Asset Integrity Management
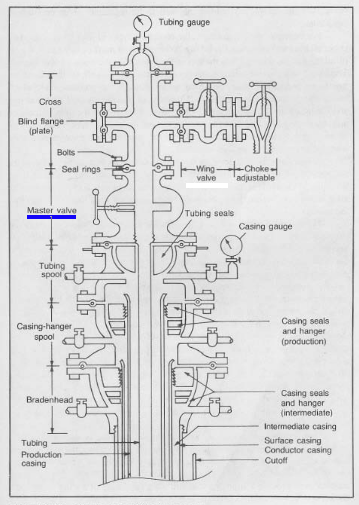
Master Valve
The Master Valve: The Guardian of Oil and Gas Wells
In the world of oil and gas production, safety and control are paramount. One critical component that plays a crucial role in ensuring both is the Master Valve. This valve, often referred to as the "Christmas Tree" due to its distinctive appearance, serves as the main shut-in valve for a well, acting as a gatekeeper for the flow of hydrocarbons.
Summary Descriptions of the Master Valve:
- Primary Control: The Master Valve is the first line of defense in case of a well blowout or other emergency. It allows operators to swiftly shut off the flow of oil or gas from the well, preventing further damage and potential accidents.
- Strategic Location: The Master Valve is typically positioned at the wellhead – the point where the wellbore meets the surface. This strategic placement ensures quick access and easy operation in emergency situations.
- Multi-Function: The Master Valve is not just a simple on/off switch. It incorporates a range of features, including:
- Choke Valve: Regulates the flow rate of hydrocarbons.
- Safety Valves: Automatic pressure relief valves that prevent overpressure in the well.
- Gauges: Monitor pressure and flow rates within the well.
- Sampling Ports: Enable the collection of samples for analysis.
The Importance of Master Valves:
- Safety: By isolating the well in emergencies, Master Valves minimize the risk of leaks, explosions, and environmental damage.
- Control: They enable precise regulation of production rates, optimizing well performance and minimizing waste.
- Accessibility: Their location at the wellhead ensures swift intervention and maintenance, crucial for efficient and safe operations.
Types of Master Valves:
- Manual Valves: Operated manually by a lever or wheel, they offer simplicity and direct control.
- Hydraulic Valves: Controlled remotely using hydraulic pressure, allowing for faster and safer operation in hazardous situations.
- Electric Valves: Powered by electricity, offering remote control capabilities and integration with automation systems.
Maintenance and Inspection:
- Regular Inspections: Master Valves require regular inspections to ensure functionality and prevent malfunction.
- Testing: Periodic testing is vital to confirm that the valve is operating correctly and can effectively shut off the well.
- Maintenance: Any issues identified during inspections or testing should be addressed promptly to prevent potential safety hazards.
The Master Valve, with its vital role in controlling and securing the flow of oil and gas, stands as a testament to the dedication to safety and efficiency within the industry. Its presence on every wellhead is a silent guardian, ensuring the well's operation remains controlled and safe, even in the face of unexpected challenges.
Test Your Knowledge
Quiz: The Master Valve
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What is the primary function of the Master Valve?
a) To regulate the flow of oil and gas to a refinery. b) To act as the main shut-in valve for a well. c) To monitor pressure and flow rates within a well. d) To collect samples for analysis.
Answer
b) To act as the main shut-in valve for a well.
2. Why is the Master Valve often called the "Christmas Tree"?
a) It is decorated for the holidays. b) It is typically painted green. c) It has a distinctive appearance with multiple valves and pipes. d) It is used to extract natural gas.
Answer
c) It has a distinctive appearance with multiple valves and pipes.
3. What type of valve is used to regulate the flow rate of hydrocarbons?
a) Choke valve b) Safety valve c) Gauge d) Sampling port
Answer
a) Choke valve
4. Which type of Master Valve offers remote control capabilities?
a) Manual valve b) Hydraulic valve c) Electric valve d) All of the above
Answer
d) All of the above
5. Why is regular inspection and maintenance of Master Valves essential?
a) To ensure the valve is aesthetically pleasing. b) To comply with industry regulations. c) To prevent malfunction and ensure safety. d) To increase production efficiency.
Answer
c) To prevent malfunction and ensure safety.
Exercise: Master Valve Scenario
Scenario: Imagine you are working on an oil rig and a sudden increase in pressure is detected at the wellhead.
Task: Describe the steps you would take to address this situation, focusing on the role of the Master Valve.
Your answer should include:
- Identifying the potential danger posed by the pressure increase.
- Describing the immediate action you would take with the Master Valve.
- Mentioning other safety procedures you might follow.
Exercise Correction
Here's a possible solution:
Identify the Danger: A sudden pressure increase indicates a potential well blowout, which can result in uncontrolled release of oil and gas, leading to explosions, fires, and environmental damage.
Master Valve Action: Immediately activate the Master Valve to shut in the well, stopping the flow of oil and gas. If possible, use the choke valve to gradually reduce pressure before completely shutting in the well.
Additional Safety Procedures:
- Evacuate the immediate area around the wellhead.
- Contact the emergency response team.
- Assess the situation and determine the root cause of the pressure increase.
- Initiate any necessary well control procedures.
Books
- "Well Control: Principles and Practices" by John M. Campbell: Comprehensive guide to well control techniques, including detailed sections on master valves.
- "Oil Well Engineering" by John M. Campbell: Covers the design and operation of oil wells, with chapters dedicated to wellhead equipment like master valves.
- "Petroleum Production Handbook" by Tarek Ahmed: Encyclopedic resource for petroleum engineering, including information on wellhead equipment and master valve design.
Articles
- "Christmas Tree Design and Operation" by SPE (Society of Petroleum Engineers): Technical paper discussing the components and functionality of a Christmas Tree, including the master valve.
- "Master Valve Technology: Advances in Reliability and Safety" by Oil & Gas Journal: Explores recent advancements in master valve design and its impact on safety and efficiency.
- "Master Valve Failure Analysis and Prevention" by Journal of Petroleum Technology: Analyzes causes of master valve failures and suggests strategies for prevention.
Online Resources
- Schlumberger Oilfield Glossary: Comprehensive definition of Master Valve with detailed explanation of its function and components.
- Baker Hughes Master Valve Products: Detailed information on various master valve designs and functionalities, including hydraulic and electric controls.
- National Oilwell Varco (NOV) Wellhead Equipment: Information about master valves, chokes, and other wellhead equipment, including safety features and technical specifications.
Search Tips
- Use specific keywords: "Master Valve," "Christmas Tree," "Wellhead Equipment," "Oil & Gas Production."
- Combine keywords with specific topics: "Master Valve Safety," "Master Valve Design," "Master Valve Maintenance."
- Use quotation marks: "Master Valve" will only show results with the exact phrase.
- Use advanced search operators: "site:spe.org master valve" to limit your search to a specific website like the Society of Petroleum Engineers.
Techniques
Chapter 1: Techniques for Master Valve Operation and Maintenance
This chapter details the various techniques involved in the operation and maintenance of master valves, emphasizing safety and efficiency.
1.1 Operation Techniques:
Manual Valve Operation: This section describes the proper procedure for operating manual master valves, including the correct lever/wheel manipulation, verification of closure, and awareness of potential limitations. Safety procedures, such as lockout/tagout, will be emphasized. Diagrams illustrating correct hand placement and operational sequences will be included.
Hydraulic Valve Operation: The procedure for operating hydraulic master valves will be covered, including the steps involved in activating the hydraulic system, verifying pressure, and monitoring valve closure. Troubleshooting common hydraulic system issues will also be addressed. Safety considerations specific to hydraulic systems, such as high-pressure hazards, will be highlighted.
Electric Valve Operation: This section will detail the operation of electric master valves, including the use of control panels, remote operation procedures, and fault diagnostics. Integration with supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems will be discussed. Safety precautions related to electrical hazards will be paramount.
1.2 Maintenance Techniques:
Regular Inspection: A detailed checklist for regular inspection of master valves will be provided, covering visual inspections for leaks, corrosion, and damage, as well as functional checks of all components. Frequency of inspections based on operational conditions and regulatory requirements will be specified.
Testing Procedures: This section will outline the procedures for testing master valve functionality, including pressure testing, leak testing, and operational testing under simulated emergency conditions. Documentation requirements will be highlighted.
Repair and Replacement: Techniques for repairing and replacing components of the master valve will be described, along with the necessary tools and safety precautions. The importance of using certified parts and adhering to manufacturer's guidelines will be emphasized.
1.3 Emergency Shutdown Procedures: This section will outline the steps to be taken in the event of a wellhead emergency, emphasizing rapid and safe master valve closure. Specific protocols for different valve types will be provided.
Chapter 2: Models of Master Valves
This chapter explores the different types and models of master valves available, focusing on their design features, functionalities, and applications.
2.1 Classification by Actuation:
Manual Valves: Detailed descriptions of different manual valve designs, including their advantages (simplicity, low cost) and disadvantages (limited speed, potential for human error). Illustrations of various designs will be included.
Hydraulic Valves: This section will explore the mechanics of hydraulic actuation, including different types of hydraulic cylinders and control systems. Advantages (speed, remote operation) and disadvantages (complexity, reliance on hydraulic power) will be discussed.
Electric Valves: Different electric valve designs, including motor types and control mechanisms, will be examined. The advantages (remote control, integration with automation) and disadvantages (reliance on power, potential for electrical failures) will be discussed.
2.2 Classification by Well Type and Application:
Onshore vs. Offshore Valves: Differences in design and materials based on the operational environment will be discussed. Considerations for harsh weather conditions and corrosion protection in offshore applications will be highlighted.
High-Pressure/High-Temperature Applications: Specific design considerations for wells with extreme pressure and temperature conditions will be addressed, including the use of specialized materials and sealing techniques.
Specialized Valves: Discussion of specialized master valve designs for specific well configurations or production requirements (e.g., subsea valves).
2.3 Key Design Features and Considerations:
This section will delve into the critical design features of master valves, such as sealing mechanisms, body materials, pressure ratings, and safety features.
Chapter 3: Software and Automation for Master Valve Control
This chapter focuses on the software and automation systems used for controlling and monitoring master valves.
3.1 SCADA Systems: The role of Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems in integrating master valve control into broader well management systems will be discussed. Data logging, alarm management, and remote operation capabilities will be highlighted.
3.2 Distributed Control Systems (DCS): The use of DCS in sophisticated master valve control applications will be explained, emphasizing the advantages of distributed control architecture.
3.3 Control Algorithms: Basic control algorithms used for regulating the flow of hydrocarbons through master valves will be introduced.
3.4 Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI): The design and function of HMIs for master valve control will be explained, emphasizing user-friendliness and ease of operation in both normal and emergency situations.
3.5 Data Analytics and Predictive Maintenance: The use of data analytics to monitor master valve performance, predict potential failures, and optimize maintenance schedules will be discussed.
3.6 Cybersecurity Considerations: The importance of cybersecurity measures to protect master valve control systems from cyber threats will be highlighted.
Chapter 4: Best Practices for Master Valve Management
This chapter outlines the best practices for the safe and efficient management of master valves throughout their lifecycle.
4.1 Risk Assessment and Management: The importance of conducting thorough risk assessments to identify potential hazards associated with master valve operation and maintenance will be emphasized. Implementation of control measures to mitigate identified risks will be discussed.
4.2 Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with relevant industry regulations and standards (e.g., API, OSHA) will be discussed, including documentation requirements and safety procedures.
4.3 Training and Competency: The importance of providing adequate training to personnel responsible for master valve operation and maintenance will be stressed. Competency assessment procedures will be outlined.
4.4 Maintenance Scheduling and Optimization: Strategies for developing and implementing effective maintenance schedules based on risk assessment and predictive maintenance data will be presented.
4.5 Documentation and Record Keeping: The importance of maintaining accurate records of master valve inspections, tests, maintenance activities, and repairs will be highlighted.
4.6 Emergency Response Planning: Development and regular review of emergency response plans addressing master valve failures or wellhead emergencies will be discussed.
Chapter 5: Case Studies of Master Valve Applications
This chapter presents real-world examples of master valve applications, highlighting successful implementations and lessons learned.
5.1 Case Study 1: A successful emergency shutdown preventing environmental damage. (Details of the scenario, actions taken, and positive outcomes.)
5.2 Case Study 2: An example of preventative maintenance averting a costly failure. (Description of the preventative maintenance program, the detected problem, and the cost savings.)
5.3 Case Study 3: A case study illustrating the benefits of advanced automation in master valve control. (Description of the automation system and its impact on operational efficiency and safety.)
5.4 Case Study 4: A case study of a master valve failure and its consequences. (Analysis of the causes of the failure, the resulting damage, and the lessons learned for future operations.)
Each case study will analyze the specific circumstances, the techniques and technologies employed, and the overall impact on safety, efficiency, and environmental protection. Lessons learned from both successful and unsuccessful implementations will be highlighted.
- Autonomous Inflow Control Valves (AICV) Autonomous Inflow Control Val…
- Back Pressure Valve Back Pressure Valves: Keeping…
- Butterfly Valve Butterfly Valves: The Workhor…
- Control valve Controlling the Flow: Control…
- ball-and-seat valve Ball-and-Seat Valves: Control…
- Casing Valve Casing Valve: A Key Player in…
- Circulation Control Valve Circulation Control Valves: K…
- circulation valve Circulation Valves: A Vital C…
- Circulation Valve Circulation Valve: Keeping Oi…
- Drill Pipe Safety Valve Drill Pipe Safety Valves: A C…
- Dummy Valve Dummy Valves: Silent Guardian…
- Flapper Valve Understanding Flapper Valves …
- Ball valve Ball Valves: The Workhorses o…
- Ball Valve Ball Valves: The Reliable Gat…
- Bypass valve Bypass Valve: Keeping Oil & G…
- Bi-Directional Valve Bi-Directional Valves: Guardi…
- Block Valve The Unsung Hero of Flow Contr…
- Check Valve Check Valves: Guardians of Un…
- Check valve Check Valve: The Silent Guard…
- Crack a Valve Crack a Valve: A Subtle But C…
- Application for Expenditure Justification Navigating the Appl… Project Planning & Scheduling
- Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled ("BCWS") Understanding Budge… Cost Estimation & Control
- Battery limit Understanding Batte… General Technical Terms
- DV Tool (cementing) DV Tool: A Crucial … Drilling & Well Completion
- TOC TOC: Understanding … General Technical Terms
Comments