Geology & Exploration
2D Seismic
Unveiling Earth's Secrets: A Look at 2D Seismic Surveys
Beneath the surface of our planet lies a world of hidden structures, geological formations, and valuable resources. To peer into this subterranean realm, geologists and geophysicists rely on a powerful tool: 2D seismic surveys.
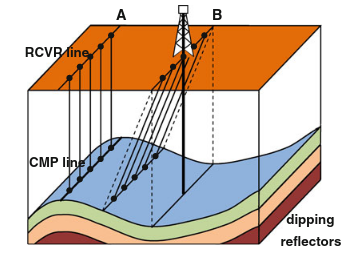
What is 2D Seismic?
Imagine sending sound waves into the earth and listening to their echoes. That's essentially what 2D seismic surveys do. They use controlled sound waves (typically generated by specialized trucks or boats) to create a detailed image of the subsurface. These surveys are called "2D" because they capture data along a single line, like a slice through the earth, providing information about the depth and structure of geological features beneath the surface.
Depth and Width Data: Unraveling the Subsurface
Depth: 2D seismic data provides information about the depth of various geological features, such as:
- Sedimentary layers: Different rock types have different acoustic properties. These variations are captured by the returning sound waves, allowing geologists to map the thickness and composition of layers of sediment.
- Faults: Fractures in the earth's crust, called faults, can be identified by analyzing the shifts and disruptions in the seismic data.
- Hydrocarbon reservoirs: The presence of oil and gas reservoirs can be detected by identifying specific geological structures, like traps, that can hold these resources.
Width: While 2D seismic surveys primarily focus on depth, they also provide limited information about the width of features. By analyzing the changes in the recorded signals along the survey line, geologists can estimate the extent of a particular structure.
Understanding the Data:
The collected seismic data is processed and interpreted using specialized software. Geologists analyze the reflected sound waves, called seismic waves, to create images known as seismic sections. These sections show the different geological layers, structures, and potential resources beneath the surface.

Applications of 2D Seismic:
2D seismic surveys are widely used in various fields, including:
- Oil and gas exploration: Identifying potential oil and gas reservoirs and understanding their geological context.
- Geotechnical engineering: Evaluating the suitability of land for construction projects.
- Mineral exploration: Locating mineral deposits and understanding their geological settings.
- Earthquake studies: Mapping fault structures and assessing seismic hazards.
- Groundwater management: Investigating the location and properties of groundwater aquifers.
Limitations of 2D Seismic:
While powerful, 2D seismic surveys have limitations. They only provide a one-dimensional view of the subsurface, meaning they cannot capture the full complexity of three-dimensional structures. For detailed and comprehensive analysis, 3D seismic surveys are often preferred.
Conclusion:
2D seismic surveys are essential tools for understanding the geology beneath our feet. They provide valuable information about the depth and structure of geological features, facilitating exploration for natural resources, infrastructure development, and managing natural hazards. As technology advances, 2D seismic data will continue to play a crucial role in revealing the secrets of our planet.
Test Your Knowledge
Quiz: Unveiling Earth's Secrets: 2D Seismic Surveys
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What is the primary function of 2D seismic surveys?
a) To map the Earth's magnetic field. b) To measure the Earth's gravitational pull. c) To create detailed images of the subsurface using sound waves. d) To analyze the composition of rocks and minerals.
Answer
c) To create detailed images of the subsurface using sound waves.
2. What type of data does 2D seismic provide information about?
a) Only depth. b) Only width. c) Both depth and width. d) None of the above.
Answer
c) Both depth and width.
3. Which of the following is NOT a geological feature that can be identified using 2D seismic data?
a) Sedimentary layers. b) Faults. c) Volcanic craters. d) Hydrocarbon reservoirs.
Answer
c) Volcanic craters.
4. What are the processed and interpreted seismic waves called?
a) Seismic sections. b) Sound waves. c) Acoustic waves. d) Electromagnetic waves.
Answer
a) Seismic sections.
5. Which of the following is NOT a common application of 2D seismic surveys?
a) Oil and gas exploration. b) Weather forecasting. c) Geotechnical engineering. d) Mineral exploration.
Answer
b) Weather forecasting.
Exercise: 2D Seismic Interpretation
Scenario: You are a geologist working on a project to explore for potential oil and gas reserves. You have been provided with a 2D seismic section (see image below).
Task:
- Identify at least three different geological features present in the seismic section.
- Explain how you can tell what these features are based on the seismic data.
- Based on your interpretation, describe the potential for oil and gas reserves in this area.
Image: Insert a simple 2D seismic section image here. It should be clear enough to identify basic features like sedimentary layers, faults, and possible traps.
Exercise Correction
The correction should provide guidance on identifying features, explaining their characteristics, and suggesting possible oil and gas potential based on the provided seismic section. It should include a detailed explanation of the features identified by the student and how they relate to oil and gas exploration. The correction should also provide a concise summary of the potential for oil and gas reserves based on the identified features.
Books
- "Seismic Exploration: An Introduction" by Robert E. Sheriff - A comprehensive and accessible introduction to seismic methods, covering both 2D and 3D techniques.
- "Geophysical Exploration: An Introduction to Geophysical Methods for Exploration Geologists" by K. Kearey and I. Brooks - A broad overview of geophysical methods, including a section on seismic exploration.
- "Seismic Data Acquisition and Processing" by P.M. Daley - Provides a detailed explanation of the acquisition and processing of seismic data, including 2D techniques.
Articles
- "2D Seismic Reflection Data Acquisition and Processing" by John C. Bancroft - A detailed article on the acquisition, processing, and interpretation of 2D seismic data.
- "The Evolution of Seismic Exploration: From 2D to 3D and Beyond" by T.J. Ulrych - A review of the development of seismic exploration techniques, discussing the importance of 2D seismic in its historical context.
- "2D Seismic Data Interpretation for Exploration and Development" by A.K. Goodman - Focuses on the interpretation of 2D seismic data in the context of hydrocarbon exploration and development.
Online Resources
- SEG (Society of Exploration Geophysicists) website: https://seg.org/ - Offers access to articles, journals, and resources related to seismic exploration.
- EAGE (European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers) website: https://www.eage.org/ - Provides resources and information on various aspects of geosciences, including seismic exploration.
- Wikipedia entry on "Seismic Reflection": https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Seismic_reflection - A comprehensive overview of seismic reflection methods, including 2D techniques.
Search Tips
- Use specific keywords: "2D seismic survey," "2D seismic data processing," "2D seismic interpretation."
- Combine keywords with industry names: "2D seismic oil and gas," "2D seismic geotechnical engineering," "2D seismic groundwater."
- Include location or specific geological formations: "2D seismic North Sea," "2D seismic Permian Basin," "2D seismic fault mapping."
- Search for academic articles: Use Google Scholar and filter by publication year and author.
Techniques
Chapter 1: Techniques
2D Seismic Acquisition: A Journey into the Earth's Depths
2D seismic surveys employ a range of techniques to capture sound waves and translate them into interpretable data. Here's a breakdown of the key steps involved:
1. Source Generation:
- Vibroseis: A specialized truck uses a vibrating plate to generate controlled seismic waves into the ground. This technique is common for land surveys.
- Airgun Arrays: In marine surveys, airguns are towed behind a vessel, releasing bursts of compressed air that create sound waves. The number and configuration of airguns influence the energy and resolution of the signal.
- Explosives: While less common today due to environmental concerns, explosive charges can be used in certain situations to generate powerful seismic waves.
2. Recording the Echoes:
- Geophones: Land surveys utilize geophones, which are sensors that convert ground vibrations into electrical signals. Geophones are deployed along a line, spaced at regular intervals.
- Hydrophones: Marine surveys employ hydrophones, which are underwater microphones that capture sound waves traveling through water. They are typically mounted on cables towed behind a vessel.
3. Data Acquisition:
- Survey Lines: 2D seismic surveys are conducted along straight lines, often kilometers in length. The line spacing and orientation are determined by the geological objectives and the desired resolution.
- Navigation and Positioning: Precise GPS systems are used to accurately record the location of the source and receivers, ensuring accurate data interpretation.
4. Data Processing and Interpretation:
- Raw Data Processing: The recorded data is processed to remove noise and enhance the signal. This involves steps like filtering, deconvolution, and migration.
- Seismic Sections: Processed data is displayed as seismic sections, which depict the subsurface in terms of reflectivity. Different geological features exhibit varying reflectivity patterns, aiding in interpretation.
5. Interpretation and Analysis:
- Geologic Expertise: Geologists analyze seismic sections, combining their understanding of the area's geology with the observed patterns. They identify faults, folds, sedimentary layers, and other features.
- Interpretation Software: Advanced software tools allow geologists to manipulate and analyze seismic data, helping to visualize and interpret the subsurface structure.
Chapter 2: Models
Understanding the Subsurface: Seismic Models in 2D Surveys
2D seismic surveys rely on models to interpret the observed data and extrapolate information about the subsurface. These models provide a framework for understanding the propagation of seismic waves and how they are affected by the geological structures encountered.
1. Acoustic Impedance Model:
- Basis: This model considers the acoustic impedance of different rock types, which is a measure of their resistance to the passage of sound waves.
- Application: Variations in acoustic impedance between layers cause reflections of seismic waves, creating the patterns seen in seismic sections.
- Limitations: This model assumes that the subsurface is composed of homogeneous layers with distinct acoustic impedance values.
2. Velocity Model:
- Basis: This model focuses on the speed at which seismic waves travel through different rock types. Velocity varies based on the density and composition of the rocks.
- Application: Velocity models help correct for variations in wave travel times, allowing accurate depth determination and structural analysis.
- Limitations: Real-world geology is often more complex than assumed in simple velocity models, requiring more sophisticated techniques.
3. Stratigraphic Model:
- Basis: This model uses geological principles to interpret the observed seismic patterns in terms of rock layers and their depositional history.
- Application: Stratigraphic models help identify different sedimentary environments, understand the sequence of geological events, and locate potential hydrocarbon traps.
- Limitations: The interpretation of seismic data requires expert geological knowledge and can be influenced by uncertainties in the model.
4. Geomechanical Model:
- Basis: This model incorporates the mechanical properties of rocks, such as strength, stiffness, and porosity, to understand the behaviour of the subsurface under stress.
- Application: Geomechanical models are crucial for optimizing drilling operations, evaluating reservoir properties, and assessing seismic risks.
- Limitations: Geomechanical models require significant data and expertise to build and validate, making them more complex than other models.
5. Reservoir Model:
- Basis: This model focuses on the characteristics of a reservoir, such as its size, shape, fluid content, and flow properties.
- Application: Reservoir models are essential for estimating the volume of hydrocarbons, predicting production rates, and designing efficient extraction strategies.
- Limitations: Reservoir models rely on multiple sources of data, including seismic surveys, well logs, and core samples. They require sophisticated techniques to integrate these data sources and account for uncertainties.
Chapter 3: Software
2D Seismic Interpretation: From Data to Insights
The raw data collected during a 2D seismic survey is just the beginning. Powerful software tools are crucial to process, visualize, and interpret the seismic data, transforming it into valuable geological insights.
1. Data Processing Software:
- Seismic Processing: Software packages like GeoGraphix and OpendTect are used for complex data processing tasks, including noise reduction, deconvolution, and migration.
- Velocity Model Building: Tools like VelocityStudio and Hampson-Russell allow building velocity models to account for variations in wave travel times.
2. Interpretation Software:
- Seismic Visualization: Programs like Petrel and Landmark provide interactive 3D visualization capabilities to analyze seismic sections and identify geological features.
- Attribute Analysis: Software like Seismic Micro-Technology and Geoteric allows extracting various attributes from seismic data to enhance interpretation and identify subtle features.
3. Modeling Software:
- Geologic Modeling: Programs like SKUA and Gocad facilitate building 3D geological models based on seismic interpretation and other data sources.
- Reservoir Simulation: Software packages like ECLIPSE and CMG allow simulating the flow of fluids in reservoirs, predicting production behavior and optimizing extraction strategies.
4. Specialized Software:
- Fault Interpretation: Tools like Fault Interpretation and Fault Seal help analyze and interpret faults, assessing their impact on reservoir integrity and hydrocarbon migration.
- Rock Physics: Software like Rock Physics Toolkit and PetroMod allows relating seismic data to rock properties, improving the accuracy of interpretation and reservoir characterization.
5. Open Source Tools:
- Seismic Unix: This powerful, open-source package provides a wide range of processing and analysis tools, making it valuable for academic research and smaller companies.
- OpendTect: This open-source software offers a user-friendly interface for seismic data interpretation, making it accessible to a wider range of users.
Chapter 4: Best Practices
Maximizing the Value of 2D Seismic: Best Practices for Success
To ensure a successful 2D seismic survey and maximize its value, adhering to best practices is crucial.
1. Planning and Design:
- Clear Objectives: Define the specific geological objectives and the information needed to achieve them.
- Survey Design: Carefully design the survey line spacing, orientation, and acquisition parameters to achieve the desired resolution and coverage.
- Environmental Considerations: Minimize environmental impact by choosing appropriate acquisition techniques and adhering to regulations.
2. Data Acquisition:
- Quality Control: Implement rigorous quality control measures to ensure data accuracy and reliability.
- Calibration and Monitoring: Regularly calibrate equipment and monitor data acquisition parameters for optimal performance.
- Documentation: Maintain thorough documentation of all acquisition parameters, data processing steps, and interpretation results.
3. Data Processing and Interpretation:
- Experienced Interpreters: Engage experienced geologists and geophysicists with expertise in the specific geological setting.
- Multidisciplinary Collaboration: Encourage collaboration between geologists, geophysicists, and engineers to integrate data from different sources and improve interpretation.
- Validation and Uncertainty Analysis: Validate interpretations against well data, core samples, and other geological information. Conduct uncertainty analysis to assess the reliability of the results.
4. Communication and Reporting:
- Clear and Concise Reports: Communicate findings effectively through comprehensive and well-organized reports.
- Visualization and Presentations: Use visualizations and presentations to effectively convey complex data and interpretations to stakeholders.
- Dissemination of Knowledge: Share findings and best practices with the wider community to foster learning and innovation.
5. Continuous Improvement:
- Stay Updated on Technology: Continuously seek and implement new technologies and techniques to improve data quality and interpretation.
- Learn from Experience: Analyze past surveys and identify areas for improvement in future projects.
- Share Lessons Learned: Disseminate knowledge about successes and challenges to guide future 2D seismic projects.
Chapter 5: Case Studies
Unveiling Earth's Secrets: Real-World Applications of 2D Seismic
2D seismic surveys have played a pivotal role in advancing our understanding of the Earth and facilitating the exploration and development of natural resources. Here are examples of real-world applications:
1. Oil and Gas Exploration:
- North Sea Discoveries: 2D seismic surveys were instrumental in identifying and characterizing numerous oil and gas reservoirs in the North Sea, contributing significantly to the region's energy production.
- Gulf of Mexico Exploration: In the Gulf of Mexico, 2D seismic surveys have helped map complex geological structures and delineate potential hydrocarbon traps, leading to the discovery of vast oil and gas reserves.
2. Mineral Exploration:
- Copper Deposits in Chile: 2D seismic surveys have been used to identify and map copper deposits in Chile, aiding in the development of new mines and supporting the country's copper industry.
- Diamond Exploration in Canada: Seismic surveys have helped explore for kimberlite pipes, which host diamond deposits, in Canada, contributing to the discovery of new diamond mines.
3. Earthquake Studies:
- San Andreas Fault Mapping: 2D seismic surveys have provided valuable insights into the structure and activity of the San Andreas Fault, helping to assess earthquake hazards and inform disaster preparedness efforts.
- Subduction Zones: Seismic surveys have been used to map subduction zones, where one tectonic plate slides beneath another, contributing to our understanding of earthquake generation and tsunami risks.
4. Groundwater Management:
- Aquifer Mapping: 2D seismic surveys can be used to map the extent and properties of groundwater aquifers, helping to manage groundwater resources and ensure sustainable water supplies.
- Contamination Detection: Seismic surveys can help identify potential sources of contamination in aquifers, allowing for timely intervention and remediation.
5. Geotechnical Engineering:
- Construction Site Evaluation: 2D seismic surveys can be used to evaluate the subsurface conditions at construction sites, ensuring safe and stable foundations for buildings and infrastructure projects.
- Tunnel Planning: Seismic surveys can aid in the planning of tunnel construction, identifying potential geological hazards and optimizing tunnel alignments.
These case studies highlight the diverse applications of 2D seismic surveys and demonstrate their crucial role in understanding the Earth's subsurface, supporting resource exploration, and mitigating natural hazards. As technology advances, 2D seismic techniques will continue to evolve, providing increasingly detailed insights into the hidden secrets of our planet.
- 3D Seismic 3D Seismic: Peering into the …
- Check Shot Survey (seismic) Unveiling Earth's Secrets: Un…
- Coherence (seismic) Coherence: Unveiling the Secr…
- Curvature (seismic) Unmasking the Hidden Depths: …
- Deconvolution (seismic) Deconvolution: Unveiling the …
- Density Contrast (seismic) Density Contrast: A Key to Un…
- Density-Depth Function (seismic) Understanding Density-Depth F…
- Depth Migration (seismic) Unraveling the Depths: Depth …
- DMO (seismic) Understanding DMO (Seismic) i…
- DZO (seismic) DZO: Elevating Seismic Resolu…
- ESS (seismic) ESS: Unveiling Secrets Beneat…
- Euler Method (seismic) Unlocking the Depths: The Eul…
- Frequency Domain (seismic) Delving into the Depths: Freq…
- Gamma (seismic) Gamma: Unlocking Earth's Secr…
- Gardner’s Equation (seismic) Gardner's Equation: A Seismic…
- Gather (seismic) Gather (Seismic): A Window in…
- Gradiometer (seismic) Gradiometers: Unlocking Secre…
- Gravity Unit (seismic) Gravity Units (gu) in Oil & G…
- High Density Basement (seismic) The Unseen Anchor: Understand…
- 4D Seismic Unveiling the Secrets of Time…
- Application for Expenditure Justification Navigating the Appl… Project Planning & Scheduling
- Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled ("BCWS") Understanding Budge… Cost Estimation & Control
- Battery limit Understanding Batte… General Technical Terms
- DV Tool (cementing) DV Tool: A Crucial … Drilling & Well Completion
- TOC TOC: Understanding … General Technical Terms
Comments