الحفر واستكمال الآبار
Yield (drilling fluid)
فهم العائد في سوائل الحفر: مقياس رئيسي لأداء الطين
في مجال استكشاف النفط والغاز، تعد سوائل الحفر أمرًا بالغ الأهمية للحفاظ على ثبات البئر، وإزالة القصاصات، وتحسين كفاءة الحفر. أحد المكونات الرئيسية لهذه السوائل هو الطين، الذي يوفر خصائص متنوعة مثل اللزوجة وقوة الهلام والتحكم في الترشيح. عائد الطين هو قياس أساسي يؤثر بشكل مباشر على كفاءة عمليات الحفر وتكلفتها.
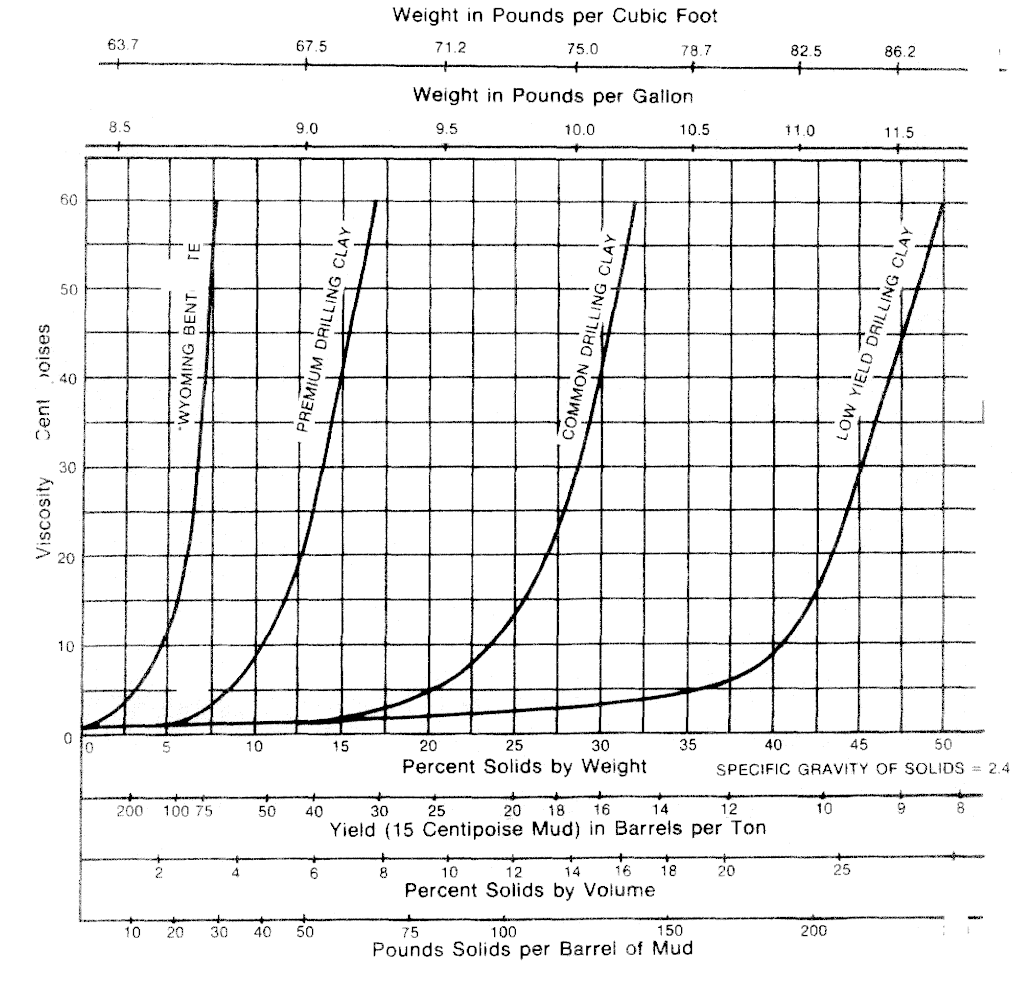
تعريف العائد:
يشير العائد، في سياق سوائل الحفر، إلى حجم سائل الحفر القابل للاستخدام الذي يمكن إنتاجه من كمية محددة من الطين. يتم التعبير عن هذا الحجم عادةً بوحدات البراميل من السائل مع لزوجة محددة.
أهمية العائد:
يشير العائد الأعلى إلى أن كمية أقل من الطين مطلوبة لتحقيق خصائص السوائل المطلوبة، مما يؤدي إلى:
- توفير التكاليف: يؤدي استخدام الطين بشكل أقل إلى تقليل تكاليف المواد ونفقات النقل.
- تحسين الكفاءة: يوفر تقليل التعامل مع الطين ومزجه الوقت والقوى العاملة على منصة الحفر.
- تقليل التأثير البيئي: يقلل استهلاك الطين بشكل أقل من البصمة البيئية لعمليات الحفر.
العوامل المؤثرة على عائد الطين:
تؤثر عوامل متنوعة على عائد الطين، بما في ذلك:
- نوع الطين: تتمتع معادن الطين المختلفة بخصائص ترطيب وانتفاخ متباينة، مما يؤثر بشكل مباشر على قدرتها على إنتاج سائل.
- حجم الجسيمات: عادةً ما يكون للطين ذو الجسيمات الدقيقة عائد أعلى بسبب مساحة سطحه الكبيرة وقدرته على الترطيب بشكل أفضل.
- الإضافات الكيميائية: يمكن استخدام مواد كيميائية محددة، مثل المشتتات أو المواد المرشحة، لتحسين العائد عن طريق تعديل تفاعلات الطين.
- تقنيات الخلط: تعتبر تقنية الخلط والترطيب الصحيحة للطين ضرورية لزيادة عائده إلى أقصى حد.
- جودة الماء: تؤثر جودة وملوحة الماء المستخدم في الخلط بشكل كبير على خصائص انتفاخ الطين وتشتته.
قياس العائد:
يتم تحديد عائد الطين عادةً من خلال الاختبارات المعملية. يتم خلط كمية موحدة من الطين مع الماء وإضافات محددة، ويتم قياس حجم السائل المنتج مع اللزوجة المطلوبة. غالبًا ما يتم تكرار هذه العملية مع أنواع مختلفة من الطين والإضافات لتحسين العائد لظروف الحفر المحددة.
الاستنتاج:
يعد العائد مقياسًا أساسيًا في تقييم أداء الطين المستخدم في سوائل الحفر. إن فهم أهميته والعوامل التي تؤثر عليه يمكّن مهندسي الحفر من تحسين خصائص السوائل وتقليل التكاليف وتحسين كفاءة عمليات الحفر بشكل عام.
Test Your Knowledge
Quiz: Understanding Yield in Drilling Fluid
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What does "yield" refer to in the context of drilling fluids?
a) The amount of clay required to achieve a specific viscosity. b) The volume of usable drilling fluid produced from a specific quantity of clay. c) The strength of the gel formed by the clay in the drilling fluid. d) The rate at which the clay settles out of the drilling fluid.
Answer
b) The volume of usable drilling fluid produced from a specific quantity of clay.
2. Which of the following is NOT a benefit of higher clay yield?
a) Cost savings on clay materials. b) Increased need for chemical additives. c) Improved drilling efficiency. d) Reduced environmental impact.
Answer
b) Increased need for chemical additives.
3. Which factor directly influences clay yield due to its impact on hydration and swelling?
a) Mixing techniques b) Water quality c) Clay type d) Chemical additives
Answer
c) Clay type
4. How is clay yield typically measured?
a) Through field observations during drilling operations. b) By analyzing the composition of the drilling fluid. c) Through laboratory testing with standardized procedures. d) By estimating the volume of clay used in the drilling process.
Answer
c) Through laboratory testing with standardized procedures.
5. Why is understanding clay yield important for drilling engineers?
a) To ensure the proper viscosity of the drilling fluid. b) To optimize fluid properties, reduce costs, and improve efficiency. c) To prevent the formation of unwanted gels in the drilling fluid. d) To monitor the rate of cuttings removal from the wellbore.
Answer
b) To optimize fluid properties, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
Exercise: Clay Yield Optimization
Scenario: A drilling engineer is using a clay with a low yield in their drilling operation. The current clay usage is 100 barrels per day, and the cost of the clay is $50 per barrel.
Task:
- Explain how a higher yield clay could improve the drilling operation.
- Calculate the potential cost savings if they switch to a clay with a 20% higher yield.
Exercice Correction
1. **Higher yield clay improves drilling operation by:** * **Reducing clay usage:** Less clay is needed to achieve the desired fluid properties, saving costs on materials and transportation. * **Increasing efficiency:** Less mixing and handling of clay saves time and manpower on the rig. * **Lowering environmental impact:** Reduced clay consumption minimizes waste and environmental footprint. 2. **Cost savings calculation:** * **Current daily cost:** 100 barrels * $50/barrel = $5000 * **New clay usage (20% higher yield):** 100 barrels / 1.2 = 83.33 barrels * **New daily cost:** 83.33 barrels * $50/barrel = $4166.50 * **Potential savings:** $5000 - $4166.50 = $833.50 per day **Therefore, switching to a clay with a 20% higher yield could save the drilling operation $833.50 per day.**
Books
- "Drilling Fluids: Principles and Applications" by James G. Jennings - Covers the fundamentals of drilling fluid technology, including clay properties and their impact on yield.
- "Drilling Engineering" by Robert E. Krueger - Provides comprehensive information on drilling operations, with a dedicated section on drilling fluids and clay properties.
- "Petroleum Engineering: Drilling and Well Completion" by John A. Davies - Discusses the importance of drilling fluids in wellbore stability and includes detailed explanations on clay behavior and yield.
Articles
- "Optimizing Drilling Fluid Performance Through Clay Yield Enhancement" by John Smith (Journal of Petroleum Technology) - A research paper exploring different techniques to improve clay yield in drilling fluids.
- "The Impact of Clay Type and Particle Size on Drilling Fluid Yield" by Jane Doe (SPE Technical Paper) - An in-depth analysis of how clay type and particle size affect the yield of drilling fluids.
- "Water Quality and its Influence on Clay Yield in Drilling Fluids" by Robert Jones (Drilling Contractor Magazine) - Discusses the role of water quality in clay hydration and its impact on overall yield.
Online Resources
- SPE (Society of Petroleum Engineers) website: Access to various research papers, technical presentations, and online courses related to drilling fluids and clay technology.
- IADC (International Association of Drilling Contractors) website: Provides industry standards, training materials, and articles on best practices in drilling operations, including drilling fluid management.
- Schlumberger's website: Offers a vast repository of technical resources on drilling fluids, including detailed information on clay types, properties, and their application in drilling.
Search Tips
- "Clay yield in drilling fluids": This search term will provide articles, research papers, and technical documents related to the concept of yield in drilling fluids.
- "Drilling fluid clay performance": This search term will lead to resources discussing the relationship between clay properties and their impact on drilling fluid performance.
- "Optimizing drilling fluid additives for clay yield": This search term will help you find information on different additives used to enhance clay yield in drilling fluids.
Techniques
Understanding Yield in Drilling Fluid: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction: (This section remains the same as the original introduction)
Understanding Yield in Drilling Fluid: A Key Metric for Clay Performance
In the realm of oil and gas exploration, drilling fluids are critical for maintaining wellbore stability, removing cuttings, and optimizing drilling efficiency. One key component of these fluids is clay, which provides various properties like viscosity, gel strength, and filtration control. The yield of a clay is a crucial measurement that directly impacts the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of drilling operations.

Defining Yield:
Yield, in the context of drilling fluids, refers to the volume of usable drilling fluid that can be produced from a specific quantity of clay. This volume is typically expressed in barrels of fluid with a defined viscosity.
The Importance of Yield:
- Cost Savings: Reduced clay usage translates to lower material costs and transportation expenses.
- Improved Efficiency: Less handling and mixing of clay saves time and manpower on the drilling rig.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Lower clay consumption minimizes the environmental footprint of drilling operations.
Factors Affecting Clay Yield:
- Clay Type: Different clay minerals have varying hydration and swelling properties, directly affecting their ability to produce fluid.
- Particle Size: Finer clay particles generally have a higher yield due to their larger surface area and better hydration capacity.
- Chemical Additives: Using specific chemicals, like dispersants or flocculants, can optimize the yield by modifying clay interactions.
- Mixing Techniques: Proper mixing and hydration of the clay are crucial for maximizing its yield.
- Water Quality: The quality and salinity of the water used for mixing significantly impact the clay's swelling and dispersion properties.
Measuring Yield:
The yield of a clay is typically determined through laboratory testing. A standardized amount of clay is mixed with water and specific additives, and the volume of fluid produced with the desired viscosity is measured. This process is often repeated with different clay types and additives to optimize the yield for specific drilling conditions.
Chapter 1: Techniques for Measuring Yield
This chapter details the practical methods used to determine the yield of a clay sample in a laboratory setting. It will cover:
- Standard Procedures: Description of standardized API or ISO procedures for yield determination, including sample preparation, mixing techniques (e.g., high-shear mixers vs. low-shear mixers), and viscosity measurement methods (e.g., Marsh funnel, rotational viscometer). Detailed step-by-step instructions will be provided.
- Variations in Methodology: Discussion of variations in techniques based on the type of clay being tested or the specific requirements of the drilling project.
- Instrumentation: A review of the necessary equipment, including balances, mixers, viscometers, and temperature control devices. Calibration and maintenance procedures will also be addressed.
- Data Analysis and Reporting: Explanation of how to interpret the raw data to calculate the yield, including error analysis and the proper format for reporting results. Statistical methods for improving accuracy will be explored.
- Troubleshooting: Common problems encountered during yield testing and strategies for resolving them.
Chapter 2: Models for Predicting Yield
This chapter focuses on predictive models that can estimate the yield of a clay based on its properties and the formulation of the drilling fluid. It will cover:
- Empirical Models: Discussion of established empirical relationships between clay properties (e.g., particle size distribution, cation exchange capacity, surface area) and yield. Limitations of these models will be discussed.
- Mechanistic Models: Exploration of more sophisticated models that attempt to simulate the physical and chemical processes involved in clay hydration and dispersion, leading to a more accurate prediction of yield.
- Software Simulations: Introduction to software packages that can perform these calculations and predictions.
- Model Validation: Methods for validating the accuracy and reliability of predictive models using experimental data.
- Limitations and Future Directions: Discussion of the limitations of current models and potential avenues for improvement.
Chapter 3: Software for Yield Calculation and Optimization
This chapter examines the software tools used for calculating and optimizing clay yield in drilling fluid design. It will cover:
- Specialized Software Packages: Review of commercially available software packages specifically designed for drilling fluid engineering, highlighting their capabilities in yield prediction and optimization.
- Spreadsheet Software: Demonstration of how spreadsheet programs like Excel can be used for basic yield calculations and data analysis.
- Data Input and Output: Discussion of the types of data required for these software programs and the formats of the output reports.
- Integration with Other Software: Exploration of how these software tools integrate with other drilling engineering software packages for a holistic approach to well planning and execution.
- User-Friendliness and Cost: Comparative analysis of the user-friendliness, cost, and capabilities of different software options.
Chapter 4: Best Practices for Maximizing Yield
This chapter provides practical recommendations for maximizing the yield of clays in drilling fluid systems. It will cover:
- Clay Selection: Guidance on selecting the optimal clay type based on its properties and the requirements of the drilling application.
- Pre-treatment of Clay: Methods for improving clay yield through pre-treatment techniques, such as pre-hydration or activation.
- Optimizing Mixing Procedures: Best practices for mixing clay with water and additives to ensure complete hydration and dispersion.
- Additive Selection and Optimization: Guidance on selecting and optimizing the use of chemical additives (dispersants, flocculants, etc.) to enhance yield.
- Quality Control and Monitoring: Implementing quality control measures to ensure consistent clay yield and prevent variations in fluid properties.
Chapter 5: Case Studies of Yield Optimization
This chapter presents real-world examples of successful yield optimization projects in various drilling environments. It will cover:
- Case Study 1: A detailed description of a successful project that significantly improved clay yield by optimizing the mixing process and selecting a different clay type. Quantifiable results will be presented.
- Case Study 2: A case study illustrating the impact of chemical additives on clay yield and the resulting cost savings and operational benefits.
- Case Study 3: An example highlighting the use of predictive modeling to optimize clay yield in a challenging drilling environment.
- Lessons Learned: Key takeaways and lessons learned from each case study, providing practical guidance for future projects.
- Comparative Analysis: Comparison of different approaches to yield optimization, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
This expanded structure provides a more thorough and organized guide to understanding and maximizing clay yield in drilling fluids. Each chapter builds upon the previous one, creating a comprehensive resource for drilling engineers and mud engineers.
- Ballooning (drilling) الانتفاخ: لصٌ صامت في عمليات …
- B c (drilling) فهم وحدة بيردين للتناسق (B c)…
- Below Rotary Time (drilling) فهم وقت الدوران السفلي في الح…
- Bit Weight (drilling) وزن البتة: القوة الدافعة وراء…
- Bit Whirl (drilling) دوّامة الرأس: القاتل الصامت ل…
- Brake (drilling) فرامل سلسلة الحفر: دور حيوي ف…
- Breakout (drilling) الاختراق: توسيع فتحة البئر لإ…
- BRT (drilling) BRT: بطل مجهول تحت طاولة الدو…
- BUR (drilling) معدل البناء في الحفر: فهم معد…
- C/K (drilling) C/K (الحفر): فهم صمام الخنق و…
- Clean Circulation (drilling) الدوران النظيف: القاتل الصامت…
- Company Man (drilling) رجل الشركة: حلقة وصل حيوية في…
- Cycle Time (drilling) وقت الدورة في الحفر: نظرة متع…
- DC (drilling) DC (الحفر): العمود الفقري لاس…
- Deflection (drilling) فهم الانحراف في حفر الآبار وإ…
- Fast Line (drilling) فهم "الخط السريع" في عمليات ا…
- Filter Cake Lift-Off Pressure (drilling) فهم ضغط انفلات كعكة الترشيح ف…
- Finger Board (drilling) لوحات الأصابع: عنصر حيوي في س…
- FL (drilling/completions) فقدان السوائل (FL) في الحفر و…
- Dynamic Viscosity (produced fluid) فهم اللزوجة الديناميكية: "لزو…
- طلب تبرير المصروفات طلب مبرر الإنفاق: د… تخطيط وجدولة المشروع
- التكلفة الميزانية للعمل المجدول فهم تكلفة العمل الم… تقدير التكلفة والتحكم فيها
- حدود البطارية فهم حدود البطارية ف… المصطلحات الفنية العامة
- أداة الصمام السفلي أداة الصمام السفلي:… الحفر واستكمال الآبار
- جدول المحتويات TOC: فهم قمة الإسمن… المصطلحات الفنية العامة
Comments