Geology & Exploration
3D Seismic
3D Seismic: Peering into the Earth with a 3D Lens
The world of oil and gas exploration relies heavily on understanding the subsurface, particularly the intricate structures of reservoirs where hydrocarbons reside. This is where 3D seismic comes into play, a powerful tool that allows us to see beneath the earth's surface with unprecedented clarity.
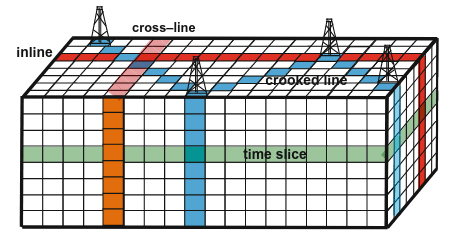
Unlike traditional 2D seismic, which captures a single line of data, 3D seismic utilizes a dense grid of 2D seismic lines. This grid is then meticulously processed using sophisticated algorithms to generate a seismic cube, a 3D representation of the subsurface. Imagine it as a digital model of the earth, providing a detailed visual roadmap of geological formations.

This 3D cube is incredibly versatile. It can be "sliced" vertically, recreating the familiar 2D seismic lines, offering a cross-sectional view of the subsurface. Alternatively, horizontal slicing reveals time slices, showcasing the geological formations at specific depths, akin to looking at a map of the subsurface.

The key advantage of 3D seismic lies in its ability to:
- Identify complex geological structures: Fault lines, folds, and other geological features that are crucial for hydrocarbon exploration can be visualized with greater precision.
- Delineate reservoir boundaries: 3D seismic allows for a more accurate determination of the size and shape of hydrocarbon reservoirs, improving resource assessment and production planning.
- Optimize drilling strategies: By understanding the subsurface structure in 3D, oil companies can design drilling trajectories that maximize hydrocarbon recovery while minimizing risks.
- Improve reservoir characterization: The 3D seismic data can be used to estimate porosity, permeability, and other key reservoir parameters, providing crucial insights for reservoir management.
3D seismic technology has revolutionized the oil and gas industry, offering significant benefits:
- Enhanced exploration success: Improved understanding of subsurface structures leads to more targeted and efficient exploration efforts.
- Increased production efficiency: Optimized drilling strategies and reservoir management plans result in higher production rates and reduced costs.
- Reduced environmental impact: By minimizing exploration and production risks, 3D seismic technology contributes to a more sustainable oil and gas industry.
While 3D seismic remains a vital tool, its evolution continues. Newer technologies like 4D seismic are emerging, adding the fourth dimension of time, allowing us to monitor changes in reservoirs over time, further enhancing our understanding and maximizing production potential.
In conclusion, 3D seismic technology has transformed our ability to explore and manage subsurface resources. It empowers us to see the earth's secrets with unprecedented clarity, paving the way for a more efficient, targeted, and sustainable future for the oil and gas industry.
Test Your Knowledge
3D Seismic Quiz
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What is the primary advantage of 3D seismic over 2D seismic?
a) 3D seismic is cheaper and faster to acquire. b) 3D seismic captures a single line of data, providing a simpler view of the subsurface. c) 3D seismic provides a detailed, three-dimensional representation of the subsurface. d) 3D seismic is only used for exploring shallow geological formations.
Answer
c) 3D seismic provides a detailed, three-dimensional representation of the subsurface.
2. What is a "seismic cube"?
a) A physical cube containing rock samples from the subsurface. b) A three-dimensional digital model of the subsurface created from 3D seismic data. c) A mathematical equation used to analyze seismic data. d) A container for storing seismic equipment.
Answer
b) A three-dimensional digital model of the subsurface created from 3D seismic data.
3. What is a "time slice" in 3D seismic data?
a) A horizontal slice through the seismic cube, showing the subsurface at a specific depth. b) A vertical slice through the seismic cube, showing a cross-section of the subsurface. c) A measurement of the time it takes for seismic waves to travel through the earth. d) A type of seismic processing technique used to enhance data quality.
Answer
a) A horizontal slice through the seismic cube, showing the subsurface at a specific depth.
4. How can 3D seismic data be used to optimize drilling strategies?
a) By identifying the exact location of oil and gas deposits. b) By providing a clear understanding of the subsurface structure, allowing for safer and more efficient drilling trajectories. c) By predicting the future movement of oil and gas reservoirs. d) By creating detailed maps of the earth's surface.
Answer
b) By providing a clear understanding of the subsurface structure, allowing for safer and more efficient drilling trajectories.
5. What is a key benefit of 4D seismic technology?
a) It provides a more detailed view of the earth's surface. b) It eliminates the need for 3D seismic data. c) It allows for monitoring changes in reservoirs over time, improving production and management. d) It provides a complete and accurate picture of the earth's interior.
Answer
c) It allows for monitoring changes in reservoirs over time, improving production and management.
3D Seismic Exercise
Scenario: An oil company is exploring a new area for potential hydrocarbon deposits. They have acquired 3D seismic data over the area and are analyzing the results. The seismic data reveals a large, dome-shaped structure in the subsurface.
Task: Based on your understanding of 3D seismic, what might this dome-shaped structure indicate? What are some potential geological formations that could create this type of structure? What implications does this structure have for hydrocarbon exploration?
Exercice Correction
The dome-shaped structure revealed by the 3D seismic data could indicate a variety of geological formations, including:
- **Anticlines:** These are upward folds in the earth's crust that can trap hydrocarbons. The dome-shaped structure could be an anticline, making it a promising target for exploration.
- **Salt Domes:** These are massive structures formed by the upward movement of salt, which can trap hydrocarbons.
- **Volcanic Intrusions:** In some cases, solidified magma can create dome-shaped structures.
- **Impact Craters:** Meteorite impacts can also create dome-like formations.
The implications of this dome-shaped structure for hydrocarbon exploration are significant:
- Increased Potential for Hydrocarbon Deposits:** The dome-shaped structure could create a trap for hydrocarbons, increasing the likelihood of finding oil or gas deposits within the structure.
- Targeted Exploration Efforts:** The 3D seismic data allows for a detailed understanding of the structure, enabling the oil company to focus their exploration efforts on the most promising areas within the dome.
- Optimized Drilling Plans:** The 3D representation of the structure helps the company design efficient drilling trajectories to reach the potential reservoir and maximize hydrocarbon recovery.
Further analysis of the 3D seismic data, combined with other geological and geophysical data, will be crucial in determining the exact nature of the dome-shaped structure and its potential for hydrocarbon exploration.
Books
- Seismic Exploration: A Practical Guide to Exploration Seismology by Robert E. Sheriff (This classic text covers both 2D and 3D seismic methods, including data acquisition, processing, and interpretation).
- Seismic Data Processing by Oscar Yilmaz (A comprehensive resource on seismic data processing techniques, including those used for 3D seismic).
- 3D Seismic Interpretation by Charles H. Thurmond (Focuses on the interpretation of 3D seismic data, providing techniques for identifying geological features and understanding reservoir properties).
- Petroleum Geoscience by John C. Wilson (This textbook provides a broad overview of petroleum exploration, including detailed sections on seismic methods, particularly 3D seismic).
Articles
- "3-D Seismic Surveys: A New Dimension in Petroleum Exploration" by R.A. Lavergne (This article provides a historical overview of the development and applications of 3D seismic).
- "The Use of 3-D Seismic Data in Reservoir Characterization" by J.P. Castagna (This article discusses how 3D seismic data can be used to improve reservoir description and enhance hydrocarbon production).
- "The Evolution of 3D Seismic Technology" by M.D. Matthews (This article explores the advancements in 3D seismic technology over time, highlighting the impact on exploration and production).
- "4D Seismic: A New Frontier in Reservoir Management" by D.W. Stewart (This article introduces 4D seismic, discussing its capabilities and potential for monitoring reservoir performance).
Online Resources
- Society of Exploration Geophysicists (SEG): https://www.seg.org/ (The SEG website offers a wealth of resources, including publications, technical articles, and educational materials on seismic exploration).
- European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers (EAGE): https://www.eage.org/ (The EAGE website provides access to research papers, conference proceedings, and other resources related to geophysics and seismic exploration).
- Schlumberger: https://www.slb.com/ (This oilfield services company offers comprehensive information on seismic exploration and production technologies, including 3D seismic).
- WesternGeco (a Baker Hughes company): https://www.westerngeco.com/ (WesternGeco is a leading provider of seismic acquisition and processing services, with a wealth of information on 3D seismic).
Search Tips
- Use specific keywords like "3D seismic exploration," "3D seismic interpretation," "3D seismic reservoir characterization," etc.
- Combine keywords with relevant industry terms like "oil and gas," "hydrocarbons," "petroleum," etc.
- Use quotation marks to search for specific phrases, such as "4D seismic technology."
- Employ Boolean operators like "AND," "OR," and "NOT" to refine your search.
- Specify your desired file format (e.g., PDF, DOC) for more targeted results.
Techniques
Chapter 1: Techniques
3D Seismic Data Acquisition: A Symphony of Sound and Sensors
3D seismic data acquisition is the foundation of the entire process, laying the groundwork for the 3D visualization of the subsurface. This intricate process involves deploying a vast network of sensors across a vast area to generate a dense grid of 2D seismic lines, ultimately creating a 3D cube.
1.1 Source and Receiver Deployment:
- Sources: Specialized vibroseis trucks or explosive charges send sound waves into the earth. Vibroseis trucks generate controlled vibrations, while explosions release a sudden burst of energy.
- Receivers: Geophones, sensitive to ground vibrations, record the sound waves as they travel through different layers of the earth.
- Grid Design: The acquisition grid consists of lines of sources and receivers strategically placed across the survey area, ensuring a dense sampling of the subsurface.
1.2 Data Acquisition in Action:
- Vibroseis: Vibroseis trucks sweep through a range of frequencies, providing a broader range of information about the subsurface.
- Explosive Charges: While cost-effective, explosive charges can generate noise and environmental concerns, prompting a shift towards vibroseis in many areas.
1.3 Challenges and Considerations:
- Terrain Variations: Rugged terrains and dense vegetation can present challenges in deploying sources and receivers efficiently.
- Environmental Impact: Minimizing environmental disruption is crucial, leading to stringent regulations and environmentally-conscious practices.
- Cost Factor: 3D seismic data acquisition is a resource-intensive process, demanding careful planning and cost optimization.
1.4 Emerging Technologies:
- Ocean Bottom Seismic (OBS): OBS technology allows for data acquisition in deep water, extending the reach of seismic exploration.
- Multi-Component Acquisition: Recording multiple wave types (pressure, shear, etc.) can provide additional insights into reservoir properties.
1.5 Conclusion:
Acquiring 3D seismic data is a complex and multifaceted process that requires careful planning, execution, and technological expertise. The resulting data forms the foundation for the powerful 3D interpretations that guide oil and gas exploration and production decisions.
Chapter 2: Models
Unraveling the Subsurface: 3D Seismic Models and Their Interpretation
The 3D seismic cube, generated from the acquired data, is just the beginning of the story. This raw data must be processed, interpreted, and ultimately transformed into a comprehensive 3D geological model that reveals the secrets hidden beneath the earth's surface.
2.1 Processing the Data:
- Pre-processing: Initial steps include removing noise, correcting for timing variations, and enhancing the quality of the raw seismic data.
- Velocity Model Building: Understanding how seismic waves travel through the subsurface is crucial for accurate imaging. Velocity models provide a detailed map of the varying speeds of sound waves in different geological formations.
- Imaging: The processed data is then migrated to create a more accurate image of the subsurface, minimizing distortions caused by the complex paths taken by seismic waves.
2.2 Building a 3D Geological Model:
- Interpretation: Geologists and geophysicists analyze the seismic data, identifying key geological features like faults, folds, and horizons (boundaries between different rock layers).
- Model Creation: Specialized software is used to build a 3D representation of the subsurface, incorporating interpreted features and incorporating additional data sources like well logs and geological maps.
- Refinement: The model is iteratively refined through analysis of additional data and the application of geological constraints.
2.3 Interpreting the Model:
- Reservoir Identification: The model allows for the identification of potential reservoir formations, assessing their size, shape, and connectivity.
- Reservoir Characterization: The model can be used to estimate key reservoir properties, including porosity, permeability, and fluid content, crucial for production planning and optimization.
- Risk Assessment: Analyzing potential risks associated with drilling and production, such as faults, shale layers, and complex geometries, is made more precise with the 3D model.
2.4 Modeling the Future:
- 4D Seismic: Integrating time as a fourth dimension allows for tracking reservoir changes over time, providing insights into production performance, fluid flow, and the impact of reservoir management practices.
- Reservoir Simulation: 3D models serve as input for complex reservoir simulation software, allowing for predictions of future production scenarios and optimization of field development strategies.
2.5 Conclusion:
3D seismic modeling is a powerful tool that transforms raw seismic data into a comprehensive and informative picture of the subsurface. This sophisticated model empowers oil and gas professionals to make informed decisions about exploration, development, and production, leading to more efficient and sustainable resource management.
Chapter 3: Software
3D Seismic Software: The Tools that Power Earth Exploration
The power of 3D seismic lies not only in the data acquisition and interpretation but also in the software that empowers geophysicists and geologists to process, visualize, and analyze the massive amounts of information involved. Specialized software packages form the backbone of 3D seismic analysis, enabling them to unlock the secrets hidden beneath the earth's surface.
3.1 Seismic Processing Software:
- Noise Attenuation: Removing unwanted noise from seismic data is crucial for accurate interpretation. Software packages offer a range of advanced filtering techniques to enhance data quality.
- Velocity Model Building: Building accurate velocity models requires sophisticated software capable of analyzing seismic data and incorporating geological constraints.
- Migration: Migrating the seismic data to correct for the complex paths of seismic waves is a complex process, requiring specialized software capable of handling large datasets.
3.2 3D Visualization and Interpretation Software:
- Interactive Visualization: Software packages offer tools for viewing, manipulating, and analyzing 3D seismic data in an interactive environment, allowing for exploration and understanding of the complex geological structures.
- Horizon Tracking: Identifying and tracking geological boundaries (horizons) within the 3D seismic data is facilitated by specialized software that automates the process, providing detailed information about the subsurface.
- Fault Interpretation: Interpreting fault planes and their relationships is crucial for reservoir analysis. Software packages offer tools for identifying faults, defining their geometries, and understanding their impact on hydrocarbon migration and trap formation.
3.3 Reservoir Characterization and Modeling Software:
- Property Estimation: Software packages enable the estimation of key reservoir properties such as porosity, permeability, and fluid saturation based on seismic data, well logs, and other available information.
- Reservoir Simulation: Modeling the flow of hydrocarbons within a reservoir requires advanced software capable of simulating complex fluid flow phenomena, allowing for predictions of production performance and the impact of different development strategies.
3.4 Emerging Technologies:
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing platforms offer scalability and cost-effectiveness for processing and analyzing large seismic datasets, enabling more efficient and flexible workflows.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being integrated into 3D seismic software, automating tasks, improving interpretation accuracy, and unlocking new insights from the data.
3.5 Conclusion:
Specialized 3D seismic software plays a vital role in the entire exploration and production process, empowering geoscientists to unlock the full potential of 3D seismic data. The constant evolution of software technology, driven by advancements in computing power and AI, continues to improve the accuracy, efficiency, and insights gained from 3D seismic analysis.
Chapter 4: Best Practices
Optimizing 3D Seismic: A Guide to Success and Sustainability
Successfully implementing 3D seismic technology requires not only technical expertise but also a commitment to best practices that ensure the accuracy, efficiency, and sustainability of the entire process. This chapter outlines key principles for optimizing 3D seismic operations.
4.1 Planning and Design:
- Clear Objectives: Defining clear project goals, including exploration targets, production goals, and risk assessment requirements, sets the stage for a successful 3D seismic project.
- Grid Design and Acquisition Parameters: Choosing the appropriate grid spacing, source and receiver configurations, and recording parameters is essential for capturing the necessary data to achieve project objectives.
- Environmental Considerations: Minimizing environmental impact is crucial. Planning surveys with minimal disturbance, using environmentally friendly acquisition methods, and adhering to regulations are essential.
4.2 Data Acquisition:
- Quality Control: Implementing rigorous quality control measures during data acquisition is vital for ensuring data accuracy and minimizing the need for costly re-acquisitions.
- Weather Monitoring: Monitoring weather conditions is important to avoid delays and potential damage to equipment.
- Communication and Coordination: Maintaining effective communication between field crews, processing teams, and interpretation teams is essential for seamless workflow and project success.
4.3 Data Processing:
- Velocity Model Accuracy: Developing an accurate velocity model is crucial for accurate imaging and interpretation. This requires careful analysis and the use of advanced software.
- Migration Techniques: Choosing the appropriate migration technique based on geological complexities and project objectives is key to achieving accurate image reconstruction.
- Quality Control and Validation: Implementing stringent quality control measures throughout the processing workflow ensures data integrity and reduces potential errors.
4.4 Interpretation and Modeling:
- Collaboration and Expertise: Integrating knowledge from geologists, geophysicists, and reservoir engineers is essential for accurate and informed interpretation.
- Multi-Disciplinary Approach: Combining seismic data with other geological and production data, such as well logs, geological maps, and production data, provides a more complete understanding of the subsurface.
- Model Validation: Regularly validating the geological model against new data and production performance is crucial for ensuring model accuracy and reliability.
4.5 Sustainability:
- Environmentally Friendly Practices: Adopting environmentally friendly acquisition and processing techniques minimizes the impact on ecosystems.
- Data Management and Sharing: Implementing efficient data management systems and fostering data sharing within the industry promotes efficient utilization of resources and reduces redundancy.
- Innovation and Technology: Embracing new technologies and innovative approaches can enhance efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and unlock new insights from 3D seismic data.
4.6 Conclusion:
By adhering to best practices, prioritizing data quality, and embracing innovative approaches, the oil and gas industry can maximize the effectiveness and sustainability of 3D seismic technology. This commitment to responsible exploration and development is crucial for ensuring a future where energy resources are managed efficiently and sustainably.
Chapter 5: Case Studies
3D Seismic in Action: Real-World Applications and Success Stories
The power of 3D seismic technology is best illustrated by real-world case studies showcasing its impact on oil and gas exploration, development, and production. This chapter presents examples of how 3D seismic has transformed the industry, leading to increased exploration success, improved reservoir management, and more efficient production.
5.1 Case Study 1: Uncovering Hidden Reservoirs in the North Sea
- Challenge: Exploring challenging and mature oil and gas fields in the North Sea required advanced techniques to identify new reservoirs and optimize production from existing fields.
- Solution: 3D seismic surveys, coupled with sophisticated processing and interpretation techniques, enabled the discovery of previously unknown reservoirs, extending the life of mature fields and unlocking new resources.
- Results: Significant increases in hydrocarbon reserves were discovered, leading to extended production lifespans and enhanced profitability.
5.2 Case Study 2: Optimizing Production in the Gulf of Mexico
- Challenge: Maximizing production from complex offshore reservoirs in the Gulf of Mexico required a deep understanding of reservoir architecture and fluid flow patterns.
- Solution: 3D seismic data, combined with reservoir simulation models, provided valuable insights into reservoir connectivity, enabling the optimization of drilling trajectories and production strategies.
- Results: Increased production rates, reduced development costs, and improved recovery factors were achieved, showcasing the power of 3D seismic for optimizing production in challenging environments.
5.3 Case Study 3: Monitoring Reservoir Performance with 4D Seismic
- Challenge: Tracking changes in reservoir properties over time, such as pressure depletion and fluid movement, is crucial for efficient reservoir management.
- Solution: 4D seismic, which adds the dimension of time, enables the monitoring of reservoir performance, providing insights into production patterns and the effectiveness of different reservoir management strategies.
- Results: Improved understanding of reservoir dynamics, optimized production strategies, and enhanced recovery factors have been achieved through the application of 4D seismic technology.
5.4 Case Study 4: Reducing Environmental Impact Through Advanced Imaging
- Challenge: Minimizing environmental impact is a priority for oil and gas exploration and development. Advanced imaging techniques using 3D seismic data can reduce the need for exploratory drilling, minimizing disturbance.
- Solution: Utilizing high-resolution 3D seismic data and advanced interpretation tools, oil companies can more accurately define potential reservoir targets, reducing the need for exploratory drilling and minimizing the environmental footprint.
- Results: Reduced drilling activity, minimized disturbance to sensitive ecosystems, and enhanced environmental stewardship have been achieved through the application of advanced imaging techniques.
5.5 Conclusion:
These case studies demonstrate the transformative power of 3D seismic technology across various aspects of the oil and gas industry. From uncovering hidden reservoirs to optimizing production strategies and minimizing environmental impact, 3D seismic continues to play a vital role in shaping the future of the industry, driving efficiency, sustainability, and a deeper understanding of the Earth's subsurface.
- 2D Seismic Unveiling Earth's Secrets: A …
- Check Shot Survey (seismic) Unveiling Earth's Secrets: Un…
- Coherence (seismic) Coherence: Unveiling the Secr…
- Curvature (seismic) Unmasking the Hidden Depths: …
- Deconvolution (seismic) Deconvolution: Unveiling the …
- Density Contrast (seismic) Density Contrast: A Key to Un…
- Density-Depth Function (seismic) Understanding Density-Depth F…
- Depth Migration (seismic) Unraveling the Depths: Depth …
- DMO (seismic) Understanding DMO (Seismic) i…
- DZO (seismic) DZO: Elevating Seismic Resolu…
- ESS (seismic) ESS: Unveiling Secrets Beneat…
- Euler Method (seismic) Unlocking the Depths: The Eul…
- Frequency Domain (seismic) Delving into the Depths: Freq…
- Gamma (seismic) Gamma: Unlocking Earth's Secr…
- Gardner’s Equation (seismic) Gardner's Equation: A Seismic…
- Gather (seismic) Gather (Seismic): A Window in…
- Gradiometer (seismic) Gradiometers: Unlocking Secre…
- Gravity Unit (seismic) Gravity Units (gu) in Oil & G…
- High Density Basement (seismic) The Unseen Anchor: Understand…
- 4D Seismic Unveiling the Secrets of Time…
- Application for Expenditure Justification Navigating the Appl… Project Planning & Scheduling
- Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled ("BCWS") Understanding Budge… Cost Estimation & Control
- Battery limit Understanding Batte… General Technical Terms
- DV Tool (cementing) DV Tool: A Crucial … Drilling & Well Completion
- TOC TOC: Understanding … General Technical Terms
Comments