الكهرومغناطيسية
anti-Stokes scattering
عندما يكتسب الضوء دفعة ترددية: شرح تشتت مضاد ستوكس
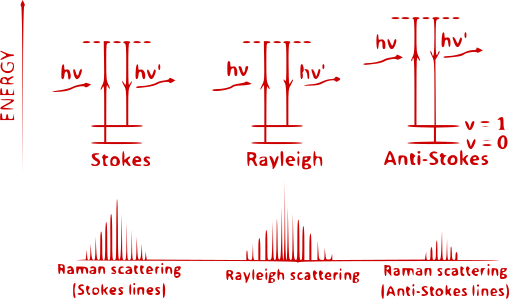
في عالم تشتت الضوء، نلاحظ عادة ظاهرة تُعرف باسم **تشتت ستوكس**، حيث يتفاعل الضوء مع المادة ويُصبح أقل ترددًا، مما يؤدي إلى تحول نحو أطوال موجية أطول (تحول أحمر). لكن ماذا يحدث عندما يكتسب الضوء الطاقة بدلاً من فقدانها؟ هنا يأتي دور **تشتت مضاد ستوكس**، وهي ظاهرة أقل شهرة تتضمن تحولًا إلى **ترددات أعلى**، أو أطوال موجية أقصر (تحول أزرق).
فهم الأساسيات
يعتمد كل من تشتت ستوكس ومضاد ستوكس على مفهوم **تشتت رامان**، وهي عملية يتفاعل فيها الضوء مع الجزيئات ويُثير مستويات طاقتها الاهتزازية. في تشتت ستوكس، يفقد الفوتون الساقط طاقة إلى الجزيء، مما يؤدي إلى انخفاض تردده. على العكس من ذلك، في تشتت مضاد ستوكس، تمتلك الجزيئة بالفعل طاقة اهتزازية وتنقلها إلى الفوتون الساقط، مما يؤدي إلى زيادة تردده.
الفرق الرئيسي: نقل الطاقة
يكمن الاختلاف الأساسي بين تشتت ستوكس ومضاد ستوكس في نقل الطاقة:
- تشتت ستوكس: يفقد الفوتون الطاقة إلى الجزيء.
- تشتت مضاد ستوكس: تفقد الجزيئة الطاقة إلى الفوتون.
يؤدي هذا نقل الطاقة إلى تحولات تردد متناقضة:
- تشتت ستوكس: تحول أحمر (تردد أقل، طول موجة أطول).
- تشتت مضاد ستوكس: تحول أزرق (تردد أعلى، طول موجة أقصر).
دور درجة الحرارة
يعتمد احتمال حدوث تشتت مضاد ستوكس بشكل كبير على درجة حرارة الوسط. بما أن درجات الحرارة الأعلى تتوافق مع مستويات طاقة اهتزازية أعلى في الجزيئات، تصبح المزيد من الطاقة متاحة لنقلها إلى الفوتونات، وبالتالي تعزز احتمال حدوث تشتت مضاد ستوكس.
التطبيقات والأهمية
على الرغم من كونه أقل شيوعًا من تشتت ستوكس، يُستخدم تشتت مضاد ستوكس في تطبيقات قيّمة في مجالات متعددة:
- مطيافية رامان: يوفر تشتت مضاد ستوكس معلومات إضافية حول مستويات طاقة اهتزاز الجزيئات، مما يعزز حساسية وخصوصية مطيافية رامان.
- قياس درجة الحرارة: ترتبط نسبة شدة الضوء المتشتت من ستوكس إلى مضاد ستوكس مباشرة بدرجة الحرارة، مما يُمكّن من قياس درجة الحرارة بدون تلامس.
- التصوير الطبي: يتم استكشاف تشتت رامان مضاد ستوكس لتطبيقات التصوير الطبي، مع إمكانية تقديم تحسينات في تصوير الأنسجة وتشخيص الأمراض.
الاستنتاج
يوفر تشتت مضاد ستوكس نظرة ثاقبة رائعة إلى تعقيدات تفاعلات الضوء مع المادة. من خلال فهم هذه الظاهرة، نكتسب فهمًا أعمق للقوانين الأساسية للفيزياء التي تحكم انتشار الضوء ونفتح إمكانيات جديدة للبحث العلمي والتقدم التكنولوجي والاختراقات الطبية. بينما يظل تشتت ستوكس هو العملية المهيمنة، يقدم تشتت مضاد ستوكس أداة قيّمة لاستكشاف عالم الضوء وتفاعلاته مع المادة.
Test Your Knowledge
Anti-Stokes Scattering Quiz
Instructions: Choose the best answer for each question.
1. What is the primary difference between Stokes and anti-Stokes scattering?
a) Stokes scattering involves a decrease in light frequency, while anti-Stokes scattering involves an increase. b) Stokes scattering occurs in gases, while anti-Stokes scattering occurs in liquids. c) Stokes scattering is more common than anti-Stokes scattering. d) Stokes scattering is used for medical imaging, while anti-Stokes scattering is used for Raman spectroscopy.
Answer
a) Stokes scattering involves a decrease in light frequency, while anti-Stokes scattering involves an increase.
2. In anti-Stokes scattering, what happens to the incident photon's energy?
a) It decreases. b) It remains the same. c) It increases. d) It is absorbed by the molecule.
Answer
c) It increases.
3. What is the effect of temperature on anti-Stokes scattering?
a) Higher temperature decreases the probability of anti-Stokes scattering. b) Temperature has no effect on anti-Stokes scattering. c) Higher temperature increases the probability of anti-Stokes scattering. d) Temperature determines the type of scattering that occurs (Stokes or anti-Stokes).
Answer
c) Higher temperature increases the probability of anti-Stokes scattering.
4. Which of these applications is NOT directly related to anti-Stokes scattering?
a) Raman spectroscopy b) Temperature sensing c) Laser cutting d) Medical imaging
Answer
c) Laser cutting
5. What is the term for the shift in light frequency towards shorter wavelengths?
a) Red shift b) Blue shift c) Doppler shift d) Raman shift
Answer
b) Blue shift
Anti-Stokes Scattering Exercise
Scenario: You are studying a sample of a new material using Raman spectroscopy. You observe both Stokes and anti-Stokes scattered light. However, the intensity of the anti-Stokes signal is significantly lower than that of the Stokes signal.
Task: Explain two possible reasons for this observation.
Exercice Correction
Here are two possible reasons for the lower intensity of the anti-Stokes signal:
- **Low temperature:** The probability of anti-Stokes scattering is directly proportional to temperature. If the sample is at a relatively low temperature, fewer molecules will have enough vibrational energy to transfer to the incident photons, resulting in a weaker anti-Stokes signal.
- **Low concentration of molecules in excited states:** Anti-Stokes scattering requires molecules to be in an excited vibrational state. If the sample is not exposed to a strong excitation source or if the relaxation time of the excited states is short, the concentration of molecules in excited states will be low, leading to a weaker anti-Stokes signal.
Books
- "Raman Spectroscopy" by D.A. Long (Comprehensive overview of Raman scattering, including anti-Stokes scattering)
- "Introduction to Modern Spectroscopy" by J.M. Hollas (Covers the basics of Raman scattering and its variations)
- "Principles of Optics" by Max Born and Emil Wolf (Classic textbook that covers various aspects of light scattering, including Raman scattering)
Articles
- "Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering for Temperature Measurement" by E.T. Arakawa et al. (Discusses the use of anti-Stokes scattering for non-contact temperature sensing)
- "Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering: A Powerful Tool for Chemical Analysis" by R.S. Czernuszewicz (Highlights the applications of anti-Stokes scattering in chemical analysis)
- "Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering in Biomedicine" by Y. Ozaki et al. (Explores the potential of anti-Stokes Raman scattering for medical imaging)
Online Resources
- Hyperphysics: Raman Scattering (Detailed explanation of Raman scattering, including anti-Stokes scattering, with interactive diagrams)
- Wikipedia: Raman scattering (A comprehensive overview of Raman scattering, with links to further resources)
- NIST: Raman Spectroscopy (A collection of resources on Raman spectroscopy, including information on anti-Stokes scattering)
Search Tips
- "Anti-Stokes Raman scattering" - Use this phrase to find articles and resources specifically focused on anti-Stokes scattering.
- "Anti-Stokes scattering applications" - Use this phrase to find information on the applications of anti-Stokes scattering in different fields.
- "Anti-Stokes scattering temperature measurement" - Use this phrase to find articles on the use of anti-Stokes scattering for temperature sensing.
- "Anti-Stokes Raman scattering spectroscopy" - Use this phrase to find information on the use of anti-Stokes scattering in Raman spectroscopy.
Techniques
Anti-Stokes Scattering: A Deeper Dive
Here's a breakdown of the topic into separate chapters, expanding on the provided introduction:
Chapter 1: Techniques for Observing Anti-Stokes Scattering
This chapter will detail the experimental methods used to detect and analyze anti-Stokes scattered light. The low intensity of anti-Stokes signals necessitates sensitive techniques.
Raman Spectroscopy: This is the primary technique. We'll discuss different configurations, including spontaneous Raman spectroscopy (measuring the inherent weak signal) and stimulated Raman scattering (enhancing the signal using intense laser pulses). Specific instrumental setups, including excitation sources (lasers with appropriate wavelengths), monochromators or spectrometers for spectral dispersion, and detectors (e.g., CCD, PMT) will be described. The challenges of separating the weak anti-Stokes signal from the much stronger Rayleigh and Stokes signals will be addressed, including techniques like notch filters and spectral subtraction.
Hyper-Raman Spectroscopy: A non-linear technique where the scattered light frequency shift is double the incident frequency. This will be briefly described as an alternative, less common method.
Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Spectroscopy (CARS): A powerful technique using two laser beams to generate a coherent anti-Stokes signal with significantly higher intensity. The principles of CARS and its advantages and limitations compared to spontaneous Raman will be explained. Different CARS variants (e.g., degenerate and non-degenerate CARS) will be discussed.
Data Acquisition and Processing: Methods for collecting and processing the raw spectral data, including background subtraction, noise reduction, and peak fitting techniques to extract quantitative information about the anti-Stokes signal will be detailed.
Chapter 2: Models Describing Anti-Stokes Scattering
This chapter focuses on the theoretical frameworks used to understand and predict the intensity and spectral characteristics of anti-Stokes scattering.
Classical Model: A description of the interaction between light and molecular vibrations using classical electromagnetism. This model explains the frequency shift and intensity dependence on temperature and molecular properties.
Quantum Mechanical Model: A more rigorous treatment based on quantum mechanics, providing a more accurate description of the interaction between photons and vibrational energy levels. This model will delve into the concepts of energy levels, selection rules, and transition probabilities.
Density Matrix Formalism: A powerful tool for analyzing the dynamics of light-matter interaction, especially relevant for understanding stimulated Raman scattering and CARS.
Statistical Mechanics: The application of statistical mechanics to model the population of vibrational energy levels at different temperatures and thus the intensity of anti-Stokes scattering. The Boltzmann distribution will play a crucial role here.
Chapter 3: Software and Data Analysis Tools for Anti-Stokes Scattering
This chapter covers the software tools and algorithms used for data acquisition, processing, and analysis in anti-Stokes scattering experiments.
Spectroscopy Software Packages: Specific examples of commercially available software packages (e.g., those from Renishaw, Horiba) and open-source alternatives used for acquiring and processing Raman spectra will be discussed. Their capabilities in peak fitting, background subtraction, and spectral analysis will be highlighted.
Data Processing Algorithms: Detailed descriptions of algorithms used for background correction, peak fitting (e.g., Gaussian, Lorentzian fits), and spectral deconvolution will be included.
Image Processing Software: For imaging applications using anti-Stokes scattering, image processing software for enhancing contrast, removing noise, and segmenting regions of interest will be examined.
Custom-Written Code: Mention of the use of programming languages like Python, MATLAB, or LabVIEW for customized data analysis and visualization. Examples of relevant libraries and packages (e.g., NumPy, SciPy, Matplotlib in Python) will be provided.
Chapter 4: Best Practices and Experimental Considerations
This chapter focuses on optimizing experimental conditions for effective measurement of anti-Stokes scattering.
Laser Selection: Choosing appropriate laser wavelengths and power to maximize signal while minimizing sample damage.
Sample Preparation: Techniques for preparing samples to minimize background fluorescence and scattering.
Data Acquisition Parameters: Optimizing integration time, spectral resolution, and other parameters for optimal signal-to-noise ratio.
Calibration and Validation: Methods for calibrating the spectrometer and validating the accuracy of measurements.
Error Analysis: Assessment of sources of error and methods for minimizing their impact on results.
Chapter 5: Case Studies of Anti-Stokes Scattering Applications
This chapter presents real-world examples of anti-Stokes scattering applications across various fields.
Temperature Sensing: Case studies demonstrating the use of anti-Stokes scattering for non-invasive temperature measurement in different environments (e.g., combustion engines, biological systems).
Medical Imaging: Examples of using anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy for biomedical imaging and diagnostics (e.g., cancer detection, tissue characterization).
Chemical Analysis: Applications of anti-Stokes Raman scattering for identifying and quantifying chemical species in different samples.
Material Science: Use of anti-Stokes scattering to characterize the properties of materials (e.g., crystalline structure, phonon modes).
This expanded structure provides a comprehensive overview of anti-Stokes scattering, going beyond the introductory information provided. Remember to include relevant citations and references throughout.
- backscattering الانتثار العكسي: صدى الموجات …
- bistatic scattering فهم الانتشار ثنائي الاتجاه: م…
- Bragg scattering انتشار براغ: توجيه الضوء باست…
- Brillouin scattering انتشار بريلوين: إضاءة رقصة ال…
- bulk scattering الانتشار المجزّأ: فهم مسار ال…
Comments