الجيولوجيا والاستكشاف
Stratigraphic Trap
الكنوز الخفية: فهم المصائد الطبقية في استكشاف النفط والغاز
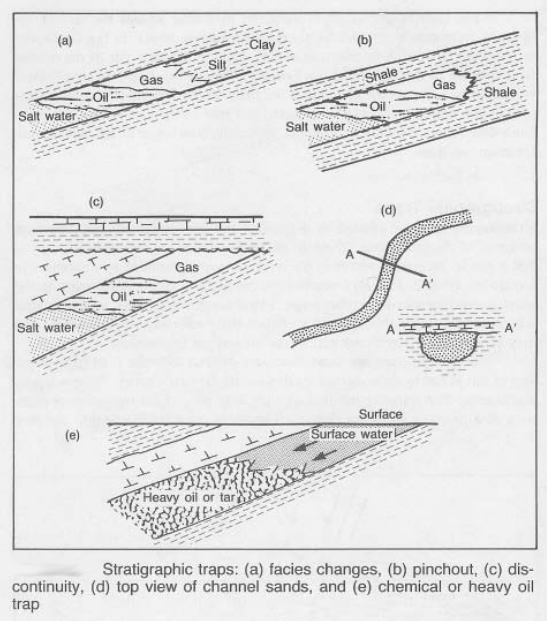
في رحلة البحث عن النفط والغاز، يسعى المستكشفون إلى تكوينات تُعرف باسم "المصائد"، حيث يمكن أن تتراكم الهيدروكربونات وتصبح قابلة للاستغلال التجاري. أحد أنواع هذه المصائد، ومنبع رئيسي لاكتشافات النفط والغاز، هو **المصيدة الطبقية**.
**ما هي المصيدة الطبقية؟**
تتشكل المصائد الطبقية بواسطة **تغيرات في طبقات الصخور (الطبقات)**، مما يخلق حاجزًا طبيعيًا يمنع الهيدروكربونات من الهجرة صعودًا والهروب. يمكن أن تحدث هذه التغييرات بسبب:
- انخفاض المسامية والنفاذية: تخيل اسفنجة. إذا ضغطت عليها، ستنخفض قدرتها على امتصاص الماء (المسامية) والسماح بتدفق الماء من خلالها (النفاذية). وبالمثل، في تشكيلات الصخور الرسوبية، يمكن أن تؤدي التغيرات في الضغط أو درجة الحرارة أو العمليات الجيولوجية إلى تقليل طبيعة الصخور المسامية، مما يشكل حاجزًا غير قابل للاختراق. هذا يحبس الهيدروكربونات أدناه.
- التغيرات الجانبية أو الرأسية في الليثولوجيا: تشير الليثولوجيا إلى الخصائص الفيزيائية للصخور. يمكن أن تؤدي التغيرات في الليثولوجيا، مثل الانتقال من حجر رملي مسامي إلى صخر طيني أقل مسامية، إلى إنشاء مانع يمنع الحركة الصاعدة للهيدروكربونات.
- التناقصات أو التقاطعات: تحدث هذه الظاهرة عندما ترقق طبقة الخزان تدريجيًا أو تنتهي فجأة، مما يشكل حاجزًا لهجرة الهيدروكربونات.
**أمثلة على المصائد الطبقية:**
- عدم التوافق: انقطاع في السجل الجيولوجي حيث تُغطى الصخور القديمة مباشرةً بصخور أحدث بكثير. يعمل سطح عدم التوافق كمانع، محبسًا الهيدروكربونات في خزان أسفله.
- التناقصات: طبقة خزان ترقق تدريجيًا إلى نقطة لا تصبح فيها مسامية بما يكفي لاحتواء الهيدروكربونات.
- الشعاب المرجانية: هذه الهياكل القديمة التي بنيت بواسطة الكائنات البحرية تخلق صخور كربونية مسامية تعمل كخزانات ممتازة. غالبًا ما تشكل حوافها حواجز، مما يمنع المزيد من الهجرة.
- رواسب القنوات: تتشكل هذه الرواسب من خلال ترسب الأنهار للرواسب في شكل يشبه القناة. يمكن أن تكون حواف القناة غير قابلة للاختراق، مما يحبس الهيدروكربونات داخل القناة نفسها.
الأهمية في استكشاف النفط والغاز:**
تُعد المصائد الطبقية ذات أهمية حيوية في استكشاف النفط والغاز لأنها توفر طريقة قابلة للتنبؤ بها وموثوقة لتحديد الخزانات المحتملة. غالبًا ما ترتبط بحقول نفط وغاز رئيسية في جميع أنحاء العالم. من خلال فهم العمليات الجيولوجية التي تخلق هذه المصائد، يمكن للمستكشفين تحديد المناطق ذات الاحتمالية العالية لتراكم الهيدروكربونات.
التحديات والابتكارات:**
بينما تُعد المصائد الطبقية أهدافًا قيمة، فإن استكشافها يطرح تحديات. تُستخدم التقنيات المتقدمة مثل التصوير الزلزالي والنمذجة ثلاثية الأبعاد وتسجيل الآبار عالية الدقة لخريطة ورسم هذه المصائد بدقة، مما يقلل من مخاطر الاستكشاف ويزيد من معدلات النجاح.
الاستنتاج:**
تُعد المصائد الطبقية مثالًا رائعًا على كيفية خلق العمليات الجيولوجية خزانات لموارد الطاقة لدينا. من خلال فهم تكوينها وتحديد خصائصها، يمكن لصناعة النفط والغاز الاستمرار في الكشف عن الكنوز الخفية تحت سطح الأرض.
Test Your Knowledge
Quiz: Stratigraphic Traps in Oil & Gas Exploration
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What is a stratigraphic trap?
(a) A trap formed by the movement of tectonic plates (b) A trap formed by changes in rock layers (c) A trap formed by volcanic activity (d) A trap formed by the presence of salt
Answer
The correct answer is **(b) A trap formed by changes in rock layers.** Stratigraphic traps are created by variations in the rock layers themselves.
2. Which of the following is NOT a factor that can create a stratigraphic trap?
(a) Decreases in porosity and permeability (b) Lateral or vertical changes in lithology (c) Pinchouts or truncations (d) The presence of faults
Answer
The correct answer is **(d) The presence of faults.** While faults can play a role in oil and gas accumulation, they are primarily associated with structural traps, not stratigraphic traps.
3. What is an unconformity?
(a) A type of rock that is particularly porous (b) A break in the geological record where older rocks are directly overlain by much younger rocks (c) A type of fold in the Earth's crust (d) A type of sediment that is easily eroded
Answer
The correct answer is **(b) A break in the geological record where older rocks are directly overlain by much younger rocks.** Unconformities are significant features in stratigraphy and can act as seals in stratigraphic traps.
4. Why are stratigraphic traps important in oil and gas exploration?
(a) They are easily identifiable from the surface (b) They are always associated with large reserves of oil and gas (c) They provide a predictable and reliable way to identify potential reservoirs (d) They are the only type of trap that can contain hydrocarbons
Answer
The correct answer is **(c) They provide a predictable and reliable way to identify potential reservoirs.** Stratigraphic traps offer a consistent and predictable way to find potential oil and gas accumulations.
5. What is a challenge associated with exploring stratigraphic traps?
(a) They are often located in remote areas (b) They can be difficult to map and characterize accurately (c) They are often associated with complex geological structures (d) All of the above
Answer
The correct answer is **(d) All of the above.** Exploring stratigraphic traps can involve several challenges, including location, complex mapping, and intricate geological features.
Exercise: Identifying Stratigraphic Traps
Scenario: You are a geologist working for an oil and gas exploration company. You are studying a subsurface geological map of a region with potential for hydrocarbon accumulation. The map shows a sequence of sedimentary rock layers:
- Layer A: Shale (impermeable)
- Layer B: Sandstone (porous and permeable)
- Layer C: Limestone (porous and permeable)
- Layer D: Shale (impermeable)
Instructions:
- Identify potential stratigraphic traps that could exist in this sequence.
- Explain the reasoning behind your identification.
- Draw a simple diagram illustrating the potential traps.
Exercice Correction
Potential Stratigraphic Traps:
- Pinchout Trap: Layer B (Sandstone) could pinch out towards the right or left, creating a barrier and trapping hydrocarbons in Layer B.
- Unconformity Trap: If there is an unconformity between Layer C and Layer D, the unconformity surface could act as a seal, trapping hydrocarbons in Layer C.
- Lateral Lithologic Change Trap: If Layer B (Sandstone) changes laterally into a shale layer (Layer D), this change in lithology would create a barrier, trapping hydrocarbons in Layer B.
Reasoning:
- Pinchout Trap: The gradual thinning or termination of a porous layer (Sandstone) creates an impermeable barrier, preventing upward migration of hydrocarbons.
- Unconformity Trap: An unconformity represents a period of erosion and deposition, creating a surface that acts as a seal, trapping hydrocarbons beneath it.
- Lateral Lithologic Change Trap: A change from a porous to an impermeable layer creates a lateral seal, trapping hydrocarbons within the porous layer.
Diagram:

Books
- Petroleum Geology: This comprehensive text covers various aspects of petroleum geology, including detailed sections on stratigraphic traps. Several authors have contributed to this field, so consider looking for recent editions from authors like:
- Gary D. Roberts: His "Petroleum Geology" book is a highly regarded resource for students and professionals.
- J.M. Hunt: His "Petroleum Geochemistry and Geology" provides insights into the formation and migration of hydrocarbons.
- William D. Rose: His "Petroleum Geology" offers a detailed exploration of sedimentary basins, reservoir rocks, and trap types.
- Reservoir Characterization: Books focusing on reservoir characterization often include sections on stratigraphic traps, exploring their formation and how to identify them. Examples include:
- Reservoir Geophysics: By R.G. Worthing
- Reservoir Sedimentology: By Gary Kocurek and Albert Galloway
- Exploration Geophysics: Books in this field often cover seismic interpretation and its application in identifying stratigraphic traps. Some examples include:
- Interpretation of 3D Seismic Data: By A.P. Hartley
- Seismic Data Acquisition and Processing: By A.T. Buller
Articles
- AAPG Bulletin: The American Association of Petroleum Geologists (AAPG) publishes articles covering various aspects of petroleum geology, including papers dedicated to specific types of stratigraphic traps. Search for keywords like "stratigraphic trap," "unconformity trap," "pinchout trap," etc.
- Journal of Petroleum Geology: This journal is a reliable source for articles on various topics related to petroleum geology, with many articles discussing stratigraphic traps.
- Search in Google Scholar: Use keywords like "stratigraphic trap types," "stratigraphic trap recognition," "seismic interpretation of stratigraphic traps," and "examples of stratigraphic traps" to find specific articles.
Online Resources
- AAPG Website: The AAPG website hosts a library of publications, including technical papers and presentations relevant to stratigraphic traps.
- SEG Website: The Society of Exploration Geophysicists (SEG) website provides resources on seismic data interpretation, which is crucial for recognizing stratigraphic traps.
- USGS Publications: The United States Geological Survey (USGS) publishes reports and articles related to geological mapping and resource assessment, often including information about stratigraphic traps.
Search Tips
- Use Specific Keywords: Employ terms like "stratigraphic trap examples," "stratigraphic trap formation," "stratigraphic trap types," etc., for targeted search results.
- Combine Keywords: Combine keywords with specific geographical locations, such as "stratigraphic traps North Sea" or "stratigraphic traps Gulf of Mexico," to find relevant research.
- Use Boolean Operators: Use "AND," "OR," and "NOT" operators to refine your search. For instance, "stratigraphic trap AND seismic interpretation" would yield results focusing on the use of seismic data in identifying stratigraphic traps.
- Explore Images: Utilize Google Image Search to visually understand the different types of stratigraphic traps and how they form.
Techniques
Chapter 1: Techniques for Identifying Stratigraphic Traps
Identifying stratigraphic traps requires a multi-faceted approach utilizing a variety of geophysical and geological techniques. The goal is to accurately map subsurface formations, delineate reservoir boundaries, and understand the seal mechanisms involved. Key techniques include:
1. Seismic Reflection Surveys: This is arguably the most crucial technique. High-resolution 2D and 3D seismic data provide images of subsurface strata, allowing geologists and geophysicists to identify changes in lithology, unconformities, and subtle changes in acoustic impedance that might indicate stratigraphic traps. Advanced processing techniques like pre-stack depth migration improve the accuracy and resolution of these images, enabling better definition of trap geometries. Seismic attributes, such as amplitude variation with offset (AVO) and spectral decomposition, can further enhance the identification of reservoir rocks and seals.
2. Well Logging: Data obtained from well logs (e.g., gamma ray, resistivity, porosity, density) provide direct measurements of rock properties in the subsurface. These logs help characterize reservoir quality, identify lithological changes, and pinpoint the boundaries of stratigraphic traps. Advanced logging tools, such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) logging, provide detailed information about pore size distribution and fluid saturation, crucial for reservoir assessment.
3. Biostratigraphy: Analysis of microfossils (foraminifera, pollen, spores) found in well cuttings and cores helps correlate strata across different wells and define the age of the formations. This is vital for understanding the geological history and identifying unconformities – key elements in stratigraphic trap formation.
4. Sequence Stratigraphy: This approach interprets sedimentary successions in terms of their depositional environments and their response to changes in sea level. It helps predict the distribution of reservoir and seal rocks within a basin, significantly aiding in the identification of potential stratigraphic traps.
5. Geochemical Analysis: Analyzing the composition of hydrocarbons and formation waters can provide insights into the source rock, migration pathways, and the timing of hydrocarbon accumulation within stratigraphic traps. This information is invaluable in assessing the prospectivity of a trap.
Chapter 2: Models of Stratigraphic Traps

Understanding the various types of stratigraphic traps requires developing geological models that incorporate the relevant geological processes and the resulting trap geometries. Key models include:
1. Unconformity Traps: These traps are formed by an unconformity – a buried erosional surface separating younger from older strata. The unconformity acts as a seal, trapping hydrocarbons in the underlying reservoir rocks. Models focus on understanding the geometry and extent of the unconformity, the reservoir characteristics below, and the nature of the overlying seal.
2. Pinchout Traps: These traps form when a reservoir layer gradually thins and pinches out laterally into an impermeable rock unit. Models concentrate on mapping the lateral extent of the reservoir and the precise location where the pinchout occurs.
3. Onlap/Downlap Traps: These are formed by sedimentary layers that onlap or downlap onto an underlying surface (e.g., an unconformity or a slope). The change in depositional environment leads to a change in rock properties that creates the trap. Models emphasize the understanding of the depositional system and the resulting stratigraphic architecture.
4. Reef Traps: Reef structures, formed by organisms, are often excellent reservoirs due to their high porosity and permeability. Models need to incorporate the complex three-dimensional geometry of the reef structure and its relationship to the surrounding strata, which may serve as seals.
5. Channel-Fill Traps: Sediment deposited within ancient river channels can form excellent reservoirs, with the channel margins acting as seals. Models focus on reconstructing the paleochannel geometry and understanding the distribution of reservoir and seal facies within the channel system.
Chapter 3: Software for Stratigraphic Trap Analysis

Advanced software plays a crucial role in the exploration and analysis of stratigraphic traps. These tools integrate various datasets, allowing for detailed modeling and interpretation. Key software packages include:
1. Seismic Interpretation Software: Packages like Petrel, Kingdom, and SeisWorks allow geoscientists to interpret seismic data, identify potential traps, and build 3D geological models. These programs facilitate interactive interpretation, attribute analysis, and depth conversion.
2. Well Log Analysis Software: Software like Techlog, IHS Kingdom, and Schlumberger's Petrel offer tools for processing and interpreting well log data, characterizing reservoir properties, and integrating well data with seismic data.
3. Geological Modeling Software: Software like Gocad, Petrel, and RMS enable geoscientists to construct detailed 3D geological models, simulating the subsurface geometry of stratigraphic traps, predicting reservoir properties, and simulating fluid flow.
4. Geostatistical Software: Packages like GSLIB and SGeMS allow for spatial modeling of reservoir properties based on limited data points, providing probabilistic estimates of reservoir characteristics and uncertainty analysis.
5. Visualization Software: Powerful visualization tools are essential for interpreting complex 3D datasets. Software packages often provide integrated visualization capabilities, allowing users to view seismic data, well logs, and geological models interactively.
Chapter 4: Best Practices for Stratigraphic Trap Exploration

Successful exploration of stratigraphic traps relies on adhering to best practices across all stages of the exploration workflow:
1. Regional Geological Understanding: A thorough understanding of the regional geology, tectonic history, and sedimentary basins is paramount. This includes detailed analysis of surface geology, existing well data, and regional seismic datasets.
2. Multidisciplinary Approach: Collaboration among geologists, geophysicists, petrophysicists, and reservoir engineers is essential for a successful outcome. Integrating diverse datasets and perspectives enhances the accuracy of interpretation and reduces exploration risk.
3. Data Integration and Quality Control: Accurate and reliable data are fundamental. Rigorous data quality control procedures are necessary throughout the workflow, ensuring consistent and reliable results.
4. Detailed Seismic Interpretation: Careful and thorough interpretation of seismic data, including the use of advanced processing and interpretation techniques, is crucial for identifying subtle stratigraphic features.
5. Well Planning and Execution: Strategic well placement is critical. Wells should be positioned to optimally test the identified traps and provide crucial data for reservoir characterization.
6. Uncertainty Analysis: Geological modeling should incorporate uncertainty analysis to quantify the risk associated with exploration. This provides a realistic assessment of the potential success of the exploration venture.
Chapter 5: Case Studies of Stratigraphic Traps

Several notable oil and gas fields worldwide demonstrate the importance of stratigraphic traps:
1. The giant Brent Field (North Sea): This field is a prime example of a reservoir trapped by an unconformity. The reservoir rocks are deeply buried sandstones, sealed by an overlying unconformity surface.
2. Fields in the Permian Basin (USA): Many fields in this basin are associated with stratigraphic traps formed by various mechanisms, including channel-fill deposits, pinchouts, and reef structures. These fields showcase the variety of stratigraphic traps that can exist within a single basin.
3. Giant gas fields of the Middle East: Several fields in the Middle East demonstrate the importance of stratigraphic traps, often associated with complex carbonate platforms and unconformities.
4. Fields along the US Gulf Coast: Numerous fields in this region highlight the significance of shallow-water carbonate systems and their associated stratigraphic traps.
5. Fields in the Niger Delta: This area demonstrates the significance of channel-fill deposits and other fluvial-deltaic systems forming stratigraphic traps.
Each case study provides valuable insights into the geological settings, reservoir characteristics, and exploration challenges associated with different types of stratigraphic traps. Analyzing these case studies offers lessons for future exploration efforts.
- Combination Trap مصيدة التكوين: سيف ذو حدين في…
- Diagenetic Trap مصائد التحول: حيث تتحول الصخو…
- Fault Trap مصائد الفوالق: لاعب رئيسي…
- Structural Trap الكنز غير المرئي: فهم الفخاخ …
- Sand Trap مصيدة الرمال: البطل الخفي في …
- Strap ربط في النفط والغاز: قياس مست…
- Trapeze المُعلّق: عنصرٌ أساسي في أنظم…
- طلب تبرير المصروفات طلب مبرر الإنفاق: د… تخطيط وجدولة المشروع
- التكلفة الميزانية للعمل المجدول فهم تكلفة العمل الم… تقدير التكلفة والتحكم فيها
- حدود البطارية فهم حدود البطارية ف… المصطلحات الفنية العامة
- أداة الصمام السفلي أداة الصمام السفلي:… الحفر واستكمال الآبار
- جدول المحتويات TOC: فهم قمة الإسمن… المصطلحات الفنية العامة
Comments