Drilling & Well Completion
Hook Load
Understanding Hook Load in Oil & Gas Operations
In the demanding world of oil and gas exploration and production, precise terminology is crucial for efficient and safe operations. One such term, hook load, plays a vital role in planning and executing wellbore operations, particularly when dealing with pipe strings.
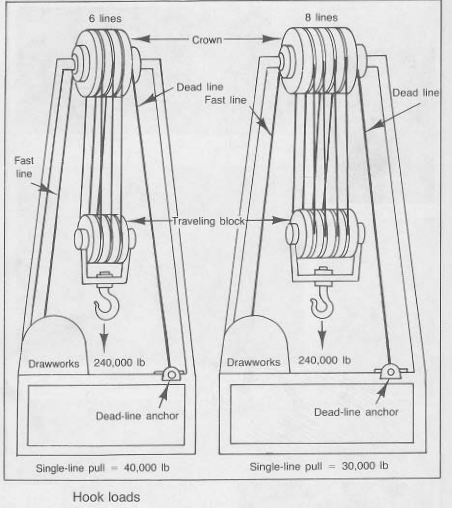
Hook load refers to the actual weight of a pipe string measured at the surface. However, this weight isn't simply the sum of the individual pipe lengths. It's influenced by various factors within the wellbore, making it a dynamic value that needs careful consideration.
Factors Affecting Hook Load:
- Buoyancy: The fluid in the wellbore exerts an upward force on the pipe string, reducing its effective weight. The density of the fluid and the depth of the pipe string both impact the buoyancy effect.
- Friction: As the pipe string moves through the wellbore, friction between the pipe and the wellbore walls creates resistance, increasing the apparent weight. This frictional force depends on the pipe's diameter, the wellbore's diameter, and the roughness of the wellbore.
- Other Factors: Other factors such as pipe weight, the weight of the drilling tools, and the configuration of the pipe string can all contribute to the hook load.
Importance of Hook Load Calculation:
Accurate hook load calculations are essential for:
- Equipment Selection: Knowing the maximum hook load helps in choosing appropriate drilling rigs and equipment capable of handling the weight.
- Safety Management: Accurate hook load predictions ensure the safe operation of the rig and prevent equipment failures due to overloading.
- Operational Efficiency: Understanding hook load allows for optimal drilling and wellbore operations, minimizing downtime and ensuring efficient pipe handling.
Calculating Hook Load:
Calculating hook load involves complex formulas that consider the factors mentioned above. Software programs and specialized tools are often used to determine the accurate hook load for specific wellbore conditions.
Conclusion:
Hook load is a crucial parameter in oil and gas operations, influencing equipment selection, safety protocols, and operational efficiency. Understanding the factors affecting hook load and employing accurate calculation methods ensures safe and successful wellbore operations.
Test Your Knowledge
Hook Load Quiz
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What is the definition of hook load? a) The total weight of the drilling rig. b) The weight of the drill pipe only. c) The actual weight of the pipe string measured at the surface. d) The weight of the drilling fluid in the wellbore.
Answer
c) The actual weight of the pipe string measured at the surface.
2. Which of the following factors DOES NOT influence hook load? a) Buoyancy b) Friction c) Pipe weight d) The weather conditions at the surface.
Answer
d) The weather conditions at the surface.
3. How does buoyancy affect hook load? a) It increases the hook load by adding weight. b) It reduces the hook load by exerting an upward force. c) It has no effect on hook load. d) It increases the hook load by creating friction.
Answer
b) It reduces the hook load by exerting an upward force.
4. Why is accurate hook load calculation important for safety management? a) To ensure the drilling rig is properly anchored. b) To prevent equipment failures due to overloading. c) To predict the volume of drilling fluid needed. d) To determine the drilling rate.
Answer
b) To prevent equipment failures due to overloading.
5. Which of the following tools is commonly used for hook load calculation? a) GPS receivers b) Seismic equipment c) Software programs and specialized tools d) Mud logging equipment
Answer
c) Software programs and specialized tools
Hook Load Exercise
Scenario: You are working on an oil well with a 3,000-meter depth. The pipe string weighs 10 kg per meter. The drilling fluid has a density of 1.1 g/cm³.
Task:
- Estimate the buoyancy force acting on the pipe string.
- Explain how this buoyancy force affects the hook load.
Exercice Correction
Here's how to approach the exercise: * **Calculate the volume of the pipe string:** You need the cross-sectional area of the pipe to do this. Assuming a standard pipe diameter, you can calculate the volume. * **Calculate the weight of the displaced drilling fluid:** Multiply the volume of the pipe string by the density of the drilling fluid. This gives you the weight of the fluid displaced by the pipe, which equals the buoyant force acting on it. * **Determine the effect on hook load:** The buoyant force reduces the hook load by acting in the opposite direction to gravity. Subtract the buoyant force from the total weight of the pipe string to get the approximate hook load. **Example:** Let's assume the pipe has a cross-sectional area of 0.1 m². * **Volume of pipe string:** 3000 m * 0.1 m² = 300 m³ * **Weight of displaced fluid:** 300 m³ * 1.1 g/cm³ * (1 kg/1000 g) * (100 cm/m)³ ≈ 330,000 kg * **Buoyant force:** 330,000 kg * **Hook load:** (3000 m * 10 kg/m) - 330,000 kg = -30,000 kg The negative hook load indicates that the pipe string is actually experiencing an upward force due to buoyancy, meaning the actual weight at the surface is less than the weight of the pipe itself.
Books
- "Drilling Engineering" by John A. Cameron: This comprehensive textbook covers all aspects of drilling engineering, including detailed explanations of hook load calculations and its importance.
- "Petroleum Engineering: Drilling and Well Completions" by William C. Lyons: Another excellent resource that provides in-depth coverage of hook load, including its impact on rig selection and wellbore operations.
- "Drilling Engineering Practices" by G.B. Maughmer: Offers practical insights into the real-world application of hook load principles and calculations.
Articles
- "Hook Load Calculations: A Practical Guide" by [Author Name]: Look for articles on industry websites and journals that offer step-by-step instructions and real-world examples of hook load calculations.
- "Understanding Hook Load and its Impact on Drilling Operations" by [Author Name]: Search for articles discussing the various factors influencing hook load and its implications for drilling efficiency and safety.
- "Hook Load Calculation Software: A Review" by [Author Name]: Explore articles comparing different software programs used for hook load calculations, focusing on their features and accuracy.
Online Resources
- Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE): This organization offers a wealth of resources on drilling engineering, including articles, publications, and online courses on hook load.
- IADC (International Association of Drilling Contractors): The IADC provides industry standards and guidelines related to hook load calculations and safe drilling practices.
- Oil & Gas Journal: This industry publication frequently features articles and reports on drilling engineering and hook load-related topics.
Search Tips
- Use specific keywords: Combine "hook load" with other relevant terms like "drilling," "wellbore," "calculation," "software," etc.
- Include relevant industry terms: Utilize terms like "oil and gas," "petroleum," "drilling engineering," etc., to narrow your search.
- Explore "related searches" and "people also ask" sections: These features can offer valuable additional insights and relevant keywords.
- Utilize Google Scholar: This tool helps you find academic articles and research papers specifically focused on hook load and related concepts.
Techniques
Understanding Hook Load in Oil & Gas Operations: A Comprehensive Guide
This guide expands on the concept of hook load, breaking it down into key chapters for better understanding.
Chapter 1: Techniques for Hook Load Calculation
The accurate determination of hook load is crucial for safe and efficient drilling operations. Several techniques are employed, ranging from simplified estimations to sophisticated software-based calculations.
1.1 Simplified Methods: These methods offer quick estimations but lack the precision of more advanced techniques. They often rely on simplified assumptions about wellbore conditions and may be suitable for preliminary planning or less critical operations. Examples include:
- Weight Calculation based on pipe dimensions and material properties: This involves calculating the submerged weight of the pipe string, considering only the weight of the pipe itself and the buoyancy effect of the drilling fluid. It ignores friction and other factors.
- Empirical Formulas: Some simplified formulas exist that attempt to account for friction based on limited well parameters. However, these formulas typically have limited accuracy and applicability.
1.2 Advanced Techniques: These techniques aim for higher accuracy by incorporating more variables and complex interactions.
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA): FEA models the pipe string as a series of interconnected elements, considering the effects of buoyancy, friction, bending, and other forces along the entire length of the string. This method provides a detailed representation of the stress distribution within the pipe string.
- Numerical Simulation: Sophisticated software packages use numerical methods (e.g., finite difference, finite volume) to solve the governing equations for fluid flow, heat transfer, and structural mechanics within the wellbore. This allows for simulating various scenarios and predicting hook load with greater accuracy.
- Data-driven approaches: Machine learning models are being increasingly used to predict hook load based on historical drilling data. This approach can account for complex, non-linear relationships between well parameters and hook load.
1.3 Measurement Techniques: While calculation is important, direct measurement also plays a role.
- Hook Load Cell: This device directly measures the tension on the drilling hook, providing a real-time measurement of the hook load. This is a crucial safety measure during drilling operations.
Chapter 2: Models for Hook Load Prediction
Accurate hook load prediction relies on robust models that account for the various factors influencing the load.
2.1 Static Models: These models assume that the pipe string is stationary, focusing primarily on the weight of the pipe string and the buoyancy effect.
2.2 Dynamic Models: These models account for the dynamic effects of pipe movement, including friction, bending, and vibrations during hoisting and lowering operations. Dynamic models are significantly more complex but provide a more accurate representation of real-world scenarios. They often incorporate factors such as:
- Fluid Dynamics: Modeling the flow of drilling fluid around the pipe string and its effect on buoyancy and friction.
- Structural Mechanics: Considering the bending and deformation of the pipe string under load.
- Friction Models: Accurate representation of the complex frictional forces between the pipe string and the wellbore. This often involves considerations of wellbore geometry, pipe roughness, and mud properties.
Chapter 3: Software for Hook Load Calculation
Numerous software packages are available to assist in hook load calculations. These packages vary in complexity and features, ranging from simple spreadsheets to sophisticated simulation platforms.
3.1 Spreadsheet Software: While basic spreadsheets can perform simple hook load calculations, their limitations in handling complex factors make them unsuitable for advanced analysis.
3.2 Specialized Software: These programs are designed specifically for wellbore operations and offer advanced features such as:
- Detailed wellbore geometry input: Allowing for accurate representation of wellbore curvature, diameter variations, and other complexities.
- Advanced friction models: Incorporating more realistic friction models to account for varying wellbore conditions.
- Dynamic simulations: Simulating the movement of the pipe string during hoisting, lowering, and other operations.
- Data visualization and reporting: Generating clear reports and visualizations of hook load predictions.
Examples of such software (note: this is not an exhaustive list, and availability may vary): [Insert Examples of relevant software here - Mentioning specific names would require research beyond this response's scope.]
Chapter 4: Best Practices for Hook Load Management
Effective hook load management involves a combination of careful planning, accurate calculations, and robust safety procedures.
4.1 Pre-Drilling Planning: Thorough planning is essential to ensure that the chosen drilling equipment and procedures are adequate for the anticipated hook loads. This includes:
- Accurate wellbore model: Developing a detailed model of the wellbore, incorporating geological data, drilling fluid properties, and other relevant information.
- Realistic Hook Load Predictions: Using appropriate software and techniques to generate realistic hook load predictions under various operational scenarios.
- Contingency Planning: Developing contingency plans to address potential issues, such as unexpected increases in hook load.
4.2 Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of hook load during drilling operations is essential for safety and operational efficiency.
- Regular Hook Load Checks: Frequent checks against predicted values help identify any unexpected deviations.
- Alarm Systems: Implementing alarm systems to warn operators of potential overloads.
4.3 Rig Selection and Equipment: Ensuring the selected drilling rig and equipment are capable of handling the maximum anticipated hook load.
Chapter 5: Case Studies of Hook Load Challenges and Solutions
[This section requires specific case studies which are beyond the scope of this response. However, a well-structured case study would involve a description of a particular drilling operation, the challenges faced with respect to hook load (e.g., unexpected high loads, equipment failure), the methods employed to address the challenges (e.g., changes in drilling fluid, adjustments to operational procedures, software-based analysis), and the lessons learned.] Examples of topics for case studies could include:
- A case study describing a situation where inaccurate hook load prediction led to equipment failure.
- A case study showcasing how the use of advanced software improved safety and efficiency in a high-risk drilling operation.
- A case study detailing how a novel approach to friction modeling improved the accuracy of hook load predictions.
This comprehensive guide provides a framework for understanding hook load in oil and gas operations. Remember that accurate hook load management is critical for ensuring safe and efficient drilling operations. Consult industry best practices and relevant regulatory requirements for specific applications.
- Axial Load Understanding Axial Load: The…
- Critical Velocity (unloading) Critical Velocity: The Minimu…
- Bed Load Bed Load: The Unsung Hero of …
- Critical Buckling Load Critical Buckling Load: A Lif…
- Lateral (load) Lateral (Load): A Sideways Pu…
- Overload Overload: A Critical Issue in…
- Overload Overload: A Critical Term in …
- Critical Flow Rate (liquids unloading) Critical Flow Rate: The Minim…
- drilling hook The Drilling Hook: A Vital Li…
- Drilling Hook and Swivel Drilling Hook and Swivel: Ess…
- Fish Hook The Fish Hook: A Sharp Turn i…
- Hook The Hook: A Crucial Component…
- Hook The Hook: A Crucial Component…
- Hook (drilling rig) The Hook: A Vital Component i…
- hook load Understanding Hook Load i…
- Hook Wall Packer Hook Wall Packers: A Crucial …
- Load Fluid Load Fluid: The Unsung Hero o…
- Hooke’s Law Hooke's Law: A Fundamental Pr…
- Indicator (mechanical load) Keeping Things Under Control:…
- Load Cell Load Cells: Weighing In on Co…
- Application for Expenditure Justification Navigating the Appl… Project Planning & Scheduling
- Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled ("BCWS") Understanding Budge… Cost Estimation & Control
- Battery limit Understanding Batte… General Technical Terms
- DV Tool (cementing) DV Tool: A Crucial … Drilling & Well Completion
- TOC TOC: Understanding … General Technical Terms
Comments