oil column height is the vertical distance between the top of the oil saturation and the OWC. * Oil saturation starts at 2,400 meters depth. * OWC is at 2,500 meters depth. Therefore, the estimated oil column height is 2,500 meters - 2,400 meters = **100 meters.**
Books
- Petroleum Geology: by K.A. Kvenvolden (Covers the fundamentals of oil and gas exploration, including reservoir characterization and oil column analysis)
- Reservoir Engineering Handbook: by Tarek Ahmed (Explains reservoir fluid properties, pressure behavior, and production optimization, all relevant to understanding oil column dynamics)
- Applied Petroleum Reservoir Engineering: by John Lee (A comprehensive guide to reservoir engineering principles, including techniques for estimating oil column size and pressure)
Articles
- "The Importance of the Oil Column in Reservoir Characterization" by [Author Name], published in [Journal Name] (This article can be found through online databases like Google Scholar or ScienceDirect)
- "Seismic Interpretation for Reservoir Characterization and Oil Column Estimation" by [Author Name], published in [Journal Name] (This article focuses on using seismic data to understand oil column dimensions)
- "Reservoir Modeling and Simulation for Oil Column Analysis" by [Author Name], published in [Journal Name] (This article covers how reservoir models can help estimate oil column size and predict production performance)
Online Resources
- SPE (Society of Petroleum Engineers): www.spe.org (This website offers access to technical papers, presentations, and other resources related to oil and gas exploration, reservoir engineering, and oil column analysis)
- OnePetro (SPE's digital library): onepetro.org (This online library provides access to a vast collection of technical articles, books, and other publications relevant to the oil and gas industry)
- Energy Information Administration (EIA): www.eia.gov (This government website offers data and information on oil and gas production, reserves, and related topics)
Search Tips
- Use specific keywords: "oil column," "reservoir characterization," "seismic interpretation," "reservoir simulation," "oil/water contact"
- Include relevant location information: "oil column Gulf of Mexico," "oil column North Sea"
- Specify publication type: "oil column PDF" or "oil column journal article"
- Use advanced operators: "oil column site:.edu" to restrict results to educational institutions
Techniques
Understanding the Oil Column: A Deeper Dive
Here's a breakdown of the oil column concept, separated into chapters:
Chapter 1: Techniques for Determining Oil Column Height
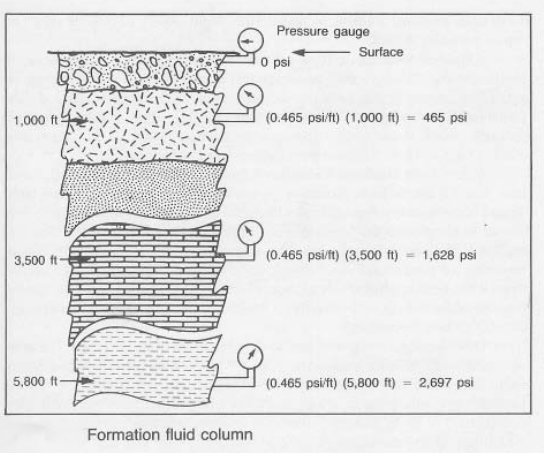
This chapter focuses on the practical methods used to determine the height of the oil column in a reservoir. Accurate measurement is crucial for reservoir characterization and production planning.
Seismic Surveys: Seismic reflection surveys provide a large-scale image of subsurface structures. By analyzing seismic data, geologists can identify potential hydrocarbon traps, estimate the extent of the reservoir, and infer the approximate height of the oil column. While not providing direct measurement, seismic data offers valuable context and helps to target drilling locations. Specific techniques include:
- Pre-stack depth migration: Provides a more accurate image of the subsurface, improving the resolution of the oil column estimation.
- AVO analysis (Amplitude Versus Offset): Helps to distinguish between different rock types and fluids, aiding in identification of hydrocarbon-bearing zones.
Well Logging: Well logs are arguably the most direct method for determining oil column height. Measurements taken while drilling provide detailed information about the properties of the formations penetrated. Key well logs include:
- Gamma ray logs: Identify shale content and help delineate reservoir boundaries.
- Resistivity logs: Measure the electrical conductivity of the formations, indicating the presence of hydrocarbons (high resistivity).
- Neutron porosity logs: Measure the porosity of the rock, which influences the amount of fluid it can hold.
- Density logs: Provide information on bulk density, helping to differentiate between oil and water.
- Pressure measurements: Directly measure reservoir pressure which is directly related to the height of the fluid column.
Formation Testing: Formation testers extract small samples of reservoir fluids, providing direct confirmation of hydrocarbon presence and composition. These tests help validate interpretations from well logs and seismic data.
Production Logging: After a well is producing, production logging tools can provide information on fluid flow patterns and help refine the understanding of oil column geometry and reservoir connectivity.
Chapter 2: Models for Oil Column Simulation and Prediction
This chapter explores the various models employed to simulate and predict oil column behavior. These models range from simple to highly complex, depending on the available data and the required level of accuracy.
Geological Models: These models integrate geological data (seismic, well logs, cores) to create a 3D representation of the reservoir. They are the foundation for reservoir simulation.
Reservoir Simulation Models: These complex numerical models simulate fluid flow within the reservoir under various conditions. They are used to predict the behavior of the oil column under different production scenarios. Factors considered include:
- Fluid properties (oil, water, gas): Density, viscosity, compressibility.
- Rock properties: Porosity, permeability, capillary pressure.
- Boundary conditions: Reservoir geometry, fault systems.
Statistical Models: Simple statistical models can be used to correlate oil column height with other reservoir parameters (e.g., trap size, porosity). These are typically used in early exploration stages when data is limited.
Geostatistical Modeling: Techniques such as kriging are used to interpolate data points and create a spatially continuous model of reservoir properties, including oil column height. This is crucial when data is sparse.
Chapter 3: Software for Oil Column Analysis
This chapter reviews the software commonly used for oil column analysis, ranging from simple visualization tools to sophisticated reservoir simulators.
Seismic Interpretation Software: (e.g., Petrel, Kingdom, SeisSpace) Used for interpreting seismic data, mapping reservoir boundaries, and estimating oil column height.
Well Log Analysis Software: (e.g., Techlog, Interactive Petrophysics) Used to analyze well log data, determine reservoir properties, and identify the oil/water contact.
Reservoir Simulation Software: (e.g., Eclipse, CMG, Schlumberger's INTERSECT) Used to build complex reservoir models and simulate fluid flow, predicting oil column behavior under various production scenarios.
Geostatistical Software: (e.g., GSLIB, Leapfrog Geo) Used for spatial analysis and creation of 3D models of reservoir properties.
Data Management Software: (e.g., Petrel, OpenWorks) Used to integrate and manage large datasets from different sources (seismic, well logs, core data).
Chapter 4: Best Practices in Oil Column Determination and Analysis
This chapter focuses on the best practices to ensure accuracy and reliability in oil column determination.
Data Quality Control: Ensuring the quality and consistency of all input data (seismic, well logs, core data) is paramount.
Integrated Workflow: Utilizing an integrated workflow that combines data from different sources (seismic, wells, geological data) provides the most robust estimate of the oil column.
Uncertainty Analysis: Accounting for uncertainties associated with data and models is crucial. Monte Carlo simulations and other probabilistic methods help quantify the uncertainty in oil column estimations.
Validation: Comparing model predictions with actual production data helps to validate the model's accuracy and reliability.
Collaboration: Effective collaboration between geologists, geophysicists, and reservoir engineers is essential for accurate and efficient oil column analysis.
Chapter 5: Case Studies of Oil Column Analysis and Interpretation
This chapter presents real-world examples of oil column analysis, highlighting the challenges and successes in different geological settings. Each case study would include:
- Geological setting: Description of the reservoir and its geological context.
- Data used: Details of the data acquired and utilized (seismic, wells, core data).
- Methodology: The techniques and software used for oil column analysis.
- Results: Presentation of the oil column estimation and its impact on reservoir development planning.
- Challenges encountered: Discussion of any difficulties encountered during the analysis process.
This expanded structure provides a more comprehensive and organized overview of the oil column concept and its importance in oil and gas exploration. Remember to replace the placeholder image with your actual image.
- Balance Point (coiled tubing or snubbing) Understanding the Balance Poi…
- Bending Cycle (coiled tubing) The Bending Cycle: Understand…
- coiled tubing Coiled Tubing: The Flexible B…
- Coiled Tubing Coiled Tubing: A Versatile To…
- Coiled Tubing Completion Coiled Tubing Completion: A V…
- Coiled Tubing Connector Connecting the Pipeline: Unde…
- Coiled Tubing Drilling Coiled Tubing Drilling: A Fle…
- Coiled Tubing Injector Head The Coiled Tubing Injector He…
- coiled-tubing unit Coiled Tubing Units: The Vers…
- Coiled Tubing Unit Coiled Tubing: A Versatile To…
- coiled-tubing workover Coiled Tubing Workover: A Ver…
- Collett Connector (coiled tubing) Collett Connector: A Secure C…
- Barrels of Oil Equivalent, BOE Unpacking the Barrel: Underst…
- Black Oil Black Gold: Understanding "Bl…
- Boiling Point Boiling Point: The Temperatur…
- Boiler Boilers: The Workhorses of th…
- Bunker C Oil Bunker C Oil: The Heavy Fuel …
- Clean Oil Clean Oil: A Pipeline Spec fo…
- Column Column: A Versatile Term in t…
- Boiler Plate Boilerplate in Oil & Gas: The…
- Application for Expenditure Justification Navigating the Appl… Project Planning & Scheduling
- Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled ("BCWS") Understanding Budge… Cost Estimation & Control
- Battery limit Understanding Batte… General Technical Terms
- DV Tool (cementing) DV Tool: A Crucial … Drilling & Well Completion
- TOC TOC: Understanding … General Technical Terms
Comments