الجيولوجيا والاستكشاف
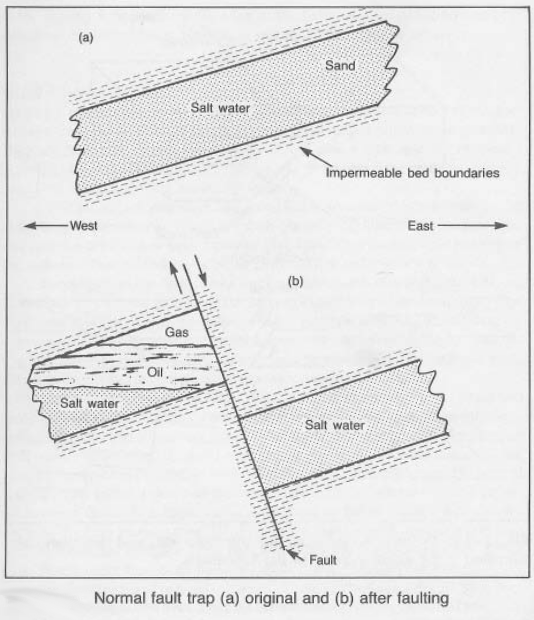
Fault Trap
مصائد الفوالق: لاعب رئيسي في لعبة النفط والغاز
البحث عن النفط والغاز مهمة معقدة، تتضمن البحث عن خزانات حيث تراكمت هذه الموارد القيمة على مدى ملايين السنين. أحد العناصر الحاسمة في هذه العملية هو وجود **مصائد الفوالق**، وهي تشكيلات جيولوجية تعمل كحاويات طبيعية، تحبس الهيدروكربونات وتمنعها من الهروب.
**ما هي مصيدة الفالق؟**
في جوهرها، مصيدة الفالق هي بنية جيولوجية تتشكل عندما يحدث كسر في قشرة الأرض، يُعرف باسم **الفالق**، مما يؤدي إلى إزاحة طبقات الصخور، مما يخلق حاجزًا يمنع حركة الهيدروكربونات. تخيل طبقة من الصخور المسامية، مثل الإسفنج، مشبعة بالنفط أو الغاز. ثم يتم تقاطع هذه الطبقة بفالق، مما يؤدي إلى تحويل تشكيلات الصخور، مما يخلق منطقة من الصخور غير المنفذة تعمل كختم. الهيدروكربونات، غير قادرة على الهجرة إلى أبعد من ذلك، تصبح محبوسة داخل طبقة الصخور المسامية.
**كيف تتشكل مصائد الفوالق؟**
يمكن أن تنشأ مصائد الفوالق من عمليات جيولوجية مختلفة:
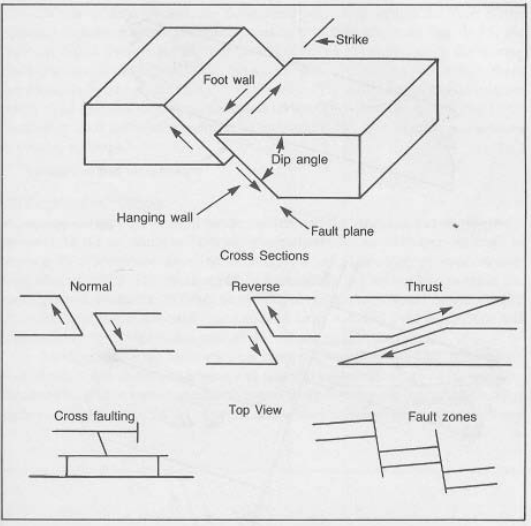
- الفوالق العادية: تحدث هذه عندما تمتد قشرة الأرض، مما يؤدي إلى فصل طبقات الصخور. يؤدي الانخفاض الناتج في طبقات الصخور إلى إنشاء خزان مائل، حيث يمكن للهيدروكربونات أن تتراكم.
- الفوالق العكسية: تتشكل هذه عندما يتم ضغط قشرة الأرض، مما يؤدي إلى انزلاق طبقات الصخور فوق بعضها البعض. يمكن أن تعمل طبقة الصخور العلوية كختم، مما يحبس الهيدروكربونات أسفلها.
- الفوالق الانزلاقية: هذه هي الحركات الأفقية لطبقات الصخور. في حين أنها لا تخلق ختمًا مباشرة، إلا أنها يمكن أن تخلق شبكة معقدة من الشقوق والمسارات التي يمكن أن تؤدي إلى تشكيل مصائد الفوالق في مكان آخر.
أهمية مصائد الفوالق:
تعتبر مصائد الفوالق مهمة للغاية في استكشاف وإنتاج النفط والغاز. فهي مسؤولة عن جزء كبير من احتياطيات الهيدروكربونات في العالم. يشير وجود مصيدة فالق إلى وجود خزان محتمل للنفط والغاز، ويمكن أن يكون عاملاً مهمًا في تحديد جدوى موقع الحفر.
أمثلة على مصائد الفوالق:
ترتبط العديد من حقول النفط والغاز الكبرى في العالم بمصائد الفوالق. بعض الأمثلة البارزة تشمل:
- حقل نفط بحر الشمال: يحتوي هذا الحقل الواسع على العديد من مصائد الفوالق التي كانت حاسمة في إنتاج مليارات البراميل من النفط والغاز.
- حقل نفط برذوه باي: يقع هذا الحقل في ألاسكا، وهو مثال رئيسي لمصيدة فالق تتشكل بواسطة فوالق عادية.
- حقل نفط الغوار: يعتبر أكبر حقل نفط في العالم، يقع في المملكة العربية السعودية، ويرتبط بنظام معقد من مصائد الفوالق.
التحديات والمخاطر:
بينما تقدم مصائد الفوالق إمكانات هائلة لاستكشاف النفط والغاز، إلا أنها تشكل أيضًا تحديات فريدة. يمكن أن تؤدي تعقيدات هياكل الفوالق إلى صعوبة التنبؤ بالموقع الدقيق لحجم الخزان. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يمكن أن تعمل الفوالق كمسارات لهجرة المياه أو السوائل الأخرى، مما قد يؤثر على جودة وإنتاجية الخزان.
خاتمة:
تعتبر مصائد الفوالق مكونات أساسية في صناعة النفط والغاز العالمية. إن فهم تشكيلها وخصائصها وتعقيداتها أمر بالغ الأهمية لنجاح الاستكشاف والإنتاج. مع استمرارنا في البحث عن مصادر طاقة جديدة، ستظل دراسة واستخدام مصائد الفوالق أمرًا حيويًا في سعينا نحو مستقبل مستدام.
Test Your Knowledge
Fault Traps Quiz
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What is a fault trap? a) A geological structure that allows hydrocarbons to escape. b) A type of rock formation that is impermeable to hydrocarbons. c) A geological structure that traps hydrocarbons and prevents their escape. d) A method used to extract hydrocarbons from the ground.
Answer
c) A geological structure that traps hydrocarbons and prevents their escape.
2. Which type of fault is most likely to form a fault trap? a) Normal Fault b) Reverse Fault c) Strike-Slip Fault d) All of the above
Answer
d) All of the above
3. What is the significance of fault traps in oil and gas exploration? a) They indicate potential areas for oil and gas exploration. b) They provide a pathway for hydrocarbons to escape. c) They help to determine the type of rock formation present. d) They are not important in oil and gas exploration.
Answer
a) They indicate potential areas for oil and gas exploration.
4. Which of the following is NOT a challenge associated with fault traps? a) Difficulty in predicting reservoir size and location. b) Potential for water or other fluids to contaminate the reservoir. c) The ease of extracting hydrocarbons from fault traps. d) The potential for complex fault structures.
Answer
c) The ease of extracting hydrocarbons from fault traps.
5. Which of the following is an example of a major oil field associated with fault traps? a) The North Sea Oil Field b) The Prudhoe Bay Oil Field c) The Ghawar Oil Field d) All of the above
Answer
d) All of the above
Fault Traps Exercise
Instructions: Imagine you are an oil and gas exploration geologist. You are studying a potential drilling site and have identified a fault that intersects a layer of porous rock.
Task: Explain how you would determine if this fault could be a potential fault trap. What geological factors would you investigate to assess the viability of this site for oil and gas exploration?
Exercice Correction
To determine if the fault is a potential fault trap, you would need to investigate several geological factors:
- **Fault Type:** Determine the type of fault (normal, reverse, or strike-slip) and its orientation. This will help predict the potential seal formation.
- **Seal Formation:** Look for evidence of an impermeable rock layer (e.g., shale, salt) that could act as a seal above or below the porous rock. This seal prevents the escape of hydrocarbons.
- **Reservoir Properties:** Analyze the porous rock layer's permeability and porosity to assess its ability to store and transmit hydrocarbons.
- **Migration Pathways:** Investigate if there are potential migration pathways for hydrocarbons to reach the fault trap from source rocks.
- **Structural Complexity:** Examine the geometry of the fault and the surrounding rock formations to assess the complexity of the structure. This complexity can affect the effectiveness of the trap.
- **Seismic Data:** Use seismic data to visualize the subsurface structures and assess the potential for a fault trap.
By analyzing these factors, you can determine if the identified fault is a viable fault trap and whether the site warrants further exploration for oil and gas resources.
Books
- Petroleum Geology: by William D. Bryant & Robert E. Cook. (Covers geological concepts including fault traps)
- Exploration and Production of Oil and Gas: by Donald R. Hedges. (Extensive discussion on fault traps in oil and gas exploration)
- Structural Geology: by Marshak & Allmendinger. (Focuses on tectonic processes and fault formation)
- Petroleum System: From Source to Trap: by Allen & Allen. (Delves into the complexities of petroleum systems, including fault traps)
Articles
- "Fault Traps in Petroleum Exploration" by A. H. S. Gray, published in the journal "Petroleum Geoscience". (Comprehensive review of fault traps in petroleum exploration)
- "The Role of Faults in Oil and Gas Accumulation" by P. M. Shearman, published in the journal "Marine and Petroleum Geology". (Explores the role of faults in hydrocarbon accumulation)
- "Fault-Related Seals and Their Impact on Petroleum Systems" by J. L. Cartwright & S. J. Davies, published in the journal "AAPG Bulletin". (Examines fault-related seals and their significance)
Online Resources
- USGS (United States Geological Survey) website: Provides information on various geological topics, including fault traps. (https://www.usgs.gov/)
- AAPG (American Association of Petroleum Geologists) website: Offers resources and publications related to petroleum geology, including fault traps. (https://www.aapg.org/)
- SPE (Society of Petroleum Engineers) website: Contains articles, technical papers, and resources on oil and gas exploration and production, including fault traps. (https://www.spe.org/)
Search Tips
- "Fault traps petroleum geology": This will return results specifically related to fault traps in the context of petroleum exploration.
- "Types of fault traps": This query will provide information on different classifications of fault traps.
- "Fault trap examples": This will return examples of known fault traps in oil and gas fields worldwide.
- "Fault trap formation": This will give you information on the geological processes involved in forming fault traps.
Techniques
Chapter 1: Techniques for Identifying Fault Traps
1.1 Seismic Surveys
- Principle: Seismic surveys utilize sound waves to map the subsurface geology. By analyzing the reflections and refractions of these waves, geologists can identify fault structures.
- Types: 2D and 3D seismic surveys provide increasingly detailed images of the subsurface.
- Advantages: High resolution imaging, capable of identifying complex fault geometries.
- Disadvantages: Expensive, time-consuming, interpretation requires expertise.
1.2 Well Logging
- Principle: Well logging involves sending various tools down a borehole to measure different physical properties of the rocks.
- Types:
- Gamma Ray Logging: Identifies radioactive elements, indicating potential shale formations.
- Resistivity Logging: Measures the electrical conductivity of rocks, helping to distinguish between porous and impermeable formations.
- Sonic Logging: Determines the speed of sound through the rock, which can indicate the presence of faults.
- Advantages: Provides direct measurements of rock properties at the well location.
- Disadvantages: Limited to the wellbore, information can be limited by well deviation.
1.3 Geological Mapping
- Principle: Examining surface outcrops, analyzing rock formations, and studying the geological history of a region.
- Types: Surface mapping, structural analysis, paleontological studies.
- Advantages: Can provide valuable insights into the geological history of a region.
- Disadvantages: Can be limited by outcrop availability, relies on interpretation.
1.4 Other Techniques
- Gravity Surveys: Measure variations in gravity, indicating density differences in the subsurface.
- Magnetic Surveys: Detect changes in the Earth's magnetic field, which can indicate the presence of magnetic minerals associated with faults.
- Remote Sensing: Satellite images and aerial photography can help identify surface features related to fault structures.
1.5 Integrated Approach
- Combining multiple techniques allows for a comprehensive understanding of the subsurface and significantly improves the accuracy of identifying and characterizing fault traps.
Chapter 2: Models of Fault Trap Formation
2.1 Normal Fault Traps
- Formation: Normal faults occur when the Earth's crust stretches and pulls apart, creating a tilted block of rock. The tilted block can form a reservoir, with the fault acting as a seal.
- Key Features: Dip-slip movement, tilted reservoir, hanging wall and footwall blocks.
- Examples: North Sea Oil Field, Prudhoe Bay Oil Field.
2.2 Reverse Fault Traps
- Formation: Reverse faults occur when the Earth's crust is compressed and rock layers slide over each other. The overlying rock can form a seal, trapping hydrocarbons in the underlying block.
- Key Features: Dip-slip movement, upthrown and downthrown blocks, possible juxtaposition of impermeable formations.
- Examples: Many fields in the Appalachian Basin, some fields in the Gulf of Mexico.
2.3 Strike-Slip Fault Traps
- Formation: Strike-slip faults involve horizontal movements of rock layers, creating fractures and pathways that can lead to the formation of traps elsewhere.
- Key Features: Lateral movement, possible juxtaposition of different rock types, formation of folds or anticlines.
- Examples: Some fields in the San Joaquin Valley of California, some fields in the Middle East.
2.4 Combination Traps
- Formation: Many fault traps involve a combination of different fault types and other geological features, creating complex structures.
- Key Features: Multiple faults, folds, unconformities, seals formed by different mechanisms.
- Examples: Ghawar Oil Field, many fields in complex geological settings.
Chapter 3: Software for Fault Trap Analysis
3.1 Seismic Interpretation Software
- Purpose: Analyze seismic data to identify fault structures, define reservoir boundaries, and estimate volume.
- Features: 2D/3D visualization, attribute analysis, fault detection algorithms, volumetric calculations.
- Examples: Petrel (Schlumberger), GeoGraphix (Landmark), Kingdom (IHS Markit).
3.2 Well Logging Software
- Purpose: Interpret well logging data to identify rock properties, correlate with seismic data, and define reservoir parameters.
- Features: Log analysis tools, depth matching, petrophysical calculations, wellbore visualization.
- Examples: Techlog (Schlumberger), Interactive Petrophysics (Halliburton), GeoFrame (Landmark).
3.3 Geological Modeling Software
- Purpose: Create 3D geological models of the subsurface, integrating data from seismic, well logs, and other sources.
- Features: Surface modeling, volume estimation, fault modeling, reservoir simulation.
- Examples: Petrel (Schlumberger), Gocad (Paradigm), GeoModeller (EarthDecision).
3.4 Other Software
- Reservoir Simulation Software: Simulate fluid flow in the reservoir, predict production performance, and optimize drilling plans.
- Geostatistical Software: Analyze spatial relationships of geological data, assess uncertainty, and create probabilistic models.
Chapter 4: Best Practices for Fault Trap Evaluation
4.1 Data Integration
- Importance: Combining data from different sources (seismic, well logs, geological mapping) to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the subsurface.
- Techniques:
- Seismic-to-well tie: Aligning seismic data with well log information.
- Correlation of different datasets: Identifying geological features in multiple data sources.
4.2 Fault Characterization
- Importance: Understanding fault geometry, displacement, and sealing capacity is crucial for reservoir assessment.
- Techniques:
- Fault interpretation: Identifying fault planes, determining fault throw, and analyzing fault patterns.
- Fault seal analysis: Evaluating the effectiveness of the fault as a seal to hydrocarbons.
4.3 Reservoir Characterization
- Importance: Defining the geometry, porosity, permeability, and fluid content of the reservoir.
- Techniques:
- Petrophysical analysis: Deriving rock properties from well log data.
- Reservoir simulation: Modeling fluid flow in the reservoir to estimate production potential.
4.4 Risk Assessment
- Importance: Quantifying uncertainties associated with the exploration and production of hydrocarbons.
- Techniques:
- Probabilistic modeling: Using statistical methods to assess the likelihood of different outcomes.
- Sensitivity analysis: Examining the impact of different parameters on the project outcome.
Chapter 5: Case Studies of Fault Trap Exploration and Production
5.1 The North Sea Oil Field
- Fault Type: Normal fault traps.
- Challenges: Complex fault network, high pressure reservoirs, harsh weather conditions.
- Successes: Development of advanced drilling and production technologies, significant oil and gas production.
5.2 The Ghawar Oil Field
- Fault Type: Combination of normal and reverse faults.
- Challenges: Vast size and complexity of the field, declining production rates.
- Successes: Long-term production, innovative reservoir management strategies.
5.3 The Prudhoe Bay Oil Field
- Fault Type: Normal fault trap.
- Challenges: Remote location, harsh Arctic environment, environmental concerns.
- Successes: Major contribution to Alaska's economy, significant oil production.
5.4 Other Notable Examples
- The Bakken Shale Play: Fault traps play a role in controlling the distribution of hydrocarbons in this shale formation.
- The Permian Basin: Complex fault systems contribute to the formation of various types of traps in this prolific oil and gas region.
5.5 Learning from Case Studies
- Case studies provide valuable lessons about the challenges and opportunities associated with fault trap exploration and production.
- Understanding the successes and failures of past projects can help improve future exploration and development strategies.
- Block Fault عيوب الكتل: أساس استكشاف النف…
- Combination Trap مصيدة التكوين: سيف ذو حدين في…
- Diagenetic Trap مصائد التحول: حيث تتحول الصخو…
- Dip Slip Fault صدوع الانزلاق: عامل حاسم في ا…
- Fault التصدعات في النفط والغاز: حيث…
- Fault الصدع: مصطلح أساسي في استكشاف…
- Fault Plane مستوى الصدع: فهم الشقوق في قش…
- Growth Fault أخطاء النمو: الشقوق في قشرة ا…
- Hinge Fault أخطاء المفصل: ميزة رئيسية في …
- Normal Fault الصدوع العادية: لاعب أساسي في…
- Stratigraphic Trap الكنوز الخفية: فهم المصائ…
- Strike-Slip Fault صدوع الانزلاق: انقسام أفقي في…
- Structural Trap الكنز غير المرئي: فهم الفخاخ …
- Default التخلف في النفط والغاز: عندما…
- Default Values قيم افتراضية: أداة أساسية في …
- overthrust fault التنقل عبر الصدوع الرافعة: فه…
- Sand Trap مصيدة الرمال: البطل الخفي في …
- Sealing Fault عطل الإغلاق: شريان الحياة في …
- Strap ربط في النفط والغاز: قياس مست…
- Supplier Default تخلف المورد: حقيقة محفوفة بال…
- طلب تبرير المصروفات طلب مبرر الإنفاق: د… تخطيط وجدولة المشروع
- التكلفة الميزانية للعمل المجدول فهم تكلفة العمل الم… تقدير التكلفة والتحكم فيها
- حدود البطارية فهم حدود البطارية ف… المصطلحات الفنية العامة
- أداة الصمام السفلي أداة الصمام السفلي:… الحفر واستكمال الآبار
- جدول المحتويات TOC: فهم قمة الإسمن… المصطلحات الفنية العامة
Comments