Drilling & Well Completion
horsepower
Horsepower: The Unsung Hero of Drilling and Well Completion
In the world of drilling and well completion, horsepower is more than just a unit of measure – it’s the driving force behind every operation. Understanding horsepower is crucial for optimizing performance, ensuring safety, and ultimately, achieving success in extracting valuable resources from beneath the earth.
Defining Horsepower:
Horsepower (hp) quantifies the rate at which work is done. One horsepower represents the amount of power required to lift 550 pounds one foot in one second. This seemingly simple definition translates into the ability of a machine to perform a specific amount of work in a given timeframe. In drilling and well completion, horsepower drives the powerful machinery that tackles the demanding tasks of drilling, cementing, and fracking.
Horsepower in Action:
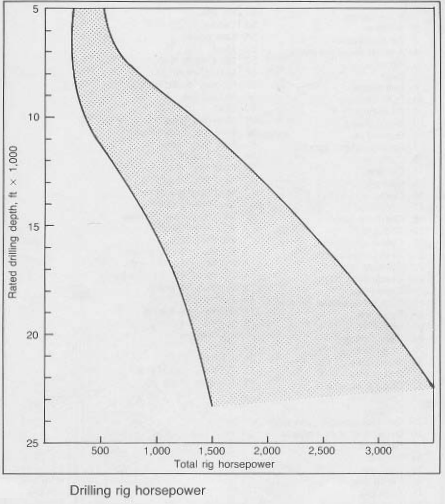
- Drilling Rigs: Horsepower fuels the rotary tables, mud pumps, and hoisting systems that propel drilling operations. The power required for a drilling rig depends on various factors including depth, formation hardness, and drilling fluid properties. More horsepower means greater drilling capacity and efficiency.
- Cementing Operations: Mixing cement slurry for wellbore cementing requires significant horsepower to ensure proper mixing and injection. Adequate horsepower ensures a smooth and consistent slurry, leading to successful cementing.
- Fracking Operations: High-pressure pumps, integral to hydraulic fracturing, rely heavily on horsepower to deliver the necessary force to create fractures in the formation and release hydrocarbons. Increased horsepower translates into faster and more efficient fracking, maximizing production.
Beyond the Numbers:
While the numerical value of horsepower is essential, it’s also vital to consider the context. In drilling and well completion, horsepower isn’t just about brute force – it's about:
- Efficiency: Optimizing horsepower usage allows for maximum output with minimal energy consumption, resulting in cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
- Safety: Adequate horsepower ensures equipment can handle the demands of the operation, preventing breakdowns and potential safety hazards.
- Reliability: Consistent horsepower delivery is crucial for maintaining continuous operations, minimizing downtime and maximizing production.
The Future of Horsepower:
As the industry evolves, the role of horsepower continues to adapt. Advances in technology, like electric and hybrid drilling rigs, are introducing new ways to utilize and manage power. However, the fundamental concept of horsepower as a measure of work remains central to the efficient and successful operation of drilling and well completion activities.
In conclusion, horsepower is the backbone of drilling and well completion. Understanding its role and optimizing its application are crucial for ensuring successful operations, maximizing efficiency, and achieving profitability in this demanding and vital industry.
Test Your Knowledge
Horsepower Quiz:
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What does horsepower measure? a) The amount of work done in a given time. b) The speed of a machine. c) The size of a machine. d) The weight a machine can lift.
Answer
a) The amount of work done in a given time.
2. Which of these operations DOES NOT directly rely on horsepower? a) Drilling. b) Cementing. c) Fracking. d) Well logging.
Answer
d) Well logging.
3. What is a benefit of optimizing horsepower usage? a) Increased safety risks. b) Lower operating costs. c) Reduced drilling speed. d) Increased environmental impact.
Answer
b) Lower operating costs.
4. What is the main advantage of using more horsepower in a fracking operation? a) Reduced risk of wellbore collapse. b) Faster and more efficient fracturing. c) Reduced environmental impact. d) Increased drilling depth.
Answer
b) Faster and more efficient fracturing.
5. Why is reliable horsepower delivery important in drilling and well completion? a) To prevent breakdowns and downtime. b) To reduce drilling speed. c) To increase drilling depth. d) To reduce the need for maintenance.
Answer
a) To prevent breakdowns and downtime.
Horsepower Exercise:
Scenario: A drilling rig is operating at a depth of 10,000 feet. The drilling mud pump has a horsepower rating of 1,500 hp. The rig operator notices a decrease in drilling rate and suspects the pump may be underpowered.
Task: Research the factors that affect drilling rate and explain how horsepower plays a role in the drilling process. Based on the scenario, provide possible reasons why the drilling rate may have decreased despite the high horsepower rating of the pump.
Exercice Correction
**Factors Affecting Drilling Rate:** * **Formation Hardness:** Harder formations require more power to penetrate. * **Drilling Fluid Properties:** Viscosity and density of the mud affect the drilling rate. * **Bit Type and Size:** Larger, more aggressive bits require higher horsepower. * **Hole Diameter:** Larger hole diameters require more mud circulation and horsepower. * **Mud Pump Capacity:** Insufficient mud pump horsepower can limit the rate of penetration. **Possible Reasons for Decreased Drilling Rate:** * **Formation Change:** The drilling rig might have encountered a harder rock layer, requiring more power. * **Mud Pump Malfunction:** The pump may not be operating at full capacity due to a mechanical issue, even though it has a high horsepower rating. * **Bit Wear:** A worn-out drill bit can reduce drilling efficiency. * **Hole Stability Issues:** Problems with hole stability (e.g., cavings) can slow down drilling progress. **Horsepower Role:** Horsepower is critical in providing the necessary energy to circulate the drilling mud, which in turn helps to remove cuttings, cool the bit, and maintain hole stability. Insufficient horsepower can lead to decreased drilling rate, increased wear on the bit, and potential wellbore stability issues.
Books
- Drilling Engineering: Principles and Practices by M.E. Economides and K.G. Nolte (This comprehensive text covers drilling operations in detail, including the role of horsepower in various aspects.)
- Petroleum Engineering: Drilling and Well Completions by S.P. C. and M.C. (This book provides a detailed analysis of drilling and well completion techniques, including the importance of horsepower in each phase.)
- Well Completion Design by E.B. and W.C. (This book focuses on the design and engineering of well completions, highlighting the essential role of horsepower in successful completions.)
Articles
- The Role of Horsepower in Drilling and Well Completion by (This article discusses the significance of horsepower in optimizing performance and efficiency in drilling and well completion.)
- Optimizing Horsepower for Enhanced Drilling Performance by (This article explores various techniques for maximizing horsepower utilization to improve drilling efficiency and minimize costs.)
- The Impact of Horsepower on Well Completion Costs by (This article examines the relationship between horsepower requirements and overall well completion costs, providing insights into cost optimization strategies.)
Online Resources
- Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE): The SPE website offers a vast library of technical papers and articles related to drilling, well completion, and related engineering aspects. Search for "horsepower" or "power" to find relevant content.
- American Petroleum Institute (API): The API website provides standards and guidelines for the oil and gas industry, including specifications for drilling equipment and horsepower requirements.
- Oil & Gas Journal (OGJ): OGJ publishes industry news, technical articles, and research related to all aspects of oil and gas production, including drilling and well completion. Search their archives for articles on horsepower.
- World Oil: This journal offers articles and technical information on drilling, production, and related technologies, including insights on the role of horsepower in drilling and well completion.
Search Tips
- Use specific search terms like "horsepower drilling," "horsepower well completion," "drilling rig horsepower," etc.
- Combine terms with keywords like "efficiency," "optimization," "costs," "safety," and "performance."
- Use quotation marks to search for specific phrases like "horsepower requirements for fracking."
- Explore advanced search options to refine your search results by date, source, file type, etc.
Techniques
Horsepower in Drilling and Well Completion: A Deeper Dive
This expands on the provided text, breaking it down into chapters. Note that some sections will be brief due to the inherent limitations of the original text's scope. More detailed information would require significant additional research.
Chapter 1: Techniques for Optimizing Horsepower Utilization
This chapter focuses on practical methods for maximizing the efficiency and effectiveness of horsepower in drilling and well completion operations.
- Load Management: Efficient load management is crucial. This involves matching the horsepower supplied to the actual load demands of the equipment at any given moment. Overpowering leads to wasted energy; underpowering risks equipment failure. Real-time monitoring systems and advanced control algorithms are key tools.
- Power Transmission Optimization: Minimizing power losses during transmission is critical. This requires regular maintenance of belts, chains, gears, and hydraulic systems to ensure optimal efficiency. The selection of appropriate transmission components for the specific application is also vital.
- Drilling Parameter Optimization: Careful selection of drilling parameters (weight on bit, rotary speed, mud flow rate) can significantly impact the efficiency of horsepower usage. Advanced drilling automation systems can help optimize these parameters in real-time.
- Mud System Optimization: The properties of the drilling mud significantly influence the horsepower required. Optimizing mud rheology and minimizing friction losses can reduce the horsepower needed for drilling.
- Preventative Maintenance: Regular maintenance schedules for all horsepower-consuming equipment is essential to prevent unexpected downtime and maximize operational efficiency. This includes regular inspections, lubrication, and component replacements as needed.
Chapter 2: Models for Predicting and Managing Horsepower Requirements
This chapter explores the use of models to predict horsepower needs and manage its application effectively.
- Empirical Models: Simple models based on historical data and operational experience can estimate horsepower requirements for different drilling scenarios. These can be useful for initial planning.
- Simulation Models: More sophisticated simulation models, often using finite element analysis (FEA) or computational fluid dynamics (CFD), can provide a detailed prediction of horsepower demands under various conditions. These are particularly valuable for complex operations.
- Predictive Maintenance Models: Data-driven models can predict potential equipment failures based on operational parameters and historical data, allowing for proactive maintenance to prevent unexpected downtime related to horsepower loss.
Chapter 3: Software and Technology for Horsepower Monitoring and Control
This chapter examines the software and technologies used to monitor and manage horsepower in drilling and well completion.
- Drilling Automation Systems: These systems use sensors and control algorithms to optimize drilling parameters in real-time, maximizing the use of available horsepower.
- Real-Time Monitoring Systems: These systems continuously monitor the power consumption of various equipment components, allowing for early detection of anomalies and potential problems.
- Data Acquisition and Analysis Software: Specialized software packages are used to collect, analyze, and visualize data on horsepower consumption, enabling better understanding of operational efficiency and identifying areas for improvement.
- Predictive Maintenance Software: Software capable of predicting equipment failures based on operational data can minimize unscheduled downtime and optimize horsepower utilization.
Chapter 4: Best Practices for Horsepower Management in Drilling and Well Completion
This chapter outlines best practices to ensure safe and efficient use of horsepower.
- Regular Training and Competency Assessment: Personnel must be adequately trained in the safe operation and maintenance of high-powered equipment.
- Strict Adherence to Safety Regulations: All operations should comply with relevant safety regulations and standards to prevent accidents and injuries.
- Effective Communication and Coordination: Clear communication and coordination between different teams are essential to ensure safe and efficient operations.
- Proactive Maintenance Strategy: Implementing a proactive maintenance strategy, focusing on preventative measures, is key to minimizing downtime.
- Continuous Improvement Initiatives: Regular review of operations and implementation of continuous improvement initiatives can further optimize horsepower usage.
Chapter 5: Case Studies of Horsepower Optimization in Drilling and Well Completion
This chapter would showcase real-world examples of successful horsepower optimization projects. (Due to the lack of specific data in the original text, this section cannot be fully fleshed out here. Real-world case studies would require independent research.) Examples could include:
- A case study illustrating how improved mud system design reduced horsepower requirements, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
- A case study demonstrating the effectiveness of predictive maintenance in preventing costly downtime associated with power equipment failures.
- A case study showing how real-time monitoring systems improved the efficiency of a drilling operation by optimizing drilling parameters.
This expanded structure provides a more comprehensive overview of horsepower's critical role in drilling and well completion. Remember that each chapter would require significant expansion with detailed information and specific examples.
- Application for Expenditure Justification Navigating the Appl… Project Planning & Scheduling
- Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled ("BCWS") Understanding Budge… Cost Estimation & Control
- Battery limit Understanding Batte… General Technical Terms
- DV Tool (cementing) DV Tool: A Crucial … Drilling & Well Completion
- TOC TOC: Understanding … General Technical Terms
Comments